|
Gamma Cassiopeiae Variable
A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae. Variability γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically have amplitudes of the order of a magnitude. For example, γ Cassiopeiae is usually about magnitude 2.5 and has varied between magnitudes 1.6 and 3.0. The variations are associated with changes in the spectrum between normal absorption spectra and Be star spectra, often also including shell star characteristics. Pleione and γ Cassiopeiae itself are both variable stars that have intermittent shell episodes where strong shell features appear in the spectrum and the brightness increases or decreases significantly. At other times the shell is not detectable in the spectrum, and even the emission lines may disappear. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) categorises γ Cassiopeiae stars as eruptive variables and describes them as r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Cassiopeiae
Gamma Cassiopeiae, Latinized from γ Cassiopeiae, is a bright star at the center of the distinctive "W" asterism in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cassiopeia. Although it is a fairly bright star with an apparent visual magnitude that varies from 1.6 to 3.0, it has no traditional Arabic or Latin name. It sometimes goes by the informal name Navi. Gamma Cassiopeiae is a Be star, a variable star, and a multiple star system. Based upon parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos satellite, it is located at a distance of roughly 550 light-years from Earth. Together with its common-proper-motion companion, HD 5408, the system could contain a total of eight stars. Physical properties Gamma Cassiopeiae is an eruptive variable star, whose apparent magnitude changes irregularly between +1.6 and +3.0. It is the prototype of the class of Gamma Cassiopeiae variable stars. In the late 1930s it underwent what is described as a ''shell episode'' and the brightness incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Binary
X-ray binaries are a class of binary stars that are luminous in X-rays. The X-rays are produced by matter falling from one component, called the ''donor'' (usually a relatively normal star), to the other component, called the ''accretor'', which is very compact: a neutron star or black hole. The infalling matter releases gravitational potential energy, up to several tenths of its rest mass, as X-rays. (Hydrogen fusion releases only about 0.7 percent of rest mass.) The lifetime and the mass-transfer rate in an X-ray binary depends on the evolutionary status of the donor star, the mass ratio between the stellar components, and their orbital separation. An estimated 1041 positrons escape per second from a typical low-mass X-ray binary. Classification X-ray binaries are further subdivided into several (sometimes overlapping) subclasses, that perhaps reflect the underlying physics better. Note that the classification by mass (high, intermediate, low) refers to the optically vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Persei
X Persei is a high-mass X-ray binary system located in the constellation Perseus, approximately 950 parsecs away. It is catalogued as 4U 0352+309 in the final Uhuru catalog of X-ray objects. The conventional star component of X Persei has been classified either as an O-type giant or a B-type main sequence star. It is a Be star, rotating rapidly, and at times surrounded by a disk of expelled material. This qualifies it as a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable, and the visual range is magnitude 6 - 7. In 1989 and 1990, the spectrum of X Persei changed from a Be star to a normal B class star while it faded significantly. This appears to have been caused by the loss of the excretion disk. The disk has since reformed and shows strong emission lines. The system also contains a neutron star which is a pulsar with an unusually long period of 837 seconds. The pulsar has shown period changes that are associated with mass transfer from the more massive primary star. Between 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
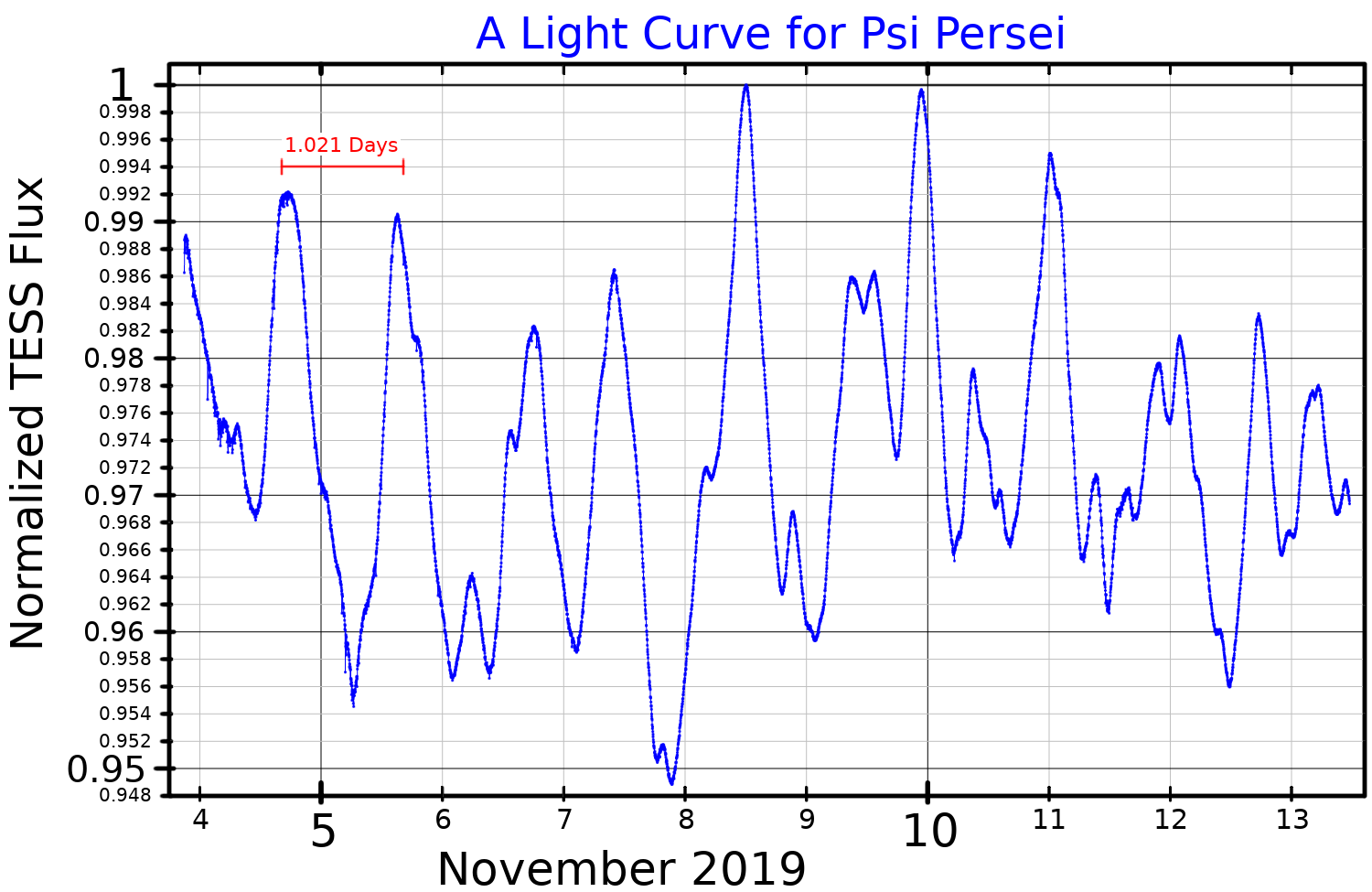
Psi Persei
Psi Persei (Psi Per, ψ Persei, ψ Per) is a single Be star in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of about 4.2, so it is visible to the naked eye at night under suitably dark skies. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of roughly from the Earth. Properties This star has a stellar classification of B5Ve, which indicates it is a B-type main sequence star that is generating energy at its core through the nuclear fusion of hydrogen. It is a shell star with a circumstellar disc of gas surrounding the equator and extending out to about 11 times the radius of the star. As a result of this disc, the spectrum of this star shows emission lines (as indicated by the 'e' in the stellar class) and its magnitude varies over a period 1.021 days. The General Catalog of Variable Stars classifies Psi Persei as a gamma Cassiopeiae variable star, whose visual band brightness varies from magnitude 4.17 to 4.28 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus (constellation)
Perseus is a constellation in the Northern celestial hemisphere, northern sky, being named after the Greek mythology, Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia (constellation), Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries (constellation), Aries and Taurus (constellation), Taurus to the south, Auriga (constellation), Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some Celestial cartography, star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose Asterism (astronomy), asterism was named together as ''Perseus e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
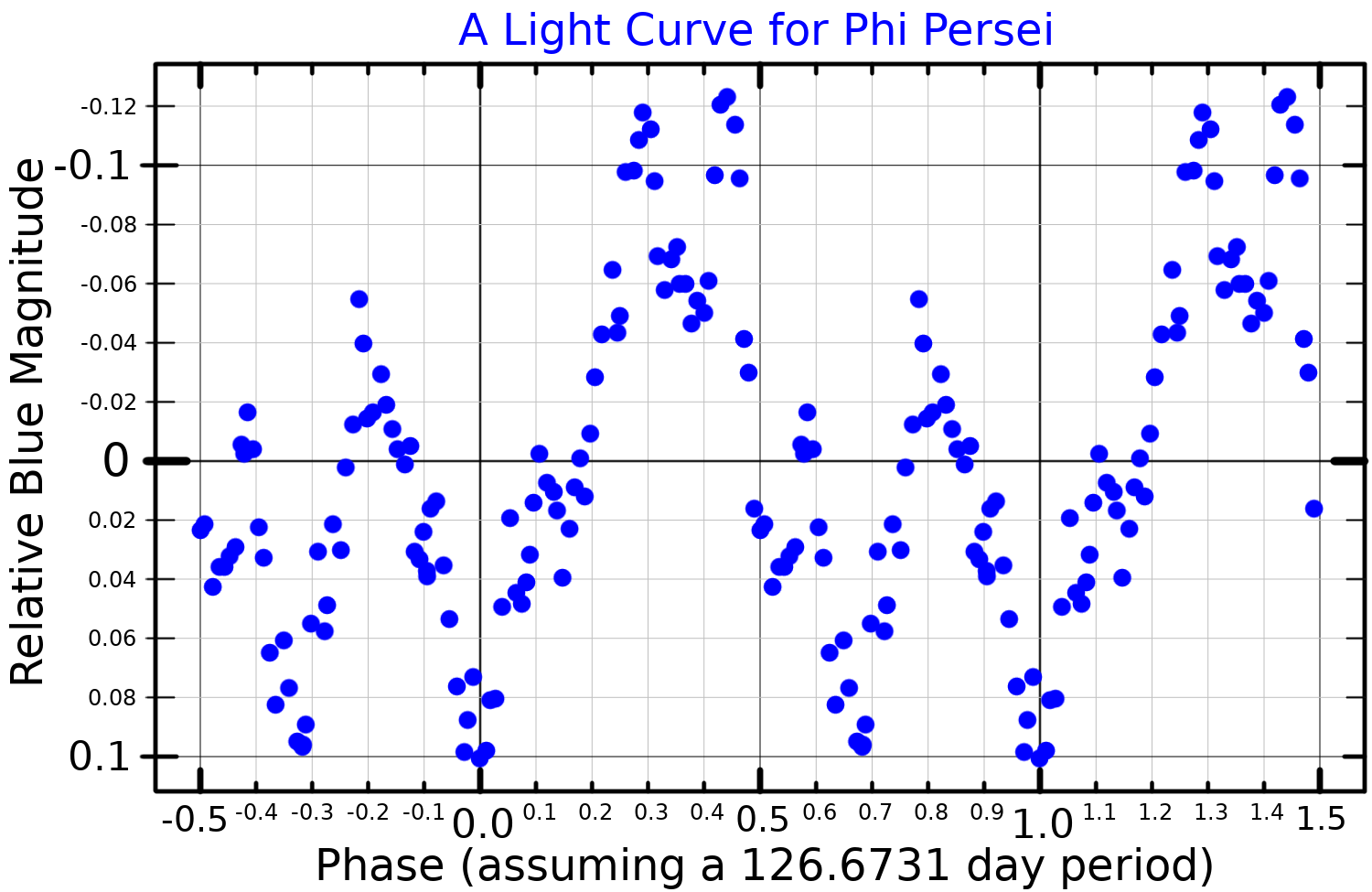
Phi Persei
Phi Persei (Phi Per, φ Persei, φ Per) is a Class B2Vpe fourth-magnitude star in the constellation Perseus, location about 720 light-years from Earth. System Phi Persei is spectroscopic binary consisting of a blue main sequence primary of class B2 and a hot subdwarf secondary. The two stars have an orbit of 217 days and are separated by about . Phi Persei is a runaway star and extrapolating its space velocity backwards by the modelled age of the system (57 million years) places it within the Alpha Persei cluster. The primary star rotates rapidly with a projected equatorial velocity of . Due to its rapid rotation, the primary star has a polar radius about and an equatorial radius of about . With an effective temperature of nearly , it has a bolometric luminosity nearly 15,000 times higher than the Sun. The rapidly-spinning star is surrounded by a circumstellar disk. The binary orbit, the spin of the primary star, and the disk are all seen nearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavo (constellation)
Pavo is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky whose name is Latin for "peafowl, peacock". Pavo first appeared on a 35-cm (14 in) diameter celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas ''Uranometria'' of 1603, and was likely conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave its stars Bayer designations in 1756. The constellations Pavo, Grus (constellation), Grus, Phoenix (constellation), Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds". The constellation's brightest member, Alpha Pavonis, is also known as Peacock and appears as a 1.91-Apparent magnitude, magnitude blue-white star, but is actually a spectroscopic binary. Delta Pavonis is a nearby Sun-like star some 19.9 light-years distant. Six of the star systems in Pavo have been found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Pavonis
λ Pavonis, Romanization of Greek, Latinized as Lambda Pavonis, is a single, variable star in the southern constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. It is a blue-white hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.22. This object is located approximately 1,400 light years from the Sun, based upon stellar parallax, parallax. It is a member of the Scorpius–Centaurus association. This is a massive Be star, a rapidly rotating hot blue star which has developed a gas disk around it. It is a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable, γ Cassiopeiae variable or shell star which has occasionally brightened to magnitude 4.0. The stellar classification of B2Ve suggests it is a B-type main-sequence star that is generating energy through stellar core, core hydrogen fusion. This star is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 190 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate spheroid, oblate shape with an equato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canis Major
Canis Major is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to Canis Minor, the "lesser dog"; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion (constellation), Orion the hunter through the sky. The Milky Way passes through Canis Major and several open clusters lie within its borders, most notably Messier 41, M41. Canis Major contains Sirius, the List of brightest stars, brightest star in the night sky, known as the "dog star". It is bright because of its proximity to the Solar System. In contrast, the other bright stars of the constellation are stars of great distance and high luminosity. At magnitude 1.5, Epsilon Canis Majoris (Adhara) is the second-brightest star of the constellation and the brightest source of extreme ultraviolet radiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Canis Majoris
Kappa Canis Majoris, Latinisation of names, Latinized from κ Canis Majoris, is a solitary, blue-white hued star in the constellation Canis Major. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.87. Based upon an annual stellar parallax, parallax shift of 7.70 milliarcsecond, mas as seen from Earth, this star is located about 660 light years from the Sun. This is a B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B1.5 Ve, although Hiltner et al. (1969) classified it as B1.5 IVe suggesting it is a subgiant star. The 'e' suffix indicates it is a rapidly rotating Be star with a circumstellar decretion disk of heated gas. The radius of the emitting disk is about , or about 3.7 times the radius of the star. It is classified as a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable, Gamma Cassiopeiae type variable star and its brightness varies from magnitude +3.4 to +3.97. The star became 50% brighter between 1963 and 1978, increasing from magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |