|
Olm
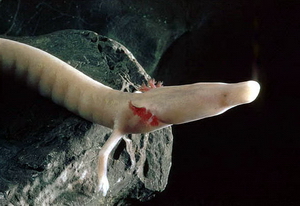
The olm or proteus (''Proteus anguinus'') is an aquatic salamander in the family Proteidae, the only exclusively cave-dwelling chordate species found in Europe. In contrast to most amphibians, it is entirely aquatic, eating, sleeping, and breeding underwater. Living in caves found in the Dinaric Alps, it is endemic to the waters that flow underground through the extensive limestone bedrock of the karst of Central and Southeastern Europe in the basin of the Soča River ( it, Isonzo) near Trieste, Italy, southwestern Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Introduced populations are found near Vicenza, Italy, and Kranj, Slovenia. It is also called the "human fish" by locals because of its fleshy skin color (translated literally from sl, človeška ribica, mk, човечка рипка, hr, čovječja ribica, bs, čovječja ribica sr, човечја рибица), as well as "cave salamander" or "white salamander". In Slovenia, it is called ''močeril'' (from *''močerъ'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteidae
The family Proteidae is a group of aquatic salamanders found today in the Balkan Peninsula and North America. The range of the genus ''Necturus'' (commonly known as waterdogs or mudpuppies) runs from southern central Canada, through the midwestern United States, east to North Carolina and south to Georgia and Mississippi. The range of the olm, the only extant member of the genus ''Proteus'', is limited to the Western Balkans. The fossil record of the family extends into the end of the Late Cretaceous, with '' Paranecturus'' being known from the Maastrichtian of North America. Taxonomy Proteidae, is divided into two extant genera, ''Necturus'' with five North American species, and ''Proteus'' with one extant European species, the olm. A number of extinct genera are known extending back to the end of the Late Cretaceous. Family Proteidae * Genus ''Necturus'' **Alabama waterdog (''N. alabamensis'') ** Western waterdog (''N. beyeri'') ** Neuse River waterdog (''N. lewisi'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postojna Cave
Postojna Cave ( sl, Postojnska jama; german: Adelsberger Grotte; it, Grotte di Postumia) is a long karst cave system near Postojna, southwestern Slovenia. It is the second-longest cave system in the country (following the Migovec System) as well as one of its top tourism sites. The caves were created by the Pivka River. History The cave was first described in the 17th century by the pioneer of study of karst phenomena, Johann Weikhard von Valvasor, although graffiti inside dated to 1213 indicates a much longer history of use. In 1818, when the cave was being prepared for a visit by Francis I, the first Emperor of the Austria-Hungary, a new area of the cave was discovered accidentally by Luka Čeč, a local man in charge of lighting lamps in the cave. In the 1850s, the Austrian-Czech geographer Adolf Schmidl published the first comprehensive scientific overview of the Postojna caves and the Pivka Basin, which became a standard reference point in the study of speleology. Fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Salamander
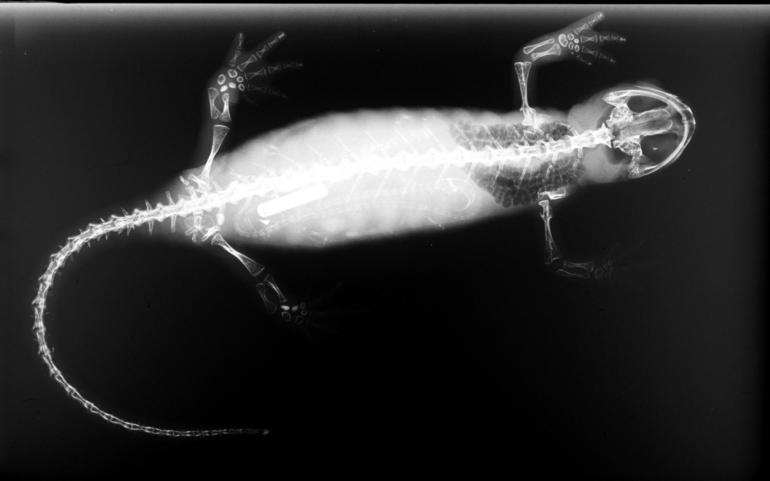
A cave salamander is a type of salamander that primarily or exclusively inhabits caves, a group that includes several species. Some of these animals have developed special, even extreme, adaptations to their subterranean environments. Some species have only rudimentary (or even absent) eyes (''blind salamanders''). Others lack pigmentation, rendering them a pale yellowish or pinkish color (e.g., '' Eurycea rathbuni''). With the notable exception of '' Proteus anguinus'', all "cave salamanders" are members of the family Plethodontidae ("lungless salamanders"). History The first dedicated scientific study of a cave animal was focused upon a cave salamander, '' Proteus anguinus''. It was originally identified as a "dragon's larva" by Johann Weikhard von Valvasor in 1689. Later, the Austrian naturalist Joseph Nicolaus Lorenz described it scientifically in 1768. Another early scientific description of a cave salamander was undertaken by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in 1822 while h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of 2.1 million (2,108,708 people). Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Weikhard Von Valvasor
Johann Weikhard Freiherr von Valvasor or Johann Weichard Freiherr von Valvasor ( sl, Janez Vajkard Valvasor, ) or simply Valvasor (baptised on 28 May 1641 – September or October 1693) was a natural historian and polymath from Carniola, present-day Slovenia, and a fellow of the Royal Society in London. He is known as a pioneer of study of karst studies. Together with his other writings, until the late 19th century his best-known work—the 1689 ''Glory of the Duchy of Carniola'', published in 15 books in four volumes—was the main source for older Slovenian history, making him one of the precursors of modern Slovenian historiography. Biography Valvasor was born in the town of Ljubljana, then Duchy of Carniola, now the capital of Slovenia. In the 16th century, it was Johann Baptist Valvasor who established the family Valvasor in the Duchy of Carniola in central Europe in a part of Austria that is now the Republic of Slovenia. In medieval Latin " Valvasor" or "Valvasore" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Glory Of The Duchy Of Carniola
''The Glory of the Duchy of Carniola'' (german: Die Ehre deß Hertzogthums Crain, sl, Slava vojvodine Kranjske) is an encyclopedia published in Nuremberg in 1689 by the polymath Johann Weikhard von Valvasor. It is the most important work on his homeland, the Duchy of Carniola, the present-day central part of Slovenia. Content Written in New High German, the anthology was published in four volumes, subdivided into 15 books with 3,552 large-format pages and 24 annexes. It was lavishly illustrated with 528 copperplate engravings. The work refers to history, geography, topography, medicine, biology, geology, theology, customs and folklore of the Carniolan region that makes up a large part of present-day Slovenia. Valvasor could rely on older accounts, nevertheless the meticulously researched and scientifically sound collection was pioneering at that time. From 2009 until 2012, it was translated into Slovene by Doris, Primož and Božidar Debenjak. The initiator, project manager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestigiality
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicenza
Vicenza ( , ; ) is a city in northeastern Italy. It is in the Veneto region at the northern base of the '' Monte Berico'', where it straddles the Bacchiglione River. Vicenza is approximately west of Venice and east of Milan. Vicenza is a thriving and cosmopolitan city, with a rich history and culture, and many museums, art galleries, piazzas, villas, churches and elegant Renaissance '' palazzi''. With the Palladian Villas of the Veneto in the surrounding area, and his renowned '' Teatro Olimpico'' (Olympic Theater), the "city of Palladio" has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1994. In December 2008, Vicenza had an estimated population of 115,927 and a metropolitan area of 270,000. Vicenza is the third-largest Italian industrial centre as measured by the value of its exports, and is one of the country's wealthiest cities, in large part due to its textile and steel industries, which employ tens of thousands. Additionally, about one fifth of the country's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system receives signals from the senses which continuously receive information from the environment, interprets these signals, and causes the body to respond, either chemically or physically.) Although traditionally five human senses were identified as such (namely sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing), it is now recognized that there are many more. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought. In organisms, a sensory organ consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as winged, horned, and capable of breathing fire. Dragons in eastern cultures are usually depicted as wingless, four-legged, serpentine creatures with above-average intelligence. Commonalities between dragons' traits are often a hybridization of feline, reptilian and avian features. Scholars believe huge extinct or migrating crocodiles bear the closest resemblance, especially when encountered in forested or swampy areas, and are most likely the template of modern Oriental dragon imagery. Etymology The word ''dragon'' entered the English language in the early 13th century from Old French ''dragon'', which in turn comes from la, draconem (nominative ) meaning "huge serpent, dragon", from Ancient Greek , (genitive , ) "serpent, gian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)

