|
Oechalia (Trachis)
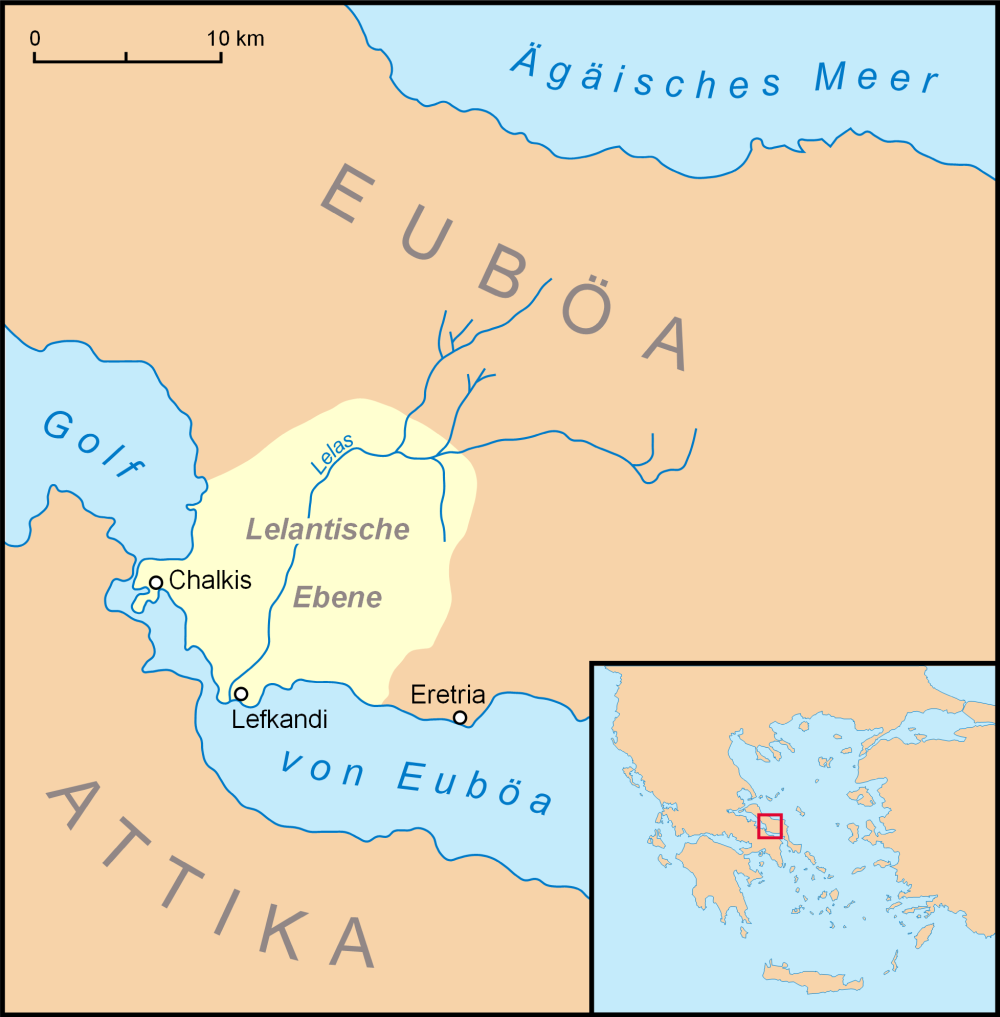
Oechalia or Oichalia ( grc, Οἰχαλία) was a town in Trachis, in ancient Thessaly. According to Greek mythology, King Eurytus of Oechalia had promised the hand of his beautiful daughter Iole to whoever defeated him in an archery competition. Heracles beat him but Eurytus refused to keep his promise, so Heracles sacked the city, killed Eurytus and kidnapped Iole. However, there was great discussion in antiquity about whether this Oechalia referred to this city, that of Euboea, or another also located in Thessaly, or even to others that were located in Arcadia or Messenia. The author of the epic poem ''Capture of Oechalia'' (usually attributed to Creophylus of Samos), Sophocles (in ''The Trachiniae'') and Hecataeus of Miletus (who locates Oechalia near Eretria) were aligned among with those who identified this Oechalia with the Euboean location. Homer, equivocally, and Apollodorus of Athens and Aristarchus of Samothrace placed it in Thessaly. Also, Demetrius of Scepsis placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachis
Trachis ( grc-gre, , ''Trakhís'') was a region in ancient Greece. Situated south of the river Spercheios, it was populated by the Malians. It was also a polis (city-state). Its main town was also called ''Trachis'' until 426 BC, when it was refounded as a Spartan colony and became Heraclea Trachinia. It is located to the west of Thermopylae. Trachis is located just west of the westernmost tip of the island of Euboea, north of Delphi. Near this place archaeologists discovered tombs from the Mycenaean period. According to Greek mythology Trachis was the home of Ceyx and Alcyone. Heracles went to Trachis after the death of Eunomus. The town is mentioned by Homer (as one of the cities subject to Achilles) and for the last time in antiquity by Pausanias. Trachis/Heraclea in ancient and modern times In antiquity the settlement was famous for being at the base of the mountain where Heracles is said to have died (Mount Oeta) as well as being the place where the descendants of Heracl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hecataeus Of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer. Biography Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Persian rule in the satrapy of Lydia. He was active during the time of the Greco-Persian Wars. After having travelled extensively, he settled in his native city, where he occupied a high position, and devoted his time to the composition of geographical and historical works. When Aristagoras, acting tyrant of Miletus, held a council of leading Ionians at Miletus to organize a revolt against Persian rule, Hecataeus tried in vain to dissuade his countrymen from the undertaking. In 494 BC, when the defeated Ionians were obliged to sue for terms, he was one of the ambassadors to the Persian satrap Artaphernes, whom he persuaded to restore the constitution of the Ionic cities. Hecataeus is the first known Greek historian and was one of the first c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Greece
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( /pɔːˈseɪniəs/; grc-gre, Παυσανίας; c. 110 – c. 180) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his ''Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology. Biography Not much is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is mostly certain that he was born c. 110 AD into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From c. 150 until his death in 180, Pausanias travelled through the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing ''Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together a lasting written account of "all things Greek", or ''panta ta hellenika''. Living in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pherecydes Of Athens
Pherecydes of Athens ( grc, Φερεκύδης) (fl. c. 465 BC), described as an historian and genealogist, wrote an ancient work in ten books, now lost, variously titled "Historiai" (''Ἱστορίαι'') or "Genealogicai" (''Γενελογίαι''). He is one of the authors (= ''FGrHist'' 3) whose fragments were collected in Felix Jacoby's ''Die Fragmente der griechischen Historiker''. He is generally thought to be different from the sixth-century Pre-Socratic philosopher Pherecydes of Syros, who was sometimes mentioned as one of the Seven Sages of Greece and was reputed to have been the teacher of Pythagoras. Although the ''Suda'' considers them separately, he is possibly the same person as Pherecydes of Leros.Sweeneypp. 47–48 ''Suda The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, Σοῦδα, Soûda; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (Σούδας) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Iliad'', the poem is divided into 24 books. It follows the Greek hero cult, Greek hero Odysseus, king of Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, and his journey home after the Trojan War. After the war, which lasted ten years, his journey lasted for ten additional years, during which time he encountered many perils and all his crew mates were killed. In his absence, Odysseus was assumed dead, and his wife Penelope and son Telemachus had to contend with a Suitors of Penelope, group of unruly suitors who were competing for Penelope's hand in marriage. The ''Odyssey'' was originally composed in Homeric Greek in around the 8th or 7th century BCE and, by the mid-6th century BCE, had become part of the Greek literary canon. In Classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version, and was written in dactylic hexameter. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the siege's final weeks. In particular, it depicts a fierce quarrel between King Agamemnon and a celebrated warrior, Achilles. It is a central part of the Epic Cycle. The ''Iliad'' is often regarded as the first substantial piece of European literature. The ''Iliad'', and the ''Odyssey'', were likely written down in Homeric Greek, a literary amalgam of Ionic Greek and other dialects, probably around the late 8th or early 7th century BC. Homer's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrius Of Scepsis
Demetrius of Scepsis ( grc, Δημήτριος ὁ Σκήψιος) was a Greek grammarian of the time of Aristarchus and Crates ( Strab. xiii. p. 609), the first half of the second century BC. He is sometimes simply called the Scepsian (Strab. ix. pp. 438, 439, x. pp. 456, 472, 473, 489), and sometimes simply Demetrius (Strab. xii. pp. 551, 552, xiii. pp. 596, 600, 602). Diogenes Laërtius mention him as one in a list of well-known namesakes. He was the author of a very extensive work which is very often referred to, and bore the title . It consisted of at least twenty-six books (Strab. xiii. p. 603 and passim; Athen. iii. pp. 80, 91; Steph. Byz. s.v. ). This work was an historical and geographical commentary on that part of the second book of the Iliad in which the forces of the Trojans are enumerated, known as the Trojan Battle Order or Trojan Catalogue (compare Harpocrat. s. vv. , ; Schol. ad Apollon. Rhod. i. 1123, 1165). The numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarchus Of Samothrace
Aristarchus of Samothrace ( grc-gre, Ἀρίσταρχος ὁ Σαμόθραξ ''Aristarchos o Samothrax''; c. 220 – c. 143 BC) was an ancient Greek grammarian, noted as the most influential of all scholars of Homeric poetry. He was the head librarian of the Library of Alexandria and seems to have succeeded his teacher Aristophanes of Byzantium in that role. Life Aristarchus left the island of Samothrace at a young age and went to Alexandria, where he studied with the director of the library. Later, he was a teacher at the royal courtyard, and then director of the library from 153 to 145 BC. After he was persecuted by his disciple Ptolemy the Benefactor, he found refuge in Cyprus, where he died. It said that Aristarchus had a remarkable memory and was completely indifferent as to his external appearance. Accounts of his death vary, though they agree that it was during the persecutions of Ptolemy VIII of Egypt. One account has him, having contracted an incurable dropsy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollodorus Of Athens
Apollodorus of Athens ( el, Ἀπολλόδωρος ὁ Ἀθηναῖος, ''Apollodoros ho Athenaios''; c. 180 BC – after 120 BC) son of Asclepiades, was a Greek scholar, historian, and grammarian. He was a pupil of Diogenes of Babylon, Panaetius the Stoic, and the grammarian Aristarchus of Samothrace, under whom he appears to have studied together with his contemporary Dionysius Thrax. He left (perhaps fled) Alexandria around 146 BC, most likely for Pergamon, and eventually settled in Athens. Literary works * ''Chronicle'' (''Χρονικά'', ''Chronika''), a Greek history in verse from the fall of Troy in the 12th century BC to roughly 143 BC (although later it was extended as far as 109 BC), and based on previous works by Eratosthenes of Cyrene. Its dates are reckoned by its references to the archons of Athens. As most archons only held office for one year, scholars have been able to pin down the years to which Apollodorus was referring. The poem is written in comic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |