|
Octacube (sculpture)
The ''Octacube'' is a large, stainless steel sculpture displayed in the mathematics department of Pennsylvania State University in State College, PA. The sculpture represents a mathematical object called the 24-cell or "octacube". Because a real 24-cell is four-dimensional, the artwork is actually a projection into the three-dimensional world. ''Octacube'' has very high intrinsic symmetry, which matches features in chemistry (molecular symmetry) and physics (quantum field theory). The sculpture was designed by Adrian Ocneanu, a mathematics professor at Pennsylvania State University. The university's machine shop spent over a year completing the intricate metal-work. ''Octacube'' was funded by an alumna in memory of her husband, Kermit Anderson, who died in the September 11 attacks. Artwork The ''Octacube's'' metal skeleton measures about 6 feet (2 meters) in all three dimensions. It is a complex arrangement of unpainted, tri-cornered flanges. The base is a 3-foot (1 meter) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecahedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120. Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular: The pyritohedron, a common crystal form in pyrite, has pyritohedral symmetry, while the tetartoid has tetrahedral symmetry. The rhombic dodecahedron can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry. The elongated dodecahedron and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
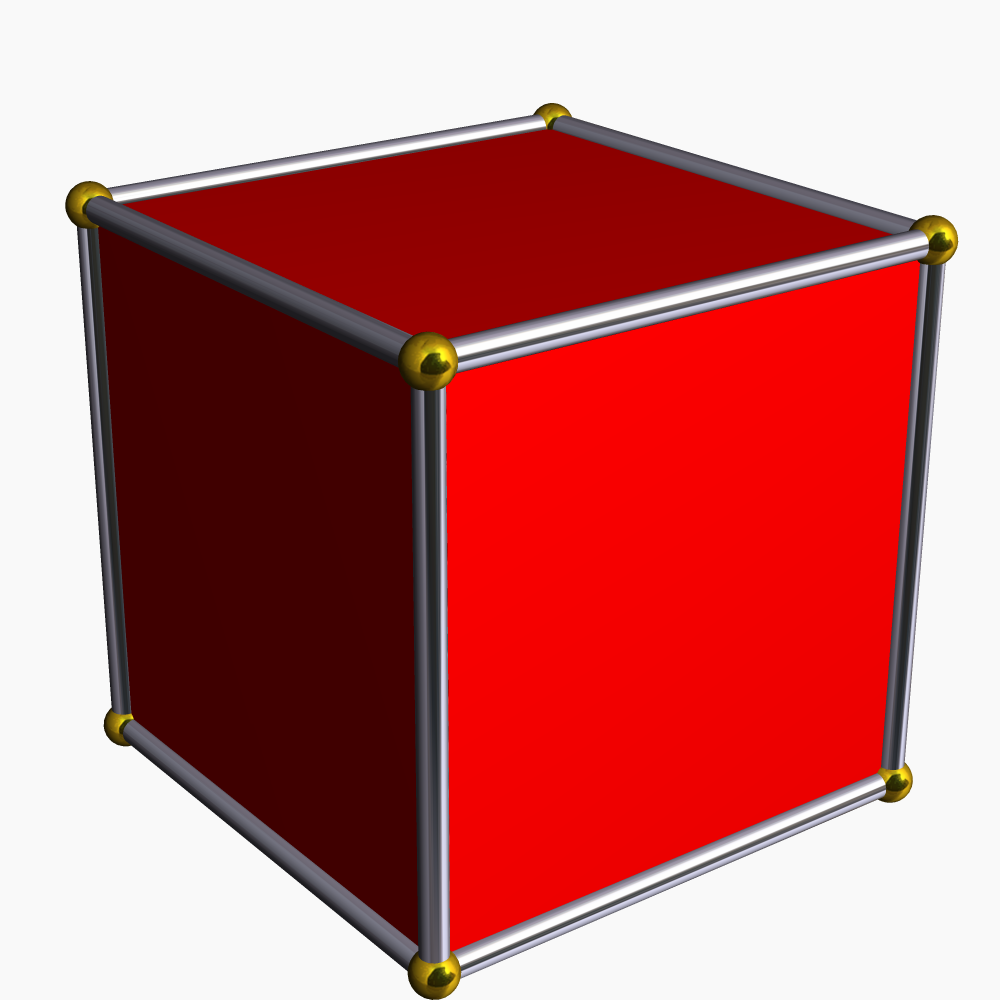
8-cell
In geometry, a tesseract is the four-dimensional analogue of the cube; the tesseract is to the cube as the cube is to the square. Just as the surface of the cube consists of six square faces, the hypersurface of the tesseract consists of eight cubical cells. The tesseract is one of the six convex regular 4-polytopes. The tesseract is also called an 8-cell, C8, (regular) octachoron, octahedroid, cubic prism, and tetracube. It is the four-dimensional hypercube, or 4-cube as a member of the dimensional family of hypercubes or measure polytopes. Coxeter labels it the \gamma_4 polytope. The term ''hypercube'' without a dimension reference is frequently treated as a synonym for this specific polytope. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the word ''tesseract'' to Charles Howard Hinton's 1888 book ''A New Era of Thought''. The term derives from the Greek ( 'four') and from ( 'ray'), referring to the four edges from each vertex to other vertices. Hinton originally spelle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-cell
In geometry, the 5-cell is the convex 4-polytope with Schläfli symbol . It is a 5-vertex four-dimensional object bounded by five tetrahedral cells. It is also known as a C5, pentachoron, pentatope, pentahedroid, or tetrahedral pyramid. It is the 4- simplex (Coxeter's \alpha_4 polytope), the simplest possible convex 4-polytope, and is analogous to the tetrahedron in three dimensions and the triangle in two dimensions. The 5-cell is a 4-dimensional pyramid with a tetrahedral base and four tetrahedral sides. The regular 5-cell is bounded by five regular tetrahedra, and is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes (the four-dimensional analogues of the Platonic solids). A regular 5-cell can be constructed from a regular tetrahedron by adding a fifth vertex one edge length distant from all the vertices of the tetrahedron. This cannot be done in 3-dimensional space. The regular 5-cell is a solution to the problem: ''Make 10 equilateral triangles, all of the same size, using 10 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Regular Polychoron
In mathematics, a regular 4-polytope is a regular four-dimensional polytope. They are the four-dimensional analogues of the regular polyhedra in three dimensions and the regular polygons in two dimensions. There are six convex and ten star regular 4-polytopes, giving a total of sixteen. History The convex regular 4-polytopes were first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century. He discovered that there are precisely six such figures. Schläfli also found four of the regular star 4-polytopes: the grand 120-cell, great stellated 120-cell, grand 600-cell, and great grand stellated 120-cell. He skipped the remaining six because he would not allow forms that failed the Euler characteristic on cells or vertex figures (for zero-hole tori: ''F'' − ''E'' + ''V'' 2). That excludes cells and vertex figures such as the great dodecahedron and small stellated dodecahedron . Edmund Hess (1843–1903) publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Schläfli
Ludwig Schläfli (15 January 1814 – 20 March 1895) was a Swiss mathematician, specialising in geometry and complex analysis (at the time called function theory) who was one of the key figures in developing the notion of higher-dimensional spaces. The concept of multidimensionality is pervasive in mathematics, has come to play a pivotal role in physics, and is a common element in science fiction. Life and career Youth and education Ludwig spent most of his life in Switzerland. He was born in Grasswil (now part of Seeberg), his mother's hometown. The family then moved to the nearby Burgdorf, where his father worked as a tradesman. His father wanted Ludwig to follow in his footsteps, but Ludwig was not cut out for practical work. In contrast, because of his mathematical gifts, he was allowed to attend the Gymnasium in Bern in 1829. By that time he was already learning differential calculus from Abraham Gotthelf Kästner's ''Mathematische Anfangsgründe der Analysis des Unendli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or -faces (for all , where is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension . Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians. Classically, a regular polytope in dimensions may be defined as having regular facets (-faces) and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes. A reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes and . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the (convex, non- stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, and is represented by its Schläfli symbol , con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexahedron
A hexahedron (plural: hexahedra or hexahedrons) or sexahedron (plural: sexahedra or sexahedrons) is any polyhedron with six faces. A cube, for example, is a regular hexahedron with all its faces square, and three squares around each vertex. There are seven topologically distinct ''convex'' hexahedra, one of which exists in two mirror image forms. There are three topologically distinct concave hexahedra. Two polyhedra are "topologically distinct" if they have intrinsically different arrangements of faces and vertices, such that it is impossible to distort one into the other simply by changing the lengths of edges or the angles between edges or faces. Convex, Cuboid Convex, Others Concave There are three further topologically distinct hexahedra that can only be realised as ''concave'' figures: A digonal antiprism can be considered a degenerate form of hexahedron, having two opposing digonal faces and four triangular faces. However, digons are usually disregarded in the defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)