|
Occitan Orthography
The Occitan alphabet consists of the following 23 Latin letters: : The letters '' K, W'' and '' Y'' are considered foreign by Occitanians and are used only in words of foreign origin, incrementally integrated into Occitan, such as ''whisky'', ''watt'', ''Kenya''. They may be included in the Occitan alphabet following the order in the international alphabet. Letter names The letter names are usually feminine. They may also be masculine, in which case the feminine names (''B''), (''V''), (''W'') and (''Y'') become masculine , , and . Elision is common before a letter starting with a vowel. Diacritics Several diacritics serve to modify the pronunciation of the letters of the Occitan alphabet. * The grave accent () _̀ found on à, è, ò. * The acute accent () _́ found on á, é, í, ó, ú. * The diaeresis () ¨ found on ï, ü. * The cedilla () ¸ found under ç. * The interpunct () · found between two consecutive consonants: n·h and s·h. This is used in Gascon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
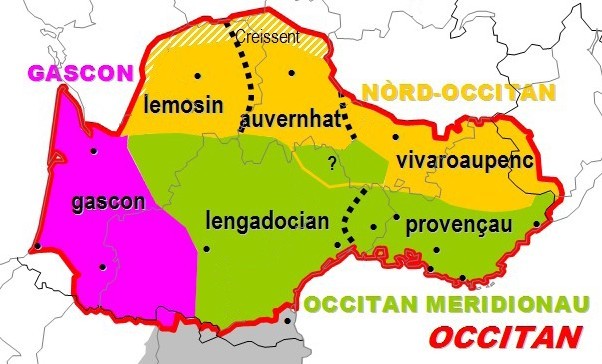
Occitan Language
Occitan (; oc, occitan, link=no ), also known as ''lenga d'òc'' (; french: langue d'oc) by its native speakers, and sometimes also referred to as ''Provençal'', is a Romance languages, Romance language spoken in Southern France, Monaco, Italy's Occitan Valleys, as well as Spain's Val d'Aran; collectively, these regions are sometimes referred to as Occitania, Occitània. It is also spoken in Calabria (Southern Italy) in a linguistic enclave of Cosenza area (mostly Guardia Piemontese). Some include Catalan language, Catalan in Occitan, as the Linguistic distance, distance between this language and some Occitan dialects (such as the Gascon language) is similar to the distance between different Occitan dialects. Catalan was considered a dialect of Occitan until the end of the 19th century and still today remains its closest relative. Occitan is an official language of Catalonia, where a subdialect of Gascon known as Aranese dialect, Aranese is spoken in the Val d'Aran. Since Sept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umlaut (diacritic)
The umlaut () is the diacritical mark used to indicate in writing (as part of the letters , , and ) the result of the historical sound shift due to which former back vowels are now pronounced as front vowels (for example , , and as , , and ). (The term ermanicumlaut is also used for the underlying historical sound shift process.) In its contemporary printed form, the mark consists of two dots placed over the letter to represent the changed vowel sound. It looks identical to the diaeresis mark used in other European languages and is represented by the same Unicode code point. The word '' trema'' (french: tréma), used in linguistics and also classical scholarship, describes the form of both the umlaut diacritic and the diaeresis rather than their function and can therefore be used to refer to both. German origin and current usage (literally "changed sound") is the German name of the sound shift phenomenon also known as ''i-mutation''. In German, this term is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occitan Phonology
This article describes the phonology of the Occitan language. Consonants Below is a consonant chart that covers multiple dialects. Where symbols for consonants occur in pairs, the left represents a voiceless consonant and the right represents a voiced consonant. ; Notes: * The phoneme is mostly found in Southern Occitan (written in Gascon, in Provençal, and in Languedocien). * The distinction between and is general in Provençal, Vivaro-Alpine, Auvergnat and Limousin. However, in Languedocien and Gascon, the phonemes and are neutralized as (thus has disappeared). * In Languedocien: ** the phonemes indicate three kinds of sounds, depending on what surrounds them: *** a voiced plosive sound by default *** devoiced to phrase-finally or before a voiceless sound *** a voiced fricative when both preceded and followed by voiced continuants (i.e., vowels or ) within the same phrase. ** the phonemes and and the sequences are neutralized as (thus , and have dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occitan Conjugation
This article discusses the conjugation of verbs in a number of varieties of the Occitan language, including Old Occitan and Catalan. Each verbal form is accompanied by its phonetic transcription. The similarities with Catalan are more noticeable in the written forms than in pronunciation. First group verbs (-ar verbs) This is the group most Occitan verbs belong to. Examples include ''aimar'' ("to love"), ''esperar'' ("to wait" and "to hope"), ''manjar'' ("to eat") and ''pensar'' ("to think"). ''Parlar'' ("to speak") *''Note: Because the Languedocian dialect is often considered as a basis for standard Occitan, it is colored .'' ''Portar'' ("to carry") This verb is conjugated like ''parlar''; but in the first-person singular, second-person singular, third-person singular, and third-person plural present (both indicative and subjunctive) and second-person singular imperative tenses, its stems changed to ''pòrt-'' (''pòrti''). This change also happened on verbs such as ''cremar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivaro-Alpine
Vivaro-Alpine ( oc, vivaroalpenc, vivaroaupenc) is a variety of Occitan language, Occitan spoken in southeastern France (namely, around the Dauphiné area) and northwestern Italy (the Occitan Valleys of Piedmont and Liguria). There is also a small Vivaro-Alpine enclave in the Guardia Piemontese, Calabria, where the language is known as ''gardiòl''. It belongs to the Northern Occitan dialect bloc, along with Auvergnat and Limousin. The name “vivaro-alpine” was coined by Pierre Bec in the 1970s. The Vivaro-Alpine dialects are traditionally called "gavot" from the Maritime Alps to the Hautes-Alpes. Naming and classification ''Vivaro-Alpine'' had been considered as a sub-dialect of Provençal dialect, Provençal, and named ''provençal alpin'' (Alpine Provençal) or Northern Provençal. Its use in the Dauphiné area has also led to the use of ''dauphinois'' or ''dauphinois alpin'' to name it. Jules Ronjat, ''Grammaire istorique des parlers provençaux modernes, vol. IV Les dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auvergnat
or (endonym: ) is a northern dialect of Occitan spoken in central and southern France, in particular in the former administrative region of Auvergne. Currently, research shows that there is not really a true Auvergnat dialect but rather a vast northern Occitan linguistic area. The word "Auvergnat" is above all a local historiographical creation. According to linguist Jean Roux, "It is by simplification that we use this term, because in no case Auvergnat can be considered as an autonomous linguistic entity". With around 80,000 speakers in the Auvergne region at the beginning of the 21st century, it is considered to be severely endangered. Classification Auvergnat falls under the following categories and subcategories: Indo-European, Italic, Romance, Italo-Western, Gallo-Iberian, Gallo-Romance, Occitan. History Several troubadours were from the Auvergne, including Castelloza, Dalfi d'Alvernhe, the Monje de Montaudon, the Vesques de Clarmon, Peire d'Alvernhe, Peire Rogier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Occitan
Old Occitan ( oc, occitan ancian, label=Occitan language, Modern Occitan, ca, occità antic), also called Old Provençal, was the earliest form of the Occitano-Romance languages, as attested in writings dating from the eighth through the fourteenth centuries. Old Occitan generally includes Early and Old Occitan. Middle Occitan is sometimes included in Old Occitan, sometimes in Modern Occitan. As the term ' appeared around the year 1300, Old Occitan is referred to as "Romance" (Occitan: ') or "Provençal" (Occitan: ') in medieval texts. History Among the earliest records of Occitan are the ''Tomida femina'', the ''Boecis'' and the ''Cançó de Santa Fe''. Old Occitan, the language used by the troubadours, was the first Romance language with a literary corpus and had an enormous influence on the development of lyric poetry in other European languages. The interpunct was a feature of its orthography and survives today in Catalan and Gascon language, Gascon. The official language of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occitania
Occitania ( oc, Occitània , , or ) is the historical region in Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe where the Occitan language, Occitan language was historically spoken and where it is sometimes still used as a second language. This cultural area roughly encompasses the southern third of France (with the exception of the French Basque Country and Northern Catalonia, French Catalonia) as well as part of Spain (Aran Valley), Monaco, and smaller parts of Italy (Occitan Valleys, Guardia Piemontese). Occitania has been recognized as a linguistic and cultural concept since the Middle Ages, but has never been a legal nor a political entity under this name. However, the territory was united in Roman times as the ''Septem Provinciae, Seven Provinces'' ( la, Septem Provinciæ) and in the Early Middle Ages (''Aquitanica'' or the Visigothic Kingdom#Kingdom of Toulouse, Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, or the share of Louis the Pious following Thionville ''divisio regnorum'' in 806) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpunct
An interpunct , also known as an interpoint, middle dot, middot and centered dot or centred dot, is a punctuation mark consisting of a vertically centered dot used for interword separation in ancient Latin script. (Word-separating spaces did not appear until some time between 600 and 800 CE.) It appears in a variety of uses in some modern languages and is present in Unicode as . The multiplication dot (Unicode ) is frequently used in mathematical and scientific notation, and it may differ in appearance from the interpunct. In written language Various dictionaries use the interpunct (in this context, sometimes called a hyphenation point) to indicate where to split a word and insert a hyphen if the word doesn't fit on the line. There is also a separate Unicode character, . English In British typography, the space dot was once used as the formal decimal point. Its use was advocated by laws and can still be found in some UK-based academic journals such as ''The Lancet''. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedilla
A cedilla ( ; from Spanish) or cedille (from French , ) is a hook or tail ( ¸ ) added under certain letters as a diacritical mark to modify their pronunciation. In Catalan, French, and Portuguese (called cedilha) it is used only under the ''c'' (forming ''ç''), and the entire letter is called, respectively, (i.e. "broken C"), , and (or , colloquially). It is used to mark vowel nasalization in many languages of sub-Saharan Africa, including Vute from Cameroon. Origin The tail originated in Spain as the bottom half of a miniature cursive z. The word ''cedilla'' is the diminutive of the Old Spanish name for this letter, (). Modern Spanish and isolationist Galician no longer use this diacritic (apart from , the nickname of the FC Barcelona football team), although it is used in Reintegrationist Galician, Portuguese, Catalan, Occitan, and French, which gives English the alternative spellings of ''cedille'', from French "", and the Portuguese form . An obsolete spelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |