|
Omega Pavonis
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Pavo, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also *List of stars by constellation All stars but one can be associated with an IAU constellation. IAU constellations are areas of the sky. Although there are only 88 IAU constellations, the sky is actually divided into 89 irregularly shaped boxes as the constellation Serpens is spli ... References * * * * * {{Stars of Pavo *List Pavo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Pavonis
Beta Pavonis, Latinised from β Pavonis, is a single, white-hued star in the southern constellation of Pavo. It can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 3.42. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 24.14 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 135 light-years from the Sun. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +4 km/s. Beta Pavonis is a member of the Ursa Major Moving Group, a set of stars that share a similar motion through space. Zorec and Royer (2012) list a stellar classification for this star of A5 IV, indicating it is an evolving subgiant star that has consumed the hydrogen at its core and has begun to expand onto the red giant branch. However, Houk (1979) listed a more evolved class of A7 III, suggesting it is already a giant star. It has about 2.3 times the Sun's radius and 2.51 times the mass of the Sun. At the estimated age of 305 million years, the star still has a relatively high rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
53 Persei Variable
A slowly pulsating B-type star (SPB), formerly known as a 53 Persei variable, is a type of pulsating variable star. They may also be termed a long-period pulsating B star (LPB). As the name implies, they are main-sequence stars of spectral type B2 to B9 (3 to 9 times as massive as the Sun) that pulsate with periods between approximately half a day and five days, however within this most member stars have been found to have multiple periods of oscillations. They display variability both in their light emission and in their spectral line profile. The variations in magnitude are generally smaller than 0.1 magnitudes, making it quite hard to observe variability with the naked eye in most cases. The variability increases with decreasing wavelength, thus they are more obviously variable in ultraviolet spectrum than visible light. Their pulsations are non-radial, that is, they vary in shape rather than volume; different parts of the star are expanding and contracting simultaneously. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Pavonis
ν Pavonis, Latinized as Nu Pavonis, is a possible triple star system in the southern constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint star that varies in apparent visual magnitude from 4.60 to 4.64 over a period of 0.85584 days. The system lies approximately 440 light years from the Sun based on stellar parallax, parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +17 km/s. It is a possible member of the Wolf 630 group of co-moving stars. This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary system with an orbital period of just 1.71 days in a circular orbit. The unresolved components are close enough that their tidal interaction is significant. The visible component is a slowly pulsating B-type star with a stellar classification of B7III. This implies it is an stellar evolution, evolved giant star, but it is actually more likely to be on the main sequence. An X-ray astronomy, X-ray emission has been detected from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W Virginis Variable
