|
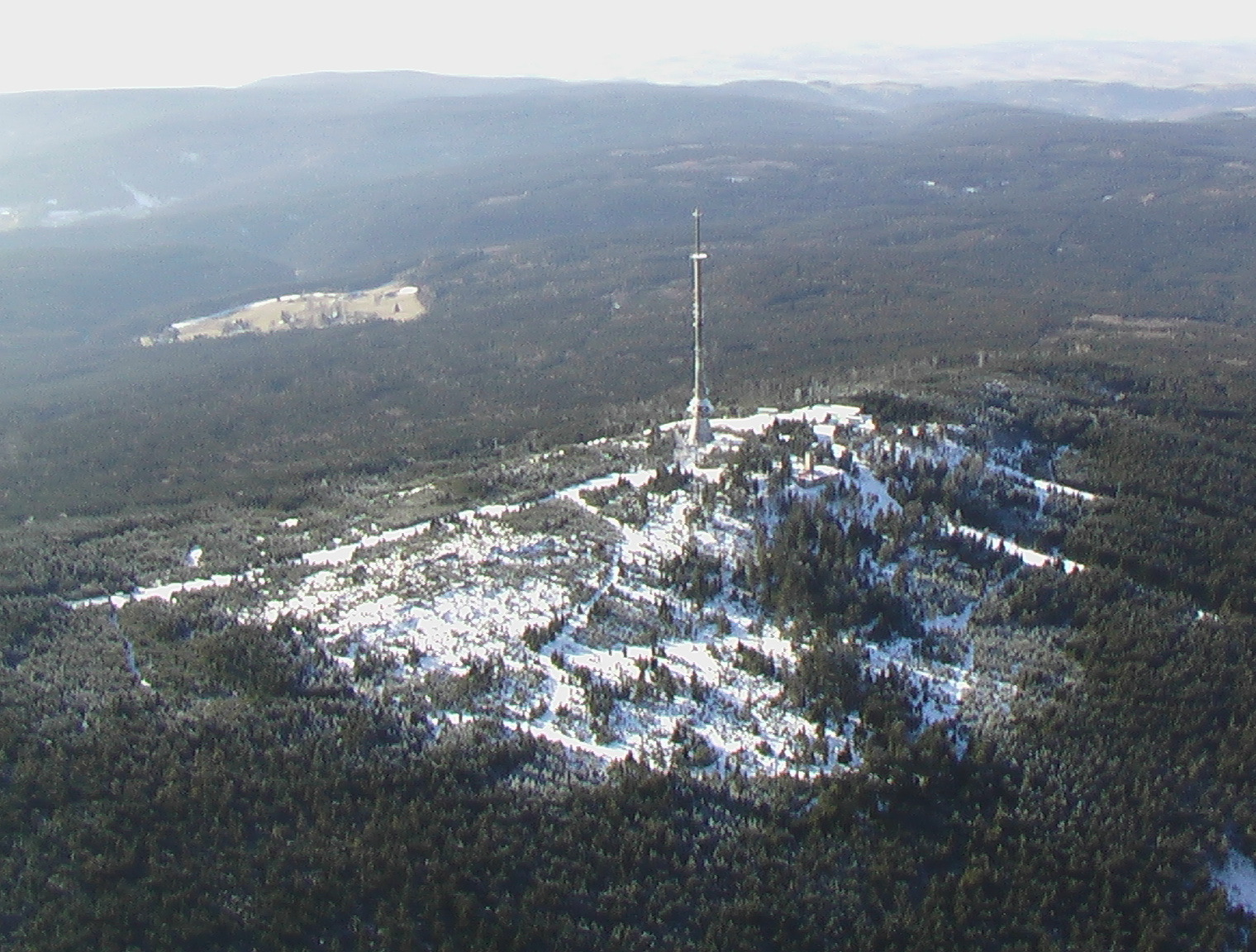
Ochsenkopf Transmitter
The Ochsenkopf Transmitter (german: Sender Ochsenkopf) is a radio and TV tower of reinforced concrete, which was built in 1958 on the summit of the Ochsenkopf mountain, the second-highest mountain in the Fichtelgebirge mountain chain in Northern Bavaria, Germany. The tower replaced a guyed steel tube TV mast that collapsed in January 1958 as result of icing. The tower, which is not accessible to the public, has a hyperbolic-shaped basement with five floors for technical equipment. Above it, there are platforms for directional antennas. The antennas for FM-transmission are on the upper part of the concrete tower, those for TV transmission on a steel tube mast on the top. Transmitting to the former GDR Ochsenkopf TV Tower played an important role in transmitting to the former GDR many West German FM and TV programs, notably ARD, West Germany's first – and between 1952 and 1963 only – television channel. Its signal could penetrate deep into the southern territor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochsenkopf Jan 2005 , a mountain in the Black Forest, Baden-Württemberg
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Ochsenkopf, German for "ox's head", may refer to: * Ochsenkopf (Malbun), a mountain on the border of Liechtenstein and Austria * Ochsenkopf (Fichtel Mountains), a mountain in Upper Franconia, Bavaria * Ochsenkopf (Jägerhaus), a mountain of Saxony, southeastern Germany * Ochsenkopf (Rittersgrün), a mountain of Saxony, southeastern Germany * Ochsenkopf (Kitzbühel Alps), a mountain of the Alps * Ochsenkopf Transmitter, a radio and TV transmitter for the Bayerischer Rundfunk See also * Hoher Ochsenkopf The Hoher Ochsenkopf ("High Ochsenkopf", literally "High Oxen Peak") is a mountain in the Northern Black Forest in the municipality of Forbach (Baden), Forbach in south Germany. At it is the highest point in Forbach and also in the county of La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Święty Krzyż TV Tower
Święty Krzyż TV Tower ( Polish: RTCN Święty Krzyż ) is the tallest free-standing TV tower in Poland. (Taller architectural structures in Poland are guyed masts or highrise buildings and chimneys equipped with antennas). Święty Krzyż TV Tower, which was built in 1966, is a 157 metre tall concrete TV tower situated near the monastery on Łysa Góra. Święty Krzyż TV Tower is not accessible by tourists. The hyperbolic-shaped basement floors resemble those of the Ochsenkopf TV Tower in Germany. Transmitted programs The tower is used for transmitting the following FM and TV programs FM radio Digital radio Digital television MPEG-4 External links Object on Emitel websiteSkyscarperpageRadioPolska websiteDVB-T in Świętokrzyskie See also * List of towers Several extant building fulfill the engineering definition of a tower: "a tall human structure, always taller than it is wide, for public or regular operational access by humans, but not for living in or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COFDM
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission and a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, used in applications such as digital television and audio broadcasting, DSL internet access, wireless networks, power line networks, and 4G/ 5G mobile communications. OFDM is a frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) scheme that was introduced by Robert W. Chang of Bell Labs in 1966. In OFDM, multiple closely spaced orthogonal subcarrier signals with overlapping spectra are transmitted to carry data in parallel.webe.org - 2GHz BAS Relocation Tech-Fair, COFDM Technology Basics 2007-03-02 Demodulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
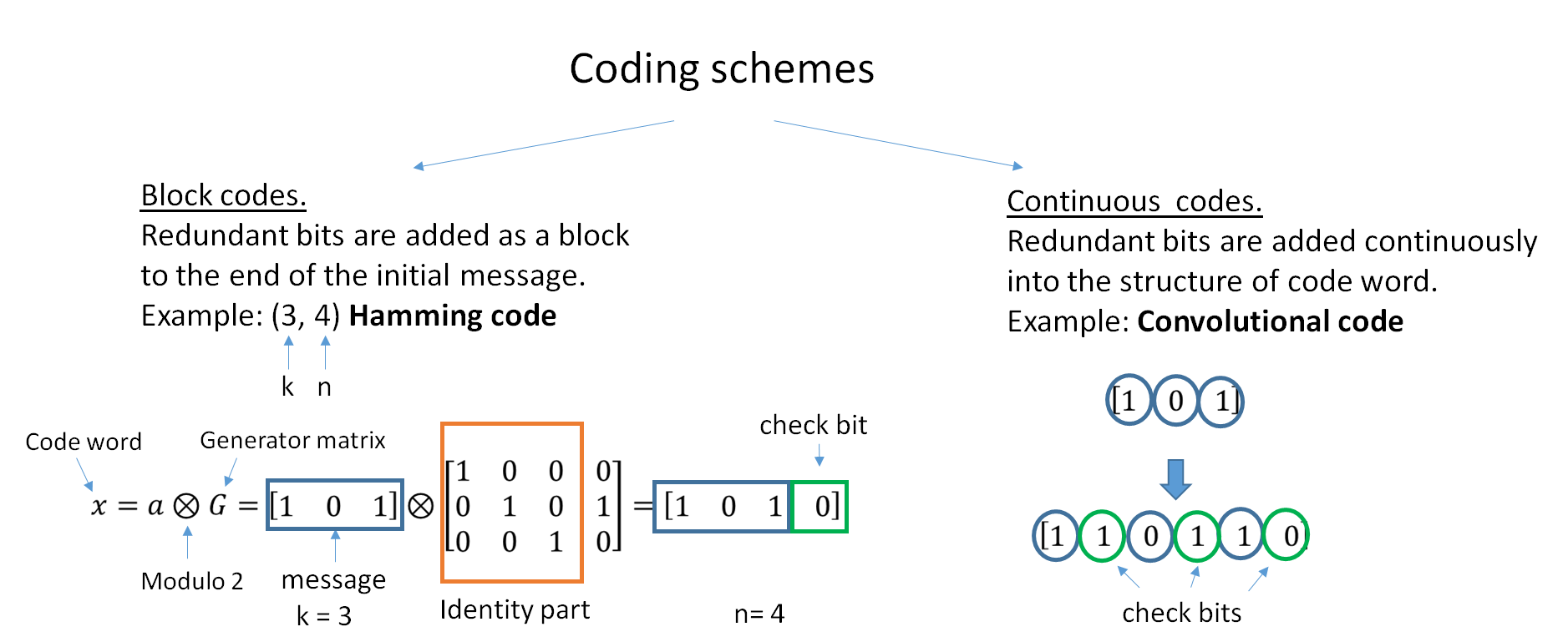
Forward Error Correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the '' carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Radiated Power
Effective radiated power (ERP), synonymous with equivalent radiated power, is an IEEE standardized definition of directional radio frequency (RF) power, such as that emitted by a radio transmitter. It is the total power in watts that would have to be radiated by a half-wave dipole antenna to give the same radiation intensity (signal strength or power flux density in watts per square meter) as the actual source antenna at a distant receiver located in the direction of the antenna's strongest beam ( main lobe). ERP measures the combination of the power emitted by the transmitter and the ability of the antenna to direct that power in a given direction. It is equal to the input power to the antenna multiplied by the gain of the antenna. It is used in electronics and telecommunications, particularly in broadcasting to quantify the apparent power of a broadcasting station experienced by listeners in its reception area. An alternate parameter that measures the same thing is ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplex (TV)
A multiplex or mux (called virtual sub-channel in the United States and Canada, and bouquet in France) is a grouping of program services as interleaved data packets for broadcast over a network or modulated multiplexed medium. The program services are split out at the receiving end. In the United Kingdom, a terrestrial ''multiplex'' (usually abbreviated ''mux'') has a fixed bandwidth of 8 MHz CODFM of interleaved H.222 packets containing a number of ''channels''. In the United States, a similar arrangement using 6 MHz 8VSB is often described as a ''channel'' with ''virtual sub-channels''. Pay television multiplexes In regards to television, the term multiplex is often used to refer to a single broadcaster offering multiple channels of programming as a single bundle to its subscribers. The term is most synonymous with premium television services, such as those devoted to films (where the term evokes the symbolism of multiplex cinemas) or sports; for instance, film services m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Channel
A television channel is a terrestrial frequency or virtual number over which a television station or television network is distributed. For example, in North America, "channel 2" refers to the terrestrial or cable band of 54 to 60 MHz, with carrier frequencies of 55.25 MHz for NTSC analog video ( VSB) and 59.75 MHz for analog audio ( FM), or 55.31 MHz for digital ATSC ( 8VSB). Channels may be shared by many different television stations or cable-distributed channels depending on the location and service provider Depending on the multinational bandplan for a given regional n, analog television channels are typically 6, 7, or 8 MHz in bandwidth, and therefore television channel frequencies vary as well. Channel numbering is also different. Digital terrestrial television channels are the same as their analog predecessors for legacy reasons, however through multiplexing, each physical radio frequency (RF) channel can carry several digital subchanne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-T
DVB-T, short for Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial, is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in Singapore in February, 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (COFDM or OFDM) modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide (including North America) for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. It is also used in the US by Amateur television operators. Basics Rather than carrying one data carrier on a single radio frequency (RF) channel, COFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulates a set of closely spaced adjacent sub-carrier frequencies. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostankino Tower
Ostankino Tower (russian: links=no, Останкинская телебашня, Ostankinskaya telebashnya) is a television and radio tower in Moscow, Russia, owned by the Moscow branch of unitary enterprise Russian TV and Radio Broadcasting Network. Standing , it was designed by Nikolai Nikitin, Pyotr Gorchakov and Yuri Kondratyuk. , it is the tallest free-standing structure in Europe and 12th tallest in the world. Between 1967 and 1974, it was the tallest in the world. The tower was the first free-standing structure to exceed in height. Ostankino was built to mark the 50th anniversary of the October Revolution. It is named after the surrounding Ostankino district of Moscow. History Construction and record holder Construction began in 1963 and was completed in 1967. Extensive use of prestressed concrete resulted in a simple and sturdy structure. It surpassed the Empire State Building to become the tallest free-standing structure in the world. It held this record for eight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitzbüheler Horn Transmitter
The Kitzbüheler Horn Transmitter (german: Sender Kitzbüheler Horn) is a transmission tower made of reinforced concrete on the summit of the Kitzbüheler Horn near Kitzbühel in Austria. The Kitzbühler Horn Transmitter does not have a cylindrical shaft. It broadcasts TV and VHF radio programmes. The tower was taken into service on 12 December 1969 as a combined radio and television transmission facility for the ORF after a difficult two-year-long construction period, preceded by lengthy and intensive negotiations with local authorities and land owners. To facilitate the switchover to DVB-T, the analogue channels ORF 1 ORF 1 (''ORF eins'') is an Austrian public television channel owned by ORF. It was the first television channel in Austria, started in 1955. ORF 1 is one of four public TV channels in Austria. It is funded by a mixture of advertising revenue an ... (Channel 5, 3 kW) and ORF 2 - Tirol (Channel 24, 30 kW) were switched off on 22 October 2007. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |