|
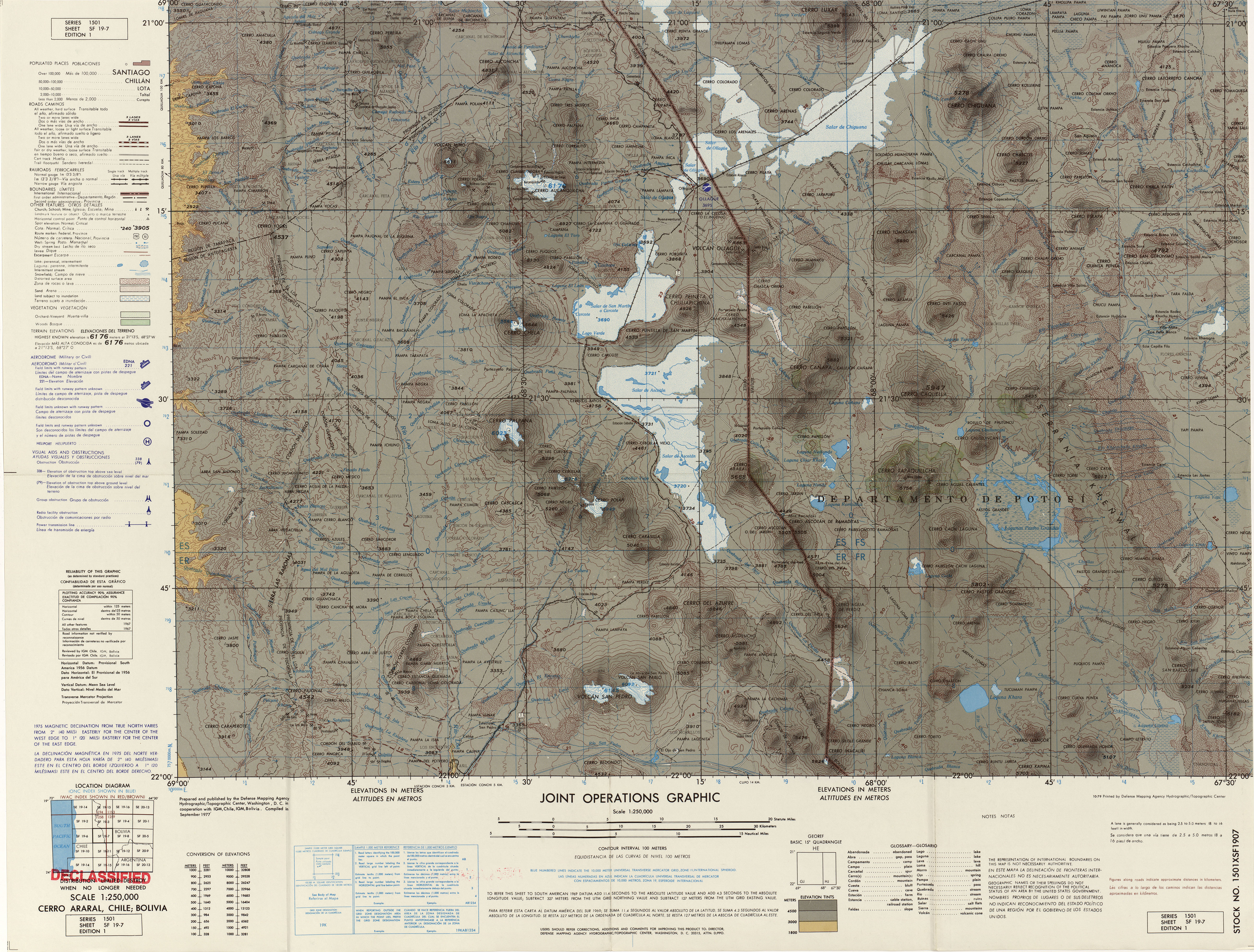
Olca
Olca is a stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. It lies in the middle of a 15 km long ridge composed of several stratovolcanos. Cerro Minchincha lies to the west and Paruma to the east. It is also close to the pre-Holocene Cerro Paruma. It is andesitic and dacitic in composition, with lava flows extending several kilometres north of the peak. The only activity from the ridge during historical times was a flank eruption from 1865 to 1867. The exact source of this eruption is unclear. Gas emissions and composition The gasses emission is comprised by a single warm spring at the base and a persistent fumarole field over at the crater's dome for at least 60 years. The fumarolic field is about 0.1 km2 and the emissions measured in situ at the crater show a highly mixed magmatic system between high temperature temperature gasses and hydrothermal fluids. The gas composition indicates low concentration of H2, CO and acidic gasses, and high concentration of H2S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olca
Olca is a stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. It lies in the middle of a 15 km long ridge composed of several stratovolcanos. Cerro Minchincha lies to the west and Paruma to the east. It is also close to the pre-Holocene Cerro Paruma. It is andesitic and dacitic in composition, with lava flows extending several kilometres north of the peak. The only activity from the ridge during historical times was a flank eruption from 1865 to 1867. The exact source of this eruption is unclear. Gas emissions and composition The gasses emission is comprised by a single warm spring at the base and a persistent fumarole field over at the crater's dome for at least 60 years. The fumarolic field is about 0.1 km2 and the emissions measured in situ at the crater show a highly mixed magmatic system between high temperature temperature gasses and hydrothermal fluids. The gas composition indicates low concentration of H2, CO and acidic gasses, and high concentration of H2S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paruma
Paruma is a stratovolcano that lies on the border of Bolivia and Chile. It is part of a ridge that contains several stratovolcanos. Paruma lies at the eastern end of the ridge, with Olca to its west. The older volcano Paruma lies to east of Paruma. Paruma has clearly been active during the Holocene, with many morphologically young lava flows on its flanks. It also has persistent fumarole A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcani ...s. One lava flow in particular extends for 7 kilometres to the south-east of the peak. Historical activity along the ridge has been confined to one eruption from 1865 to 1867, the character of which is not precisely known. Sources * Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Potosí Department Stratovolcanoes of Chile Polygenetic volcanoes Bolivia� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Bolivia
The country of Bolivia hosts numerous activeIn vulcanology and this article active volcanoes are those with Holocene eruption, that means eruptions in the last 10,000 years. and extinct volcanoes across its territory. The active volcanoes are in western Bolivia making up the Cordillera Occidental, the western limit of the Altiplano plateau. Many of the active volcanoes are international mountains shared with Chile. All Cenozoic volcanoes of Bolivia are part of the Central Volcanic Zone (CVZ) of the Andean Volcanic Belt that results due to processes involved in the subduction of Nazca Plate under the South American Plate. The Central Volcanic Zone is a major upper Cenozoic volcanic province. Apart from Andean volcanoes the geology of Bolivia host the remnants of ancient volcanoes around the Precambrian Guaporé Shield in the eastern part of the country. Image:Nevado Sajama.jpg, Sajama, a stratovolcano considered extinct. Image:Licancabur Green Lake.jpg, View of Licancabur. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Chile
The Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program lists 105 volcanoes in Chile that have been active during the Holocene. using Chile, Chile-Peru, Chile-Bolivia and Chile-Argentina options, retrieved on 10 November 2013 The country's lists 90 active volcanoes. The volcanoes of the originate from the of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia–Chile Border
The Bolivia–Chile border is an international border of South America. It separates Bolivia from Chile along Cordillera Occidental on the western edge of the Altiplano Plateau. There is an ongoing dispute about the nature of Silala River and Chile's use of its waters. Since 2021 the Bolivia–Chile border has been a major point of entry of irregular Venezuelan migrants into Chile. Migrants are aided in the crossing by human smugglers. Irregular migration has been particularly troublesome for the Chilean border town of Colchane. Indigenous Aymara communities live on both sides of the border. References Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ... Borders of Chile International borders Geography of Arica y Parinacota Region Geography of Tarapacá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor Lípez Province
Nor Lípez is a province in the Bolivian department of Potosí. Its seat is Colcha "K", also called Villa Martín. The majority of the area of the province was titled as the Nor Lípez Native Community Land on 19 April 2011. One of the largest mines of Bolivia, the San Cristóbal Mine, is located near San Cristóbal in Colcha "K" municipality. Geography Some of the highest mountains of the province are listed below: Location The province is one of sixteen provinces in the Potosí Department. It is located between 20° 27' and 22° 01' South and between 66° 18' and 68° 35' West. It is bordered by the Daniel Campos Province to the north, the Republic of Chile to the west, the Enrique Baldivieso Province and Sur Lípez Province to the south, Sud Chichas Province to the east, and the Antonio Quijarro Province to the northeast. The province extends over 270 km from east to west and 210 km from north to south. Division The province comprises two m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Pedro De Quemes Municipality
San Pedro de Quemes ( qu, Qimis) is the second municipal section of the Nor Lípez Province in the Potosí Department in Bolivia. Its seat is San Pedro de Quemes. Geography The municipality lies at the Uyuni salt flat. Some of the highest mountains of the municipality are listed below: Many of the mountains and volcanoes are a natural border to Chile. Subdivision The municipality consists of the following cantons: * Cana - 44 inhabitants (''2001'') * Chiguana - 10 inhabitants * Pajancha - 52 inhabitants * Pelcoya - 135 inhabitants * San Pedro de Quemes- 574 inhabitants The people The people are mainly not indigenous and 45,0% are citizens of Quechua Quechua may refer to: *Quechua people, several indigenous ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru *Quechuan languages, a Native South American language family spoken primarily in the Andes, derived from a common ancestral language **So ... descent.obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo/municipal/fichas/ (inactive) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cana Canton
San Pedro de Quemes ( qu, Qimis) is the second municipal section of the Nor Lípez Province in the Potosí Department in Bolivia. Its seat is San Pedro de Quemes. Geography The municipality lies at the Uyuni salt flat. Some of the highest mountains of the municipality are listed below: Many of the mountains and volcanoes are a natural border to Chile. Subdivision The municipality consists of the following cantons: * Cana - 44 inhabitants (''2001'') * Chiguana - 10 inhabitants * Pajancha - 52 inhabitants * Pelcoya - 135 inhabitants * San Pedro de Quemes- 574 inhabitants The people The people are mainly not indigenous and 45,0% are citizens of Quechua Quechua may refer to: *Quechua people, several indigenous ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru *Quechuan languages, a Native South American language family spoken primarily in the Andes, derived from a common ancestral language **So ... descent.obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo/municipal/fichas/ (inactive) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ollagüe
Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Chile, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar. Ollagüe is mostly of Pleistocene age. It started developing more than one million years ago, forming the so-called Vinta Loma and Santa Rosa series mostly of andesitic lava flows. A fault bisects the edifice and two large landslides occurred in relation to it. Later two groups of dacitic lava domes formed, Ch'aska Urqu on the southeastern slope and La Celosa on the northwestern. Another centre named La Poruñita formed at that time on the western foot of the volcano, but it is not clear wheth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Minchincha
Michincha is a stratovolcano on the border of Bolivia and Chile. It is part of an east–west trending ridge of stratovolcanoes. To its east lies Olca Olca is a stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. It lies in the middle of a 15 km long ridge composed of several stratovolcanos. Cerro Minchincha lies to the west and Paruma to the east. It is also close to the pre-Holocene Cerr .... The only historical activity from the complex was a flank eruption from 1865 to 1867. Sources Stratovolcanoes of Chile Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Potosí Department Mountains of Chile Polygenetic volcanoes Bolivia–Chile border International mountains of South America Volcanoes of Tarapacá Region Holocene stratovolcanoes {{Tarapacá-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Antofagasta Region
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)