W Virginis variables are a subclass of Type II Cepheids which exhibit pulsation periods between 10–20 days,Wallerstein, G."The Cepheids of Population II and Related Stars" ''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'', 114 p.689–699 (2002) and are of spectral class F6 – K2.W. Strohmeier, ''Variable Stars'', Pergamon (1972)Soszyński, I.; Udalski, A.; Szymański, M. K.; Kubiak, M.; Pietrzyński, G.; Wyrzykowski, Ł.; Szewczyk, O.; Ulaczyk, K.; Poleski, R"The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. The OGLE-III Catalog of Variable Stars. II.Type II Cepheids and Anomalous Cepheids in the Large Magellanic Cloud" ''Acta A.'', vol 58 (2008) They were first recognized as being distinct from classical Cepheids by Walter Baade in 1942, in a study of Cepheids in the Andromeda Galaxy that proposed that stars in that galaxy were of two populations.Webb, Stephen, ''Measuring the Universe: The Cosmological Distance Ladder'', Springer, (1999) See also *Low-dimensional chaos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
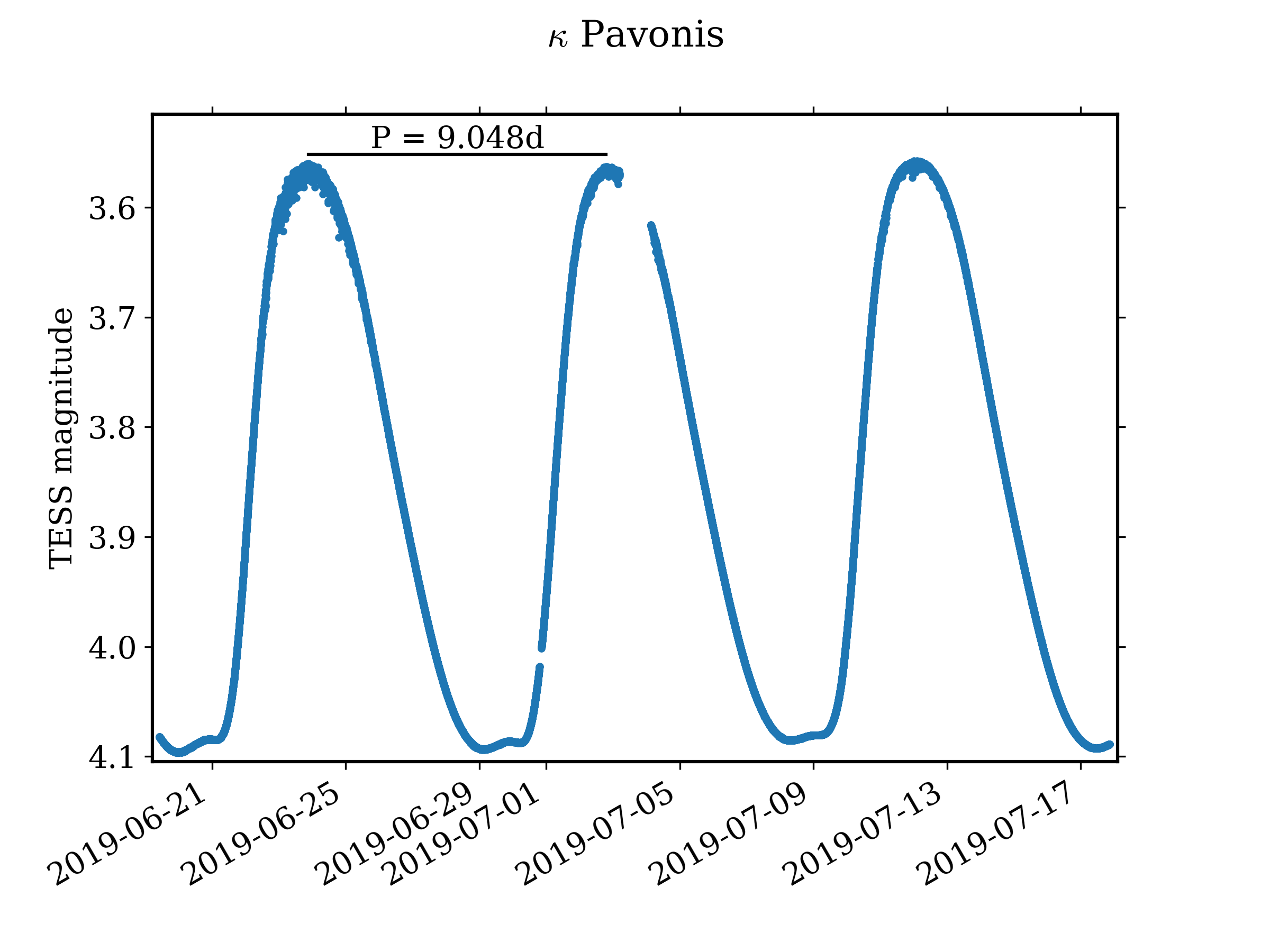
Kappa Pavonis
Kappa Pavonis (κ Pav) is a variable star in the constellation Pavo. It is the brightest W Virginis variable in the sky. Discovery In 1901, κ Pavonis was reported to be a variable star with a magnitude range of 3.8 to 5.2 with a period of 9.0908 days. Further observations revealed radial velocity variations in time with the brightness variations, but this was assumed to indicate a spectroscopic binary system. The brightness variations were then interpreted as eclipses. Less than 10 years later, was κ Pav was listed as a likely Cepheid variable. In 1937 it was used as part of the effort to calibrate the Cepheid distance scale. Only years later were the separate period luminosity relationships for population I and II Cepheid variables identified, and κ Pav was assigned to the type II group. Variability κ Pavonis ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.91 and 4.78, and spectral types F5 to G5, over a period of 9.1 days. It is a W Virginis variable, a type II C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi Pavonis
ξ Pavonis, Latinised as Xi Pavonis, is a triple star system in the southern constellation of Pavo. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.35 The system is located approximately 440 light-years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +12 km/s. This system forms the double star GLE 2, whose companion's magnitude is 8.6 with a angular separation, which was discovered by Australian amateur astronomer Walter Gale in 1894. The primary component is itself a single-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of and an eccentricity of 0.26. The visible member of this inner pair is an aging giant star with a stellar classification In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Pavonis
π Pavonis, Latinized as Pi Pavonis, is a candidate astrometric binary star system in the constellation Pavo. It is a white-hued star that is visible to the naked eye as a faint point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.33. The distance to this object is 130 light years based on parallax, but it is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −15.6 km/s. The visible component is an chemically peculiar star that displays an abundance anomaly of strontium. Grey et al. (1989) classify it as kA4hF0mF2 III, matching a giant Am star with the calcium K line of an A4 star, the hydrogen lines of a cooler F0 star, and the metal lines of a F2 star. However, Loden and Sundman (1989) don't consider it to be a giant and list it as an Ap star. It is 630 million years old with 2.15 times the mass of the Sun and 2.8 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 24.7 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Cassiopeiae Variable
A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae. Variability γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically have amplitudes of the order of a magnitude. For example, γ Cassiopeiae is usually about magnitude 2.5 and has varied between magnitudes 1.6 and 3.0. The variations are associated with changes in the spectrum between normal absorption spectra and Be star spectra, often also including shell star characteristics. Pleione and γ Cassiopeiae itself are both variable stars that have intermittent shell episodes where strong shell features appear in the spectrum and the brightness increases or decreases significantly. At other times the shell is not detectable in the spectrum, and even the emission lines may disappear. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) categorises γ Cassiopeiae stars as eruptive variables and describes them as r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Pavonis
λ Pavonis, Romanization of Greek, Latinized as Lambda Pavonis, is a single, variable star in the southern constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. It is a blue-white hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.22. This object is located approximately 1,400 light years from the Sun, based upon stellar parallax, parallax. It is a member of the Scorpius–Centaurus association. This is a massive Be star, a rapidly rotating hot blue star which has developed a gas disk around it. It is a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable, γ Cassiopeiae variable or shell star which has occasionally brightened to magnitude 4.0. The stellar classification of B2Ve suggests it is a B-type main-sequence star that is generating energy through stellar core, core hydrogen fusion. This star is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 190 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate spheroid, oblate shape with an equato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Pavonis
Gamma Pavonis, Romanization of Greek, Latinized from γ Pavonis, is a star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.22, it is a fourth-magnitude star and thereby Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, visible to the naked eye. From parallax observations with the Hipparcos satellite, the distance to this star has been estimated at . It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −30 km/s. Compared to the Sun, this star has a 21% greater mass and a 15% larger radius. It is a brighter star with 152% of the Sun's luminosity, which is it radiating from the outer envelope at an effective temperature of 6,112 K. The stellar classification of F9 V puts it in the class of F-type main sequence stars that generate energy through the nuclear fusion of hydrogen at the core. It is a metal-poor star, which means it has a low abundance of Chemical element, elements heavier than helium. Age estimates range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Pavonis
Zeta Pavonis, Latinisation of names, Latinized from ζ Pavonis, is an orange-hued star in the southern constellation Pavo (constellation), Pavo. Its apparent magnitude is 4.01, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The annual stellar parallax, parallax shift of this star is 14.93 milliarcsecond, mas as seen from Earth, which provides a distance estimate of approximately away from the Sun. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −16.30. Based upon its motion through space, this star appears to be a member of the Hyades Supercluster. This is an stellar evolution, evolved K-type star, K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, which indicates it has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its stellar core, core. The measured angular diameter of this star, after correction for limb darkening, is . At the estimated distance of this star, this yields a physical size of about 19 times the Solar radius, radius of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |