|
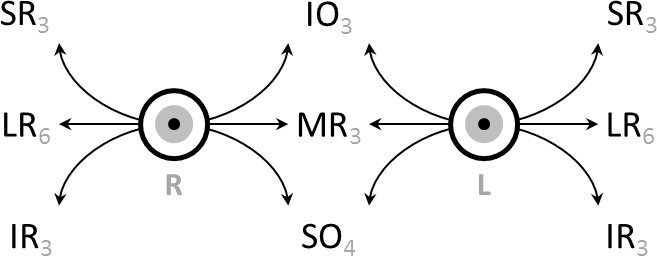
Oculomotor
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit (anatomy), orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most eye movement, movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation (ability to focus on near objects as in reading). The oculomotor nerve is derived from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves trochlear nerve, IV and abducens, VI also participate in control of Eye movement (sensory), eye movement. Structure The oculomotor nerve originates from the third nerve nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus at the level of the superior colliculus in the midbrain. The third nerve nucleus is located ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, on the pre-aqueductal grey matter. The fibers from the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Branch Of Oculomotor Nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit (anatomy), orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most eye movement, movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation (ability to focus on near objects as in reading). The oculomotor nerve is derived from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves trochlear nerve, IV and abducens, VI also participate in control of Eye movement (sensory), eye movement. Structure The oculomotor nerve originates from the third nerve nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus at the level of the superior colliculus in the midbrain. The third nerve nucleus is located ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, on the pre-aqueductal grey matter. The fibers from the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Branch Of Oculomotor Nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation (ability to focus on near objects as in reading). The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement. Structure The oculomotor nerve originates from the third nerve nucleus at the level of the superior colliculus in the midbrain. The third nerve nucleus is located ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, on the pre-aqueductal grey matter. The fibers from the two third nerve nuclei located laterally on either side of the cerebral aqueduct then pass through the red nucleus. From the red nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge from the cerebrum, and the remaining ten pairs arise from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraocular Muscles
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the other muscle, the levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction. Structure Since only a small part of the eye called the fovea provides sharp vision, the eye must move to follow a target. Eye movements must be precise and fast. This is seen in scenarios like reading, where the reader must shift gaze constantly. Although under voluntary control, most eye movement is accomplished without conscious effort. Precisely how the integration between voluntary and involuntary control of the eye occurs is a subject of continuing research."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculomotor Nucleus
The fibers of the oculomotor nerve arise from a nucleus in the midbrain, which lies in the gray substance of the floor of the cerebral aqueduct and extends in front of the aqueduct for a short distance into the floor of the third ventricle. From this nucleus the fibers pass forward through the tegmentum, the red nucleus, and the medial part of the substantia nigra, forming a series of curves with a lateral convexity, and emerge from the oculomotor sulcus on the medial side of the cerebral peduncle. The nucleus of the oculomotor nerve does not consist of a continuous column of cells, but is broken up into a number of smaller nuclei, which are arranged in two groups, anterior and posterior. Those of the posterior group are six in number, five of which are symmetrical on the two sides of the middle line, while the sixth is centrally placed and is common to the nerves of both sides. The anterior group consists of two nuclei, an antero-medial and an antero-lateral. The nucleus of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Movement (sensory)
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep. The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex. Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit, vergence shifts and saccades. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe. This is corroborated by removal of the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpeduncular Fossa
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression of the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two crura cerebri. It has been found in humans and macaques, but not in rats or mice, showing that this is a relatively new evolutionary region. Anatomy The interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain. Features The lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa bears a groove - the oculomotor sulcus - from which rootlets of the oculomotor nerve emerge from the substance of the brainstem and aggregate into a single fascicle. Anatomical relations The ventral tegmental area lies at the depth of the interpeduncular fossa. Boundaries The interpeduncular fossa is in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles. The floor of interpeduncular fossa, from behind forward, are the posterior perforated substance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Movement
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep. The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex. Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit, vergence shifts and saccades. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe. This is corroborated by removal of the frontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Oblique
The inferior oblique muscle or obliquus oculi inferior is a thin, narrow muscle placed near the anterior margin of the floor of the orbit. The inferior oblique is one of the extraocular muscles, and is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) and the posterior, inferior, lateral surface of the eye (insertion). The inferior oblique is innervated by the inferior branch of the oculomotor nerve. Structure The inferior oblique arises from the orbital surface of the maxilla, lateral to the lacrimal groove. Unlike the other extraocular muscles (recti and superior oblique), the inferior oblique muscle does ''not'' originate from the common tendinous ring ( annulus of Zinn). Passing lateralward, backward, and upward, between the inferior rectus and the floor of the orbit, and just underneath the lateral rectus muscle, the inferior oblique inserts onto the scleral surface between the inferior rectus and lateral rectus. In humans, the muscle is about 35 mm long. Innervation Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Orbital Fissure
The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus. Structure The superior orbital fissure is usually 22 mm wide in adults, and is much larger medially. Its boundaries are formed by the (caudal surface of the) lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, and (medial border of the) greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Contents The superior orbital fissure is traversed by the following structures: * (superior and inferior divisions of the) oculomotor nerve (CN III) * trochlear nerve (CN IV) * lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) * abducens nerve (CN VI) * superior ophthalmic vein and superior division of the inferior ophthalmic vein * sympathetic fibres from the cavernous nerve pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Rectus
The superior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit. It is one of the extraocular muscles. It is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). In the primary position (looking straight ahead), its primary function is elevation, although it also contributes to intorsion and adduction. It is associated with a number of medical conditions, and may be weak, paralysed, overreactive, or even congenitally absent in some people. Structure The superior rectus muscle originates from the annulus of Zinn. It inserts into the anterosuperior surface of the eye. This insertion has a width of around 11 mm. It is around 8 mm from the corneal limbus. Nerve supply The superior rectus muscle is supplied by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). Relations The superior rectus muscle is related to the other extraocular muscles, particularly to the medial rectus muscle and the lateral rectus muscle. The insertion of the superior rectus muscle is around 7.5 mm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abducens
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocular muscles responsible for outward Gaze (physiology), gaze. It is a Somatic (biology), somatic efferent nerve fiber, efferent nerve. Structure Nucleus The abducens nucleus is located in the pons, on the floor of the fourth ventricle, at the level of the facial colliculus. Axons from the facial nerve loop around the abducens nucleus, creating a slight bulge (the facial colliculus) that is visible on the dorsal surface of the floor of the fourth ventricle. The abducens nucleus is close to the midline, like the other motor nuclei that control eye movements (the Oculomotor nucleus, oculomotor and Trochlear nucleus, trochlear nuclei). Motor axons leaving the abducens nucleus run ventrally and caudally through the pons. They pass lateral to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |