|
Gamma Cassiopeiae
Gamma Cassiopeiae, Latinized from γ Cassiopeiae, is a bright star at the center of the distinctive "W" asterism in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cassiopeia. Although it is a fairly bright star with an apparent visual magnitude that varies from 1.6 to 3.0, it has no traditional Arabic or Latin name. It sometimes goes by the informal name Navi. Gamma Cassiopeiae is a Be star, a variable star, and a multiple star system. Based upon parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos satellite, it is located at a distance of roughly 550 light-years from Earth. Together with its common-proper-motion companion, HD 5408, the system could contain a total of eight stars. Physical properties Gamma Cassiopeiae is an eruptive variable star, whose apparent magnitude changes irregularly between +1.6 and +3.0. It is the prototype of the class of Gamma Cassiopeiae variable stars. In the late 1930s it underwent what is described as a ''shell episode'' and the brightness incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia (constellation)
Cassiopeia () is a constellation in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive ' W' shape, formed by five bright stars. Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North. At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is generally the brightest star in Cassiopeia, though it is occasionally outshone by the variable Gamma Cassiopeiae, which has reached magnitude 1.6. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, including the yello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Be Star
Be stars are a heterogeneous set of stars with B spectral types and emission lines. A narrower definition, sometimes referred to as ''classical Be stars'', is a non-supergiant B star whose spectrum has, or had at some time, one or more Balmer emission lines. Definition and classification Many stars have B-type spectra and show hydrogen emission lines, including many supergiants, Herbig Ae/Be stars, mass-transferring binary systems, and B stars. It is preferred to restrict usage of the term Be star to non-supergiant stars showing one or more Balmer series lines in emission. These are sometimes referred to as classical Be stars. The emission lines may be present only at certain times. Although the Be type spectrum is most strongly produced in class B stars, it is also detected in O and A shell stars, and these are sometimes included under the "Be star" banner. Be stars are primarily considered to be main sequence stars, but a number of subgiants and giant stars are also inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Bulge
An equatorial bulge is a difference between the equatorial and polar diameters of a planet, due to the centrifugal force exerted by the rotation about the body's axis. A rotating body tends to form an oblate spheroid rather than a sphere. On Earth The Earth has a rather slight equatorial bulge: it is about wider at the equator than pole-to-pole, a difference which is about 1/298 of the equatorial diameter. If the Earth were scaled down to a globe with diameter of 1 meter at the equator, that difference would be only 3 millimeters. While too small to notice visually, that difference is still more than twice the largest deviations of the actual surface from the ellipsoid, including the tallest mountains and deepest oceanic trenches. The rotation of the earth also affects the sea level, the imaginary surface that is used to measure altitudes from. This surface coincides with the mean water surface level in oceans, and is extrapolated over land by taking into account the local g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
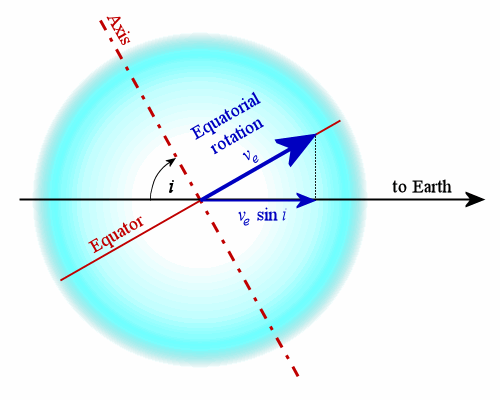
Projected Rotational Velocity
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. The magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its rate of angular velocity slows. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a star is being obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
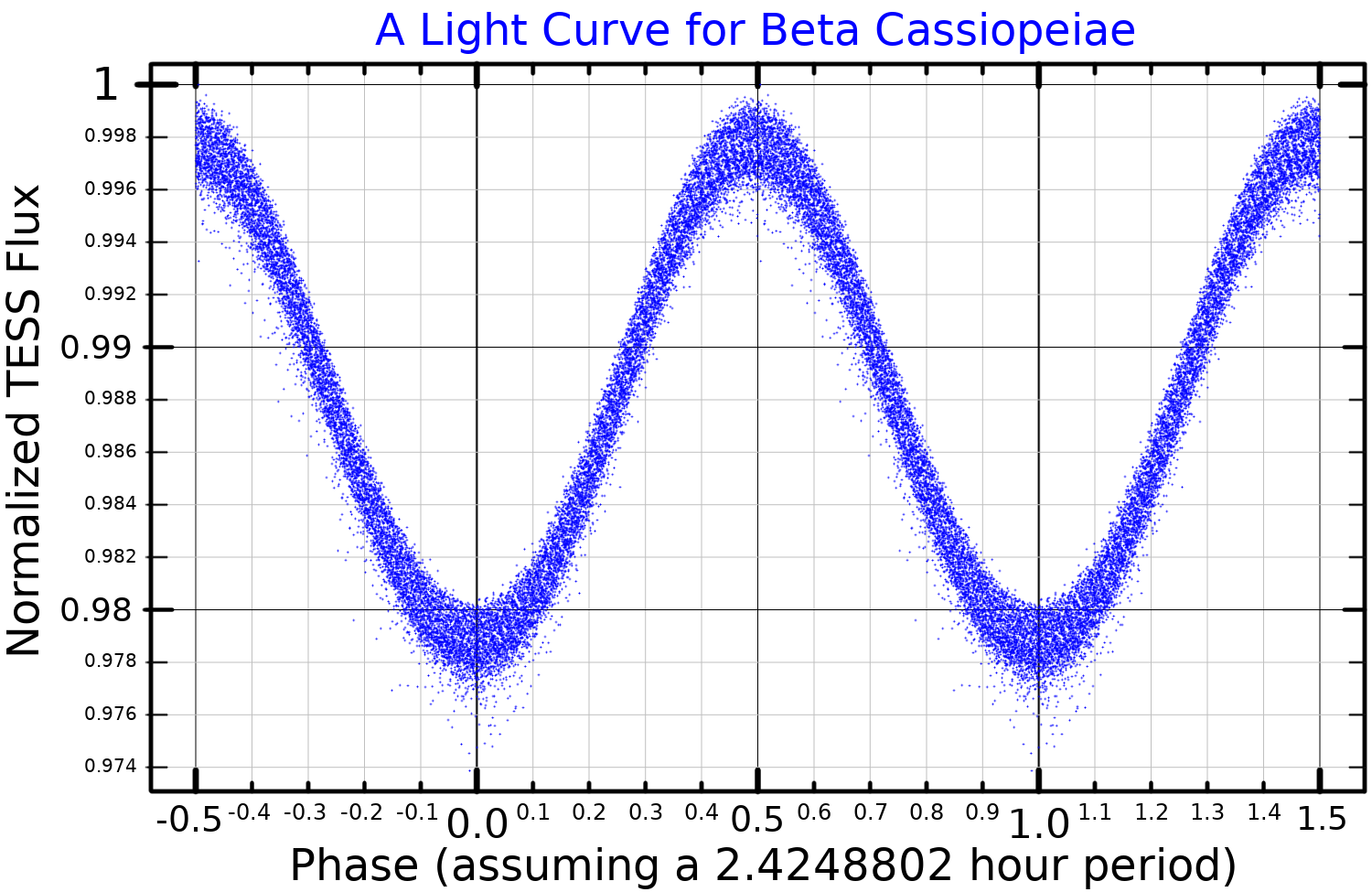
β Cassiopeiae
Beta Cassiopeiae (β Cassiopeiae, abbreviated Beta Cas or β Cas), officially named Caph , is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It is a giant star belonging to the spectral class F2. The white star of second magnitude (+2.28 mag, variable) has an absolute magnitude of +1.3 mag. Nomenclature ''Beta Cassiopeiae'' is the star's Bayer designation. It also bore the traditional names ''Caph'' (from the Arabic word ', "palm" - ''i.e.'' reaching from the Pleiades), ''Chaph'' and ''Kaff'', as well as ''al-Sanam al-Nakah'' "the Camel's Hump". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Caph'' for this star. Originally, the pre-Islamic Arabic term ''al-Kaff al-Khadib'' "the stained hand" referred to the five stars comprisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α Cassiopeiae
Alpha Cassiopeiae or α Cassiopeiae, also named Schedar (), is a second magnitude star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. Though listed as the "alpha star" by Johann Bayer, α Cas's visual brightness closely matches the 'beta' (β) star in the constellation (Beta Cassiopeiae) and it may appear marginally brighter or dimmer, depending on which passband is used. However, recent calculations from NASA's WISE telescope confirm that α Cas is the brightest in Cassiopeia, with an apparent magnitude of 2.240. Its absolute magnitude is 18 times greater than β Cas, and it is located over four times farther away from the Sun. Nomenclature ''α Cassiopeiae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Cassiopeiae'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Schedar'', which was first encountered in the Alfonsine tables of the thirteenth century. It derives from the Arabic word صدر ''şadr'', meaning "breast", a word which is derived from its relative position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. The word ''magnitude'' in astronomy, unless stated otherwise, usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale dates back to the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog listed stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined in a way to closely match this historical system. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to a brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a star of magnitude 2.0 is 2.512 times as bright as a star of magnitude 3.0, 6. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruptive Variable
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Cassiopeiae And Its Associated Nebulosity
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter represents either a voiced velar fricative or a voiced palatal fricative (while /g/ in foreign words is instead commonly transcribed as γκ). In the International Phonetic Alphabet and other modern Latin-alphabet based phonetic notations, it represents the voiced velar fricative. History The Greek letter Gamma Γ is a grapheme derived from the Phoenician letter (''gīml'') which was rotated from the right-to-left script of Canaanite to accommodate the Greek language's writing system of left-to-right. The Canaanite grapheme represented the /g/ phoneme in the Canaanite language, and as such is cognate with ''gimel'' ג of the Hebrew alphabet. Based on its name, the letter has been interpreted as an abstract representation of a camel's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |