|
Omar Torrijos International Airport
Tocumen International Airport ( es, Aeropuerto Internacional de Tocumen) is the primary international airport serving Panama City, the capital of Panama. The airport serves as the homebase for Copa Airlines and is a regional hub to and from The Caribbean, South, North and Central America and additionally features routes to some European and Asian cities. History During World War II, Panamanian airports were leased exclusively by the U.S. Armed Forces. The nearest airport to Tocumen was the ''Paitilla Point Airfield''. Several airports were built to protect the Panama Canal from foreign aggression. The 37th Pursuit Group at Albrook Field replaced the P-40 Warhawks of the 28th Pursuit Squadron at the Paitilla Point airbase from 9 December 1941 though 26 March 1942 in the immediate aftermath of the Pearl Harbor attack. Tocumen International Airport was inaugurated on June 1, 1947, by President Enrique Adolfo Jiménez, and airport operations began before the construction works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama City
Panama City ( es, Ciudad de Panamá, links=no; ), also known as Panama (or Panamá in Spanish), is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of Panama. The city is the political and administrative center of the country, as well as a hub for banking and commerce. The city of Panama was founded on 15 August 1519, by Spanish conquistador Pedro Arias Dávila. The city was the starting point for expeditions that conquered the Inca Empire in Peru. It was a stopover point on one of the most important trade routes in the American continent, leading to the fairs of Nombre de Dios and Portobelo, through which passed most of the gold and silver that Spain mined from the Americas. On 28 January 1671, the original city was destroyed by a fire when the privateer Henry Morgan sacked and set fire to it. The city was formally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrook Field
Albrook Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force facility in Panama. It was closed on 30 September 1997 as a result of the Torrijos-Carter Treaties which specified that United States military facilities in the former Panama Canal Zone be closed and the facilities be turned over to the Panamanian government. It was located on the east side of the Panama Canal just south of Fort Clayton and north of the township of Balboa, Panama. Beginning in January 1999, the air field initiated civilian air service as Albrook "Marcos A. Gelabert" International Airport. Major commands to which assigned * Panama Canal Department, 1932- 19 October 1940 * Panama Canal Air Force, 19 October 1940 - 5 August 1941 * Caribbean Air Force, 5 August 1941 - 18 September 1942 * Sixth Air Force, 18 September 1942 - 31 July 1946 * Caribbean Air Command, 31 July 1946 - 8 July 1963 * United States Air Forces Southern Command, 8 July 1963 - 1 January 1976 * Tactical Air Command : USAF Southern Air Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longest Flights
Over time, commercial airlines have established a number of scheduled ultra long-haul non-stop flights. These exceptionally long routes reduce the travel time between distant city pairs as well as the number of stops needed for passengers' travels, thereby increasing passenger convenience. For an airline, choosing to operate long flights can also build brand image as well as loyalty among a set of flyers. Thus there is competition among airlines to establish the longest flight. Definition The length of a flight can be defined in different ways. Typically, the great-circle distance between the origin and destination is used, but alternative metrics include the duration of the flight, and the actual distance flown (when a longer route can use the jet stream to reduce the total travel time). Also, although the term is most commonly used to compare between different non-stop flights, direct flights with stops (same flight number used for full journey) might also be compared on some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-stop Flight
A non-stop flight is a flight by an aircraft with no intermediate stops. History During the early age of aviation industry when aircraft range was limited, most flights were served in the form of milk run, aka there were many stops along the route. But as aviation technology develop and aircraft capability improves, non-stop flights begin to take over and have now become a dominant form of flight in the modern times. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 eventually opened up Russian airspace, allowing commercial airlines to exploit new circumpolar routes and enabling many new non-stop services, removing the need of making stopover in-between. In the late 2000s to early 2010s, rising fuel prices coupled with economic crisis resulted in cancellation of many ultra-long haul non-stop flights. As fuel prices fell and aircraft became more economical the economic viability of ultra long haul flights improved. Compare Direct flights and non-stop flights are often confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dubai International Airport
Dubai International Airport ( ar, مطار دبي الدولي) is the primary international airport serving Dubai, United Arab Emirates, and is the world's busiest airport by international passenger traffic. It is also the nineteenth-busiest airport in the world by passenger traffic, one of the busiest cargo airports in the world, the busiest airport for Airbus A380 and Boeing 777 movements, and the airport with the highest average number of passengers per flight. In 2017, the airport handled 88 million passengers and 2.65 million tonnes of cargo and registered 409,493 aircraft movements. Dubai International Airport is situated in the Al Garhoud district, east of Dubai and spread over an area of of land. Terminal 3 is the second-largest building in the world by floor space and the largest airport terminal in the world. In July 2019, Dubai International airport installed the largest solar energy system in the region's airports as part of Dubai's goal to reduce 30 percen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirates (airline)
Emirates ( ar, طَيَران الإمارات DMG: ''Ṭayarān Al-Imārāt'') is one of two flag carriers of the United Arab Emirates (the other being Etihad). Based in Garhoud, Dubai, the airline is a subsidiary of The Emirates Group, which is owned by the government of Dubai's Investment Corporation of Dubai. , it was also the largest airline in the Middle East, operating over 3,600 flights per week from its hub at Terminal 3 of Dubai International Airport. It operates to more than 150 cities in 80 countries across 6 continents through its fleet of nearly 300 aircraft. Cargo activities are undertaken by Emirates SkyCargo. Emirates is the world's fourth-largest airline by scheduled revenue passenger-kilometers flown, and the second-largest in terms of freight tonne-kilometers flown. During the mid-1980s, Gulf Air began to cut back its services to Dubai. As a result, Emirates was conceived on 15 March 1985, with backing from Dubai's royal family, with Pakistan Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Landing System
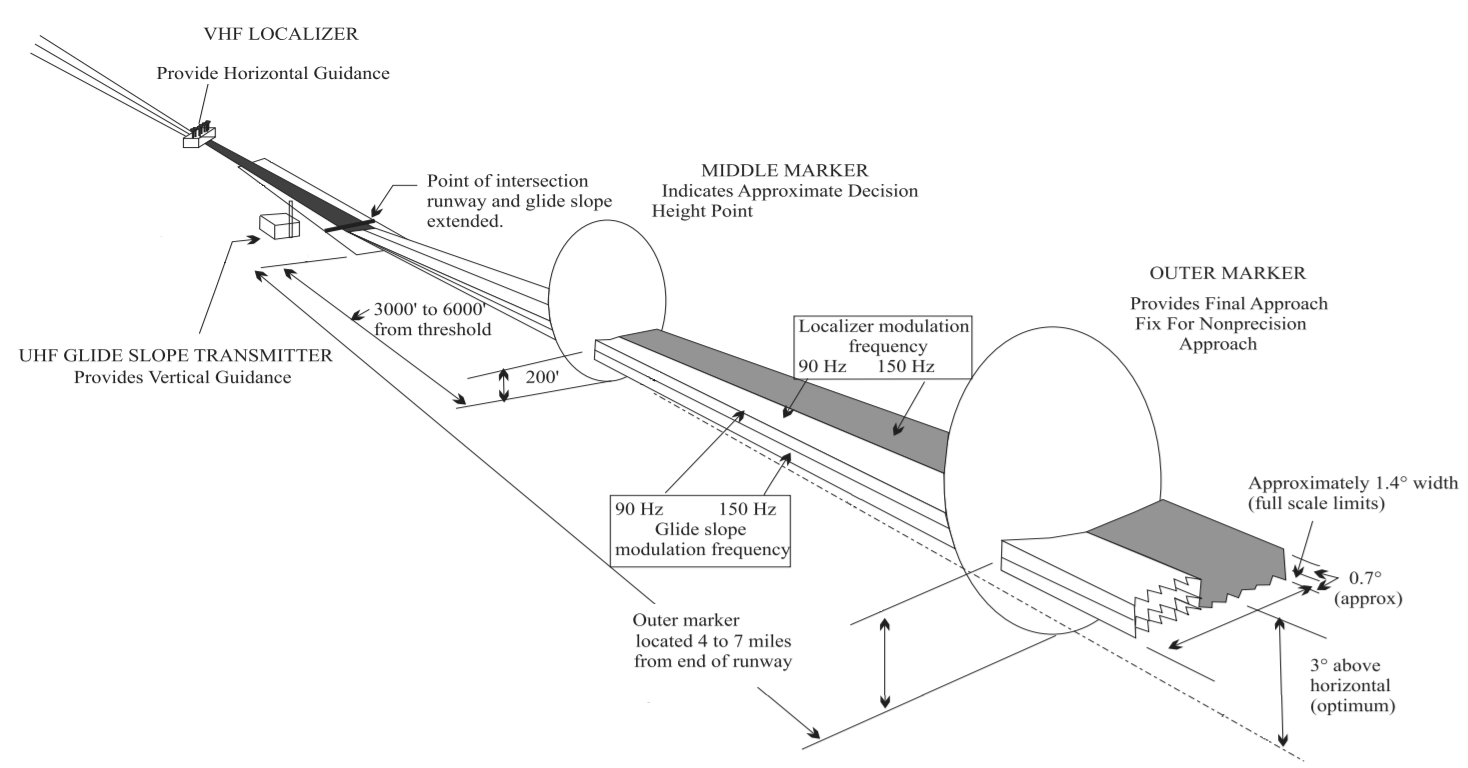
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
82nd Airborne Division
The 82nd Airborne Division is an Airborne forces, airborne infantry division (military), division of the United States Army specializing in Paratrooper, parachute assault operations into denied areasSof, Eric"82nd Airborne Division" ''Spec Ops Magazine'', 25 November 2012. Archived from thoriginalon 1 September 2017. with a United States Department of Defense, U.S. Department of Defense requirement to "respond to crisis contingencies anywhere in the world within 18 hours".82nd Airborne Division Army.mil, dated 16 May 2018, last accessed 11 September 2018 Based at Fort Bragg, Fort Bragg, North Carolina, the 82nd Airborne Division is part of the XVIII Airborne Corps. The 82nd Airborne Division is the U.S. Army's most strategically mobile division. The division was constituted, originally as the 82nd Division, in the National Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Invasion Of Panama
The United States invasion of Panama, codenamed Operation Just Cause, lasted over a month between mid-December 1989 and late January 1990. It occurred during the administration of President George H. W. Bush and ten years after the Torrijos–Carter Treaties were ratified to transfer control of the Panama Canal from the United States to Panama by January 1, 2000. The primary purpose of the invasion was to depose the ''de facto'' Panamanian leader, General Manuel Noriega. He was wanted by the United States for Racket (crime), racketeering and drug trafficking. Following the operation, the Panama Defense Forces were dissolved and President-elect Guillermo Endara was sworn into office. The United Nations General Assembly and the Organization of American States condemned the invasion as a violation of international law. Background The United States had maintained numerous military bases and a substantial garrison throughout the Panama Canal Zone, Canal Zone to protect the America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omar Torrijos
Omar Efraín Torrijos Herrera (February 13, 1929 – July 31, 1981) was the Commander of the Panamanian National Guard and military leader of Panama from 1968 to his death in 1981. Torrijos was never officially the president of Panama, but instead held titles including "Maximum Leader of the Panamanian Revolution". Torrijos took power in a ''coup d'état'' and instituted a number of social reforms. Torrijos is best known for negotiating the 1977 Torrijos–Carter Treaties that eventually gave Panama full sovereignty over the Panama Canal. The two treaties guaranteed that Panama would gain control of the Panama Canal after 1999, ending the control of the canal that the U.S. had exercised since 1903. On December 31, 1999, the final phase of the treaty, the US relinquished control of the Panama Canal and all areas in what had been the Panama Canal Zone. His son Martín Torrijos was elected president and served from 2004 to 2009. Background Torrijos was born in Santi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Antonio Remón Cantera
Colonel José Antonio Remón Cantera (11 April 1908 – 2 January 1955) was the 29th President of Panama, holding office from 1 October 1952 until his death on January 2, 1955. He was Panama's first military strongman and ruled the country behind the scenes in the late 1940s. He belonged to the National Patriotic Coalition (CNP), and was its candidate for president in May 1952. He joined the National Police in 1931, becoming its chief in 1947. In this position, he was responsible for the coup against acting president Daniel Chanis Pinzón. Beginning in 1953, his administration began to negotiate amendments to the Panama Canal treaty with the U.S. administration of President Dwight D. Eisenhower. These negotiations led to an agreement, ratified in 1955, that substantially raised the annual annuity paid to Panama (from $430,000 to $1.9 million) and resulted in the handover of approximately $20 million in property from the Panama Canal Company to Panama. General José Remón was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enrique Adolfo Jiménez
Enrique Adolfo Jiménez Brin (8 February 1888 – 28 April 1970) was President of Panama from 15 June 1945 to 7 August 1948, representing the National Liberal Party of Panama. Jiménez Brin was appointed private secretary of President Belisario Porras Barahona at the age of 25, deputy Minister of State, president of the National Bank of Panama and ambassador of Panama to the United States at Washington, D.C., an important post due to the authority exercised by the U.S. over Panama due to its ownership of the Panama Canal. He was elected the first presidential designate by the National Assembly for the 1924–1926 term and a second time for the 1934–1936 term. In June 1945, he was appointed president of the Republic of Panama by the Constituent National Assembly, and remained in office until 7 August 1948. Achievements During his term in office, Jiménez's achievements included: * Tocumen International Airport was constructed * The Colón Free Trade Zone was created * T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14597444780).jpg)