|
Obliquus Capitis Inferior
The obliquus capitis inferior muscle () is the larger of the two oblique muscles of the neck. It arises from the apex of the spinous process of the axis and passes laterally and slightly upward, to be inserted into the lower and back part of the transverse process of the atlas. It lies deep to the semispinalis capitis and trapezius muscles. The muscle is responsible for rotation of the head and first cervical vertebra (atlanto-axial joint). It forms the lower boundary of the suboccipital triangle of the neck. The naming of this muscle may be confusing, as it is the only capitis (L. "head") muscle that does NOT attach to the cranium. Function The obliquus capitis inferior muscle, like the other suboccipital muscles, has an important role in proprioception. This muscle has a very high density of Golgi organs and muscle spindles which accounts for this. It is believed that proprioception may be the primary role of the inferior oblique (and indeed the other suboccipital muscles) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis (anatomy)
In anatomy, the axis (from Latin ''axis'', "axle") or epistropheus is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The axis' defining feature is its strong odontoid process (bony protrusion) known as the dens, which rises dorsally from the rest of the bone. Structure The body is deeper in front or in the back and is prolonged downward anteriorly to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra. It presents a median longitudinal ridge in front, separating two lateral depressions for the attachment of the longus colli muscles. Odontoid Process of Axis (Dens) The dens, also called the odontoid process or the peg, is the most pronounced projecting feature of the axis. The dens exhibits a slight constriction where it joins the main body of the vertebra. The condition where the dens is separated from the body of the axis is called ''os odontoideum'' and may cause nerve and circulation compression syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Mass Of Atlas
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suboccipital Nerve
The suboccipital nerve (first cervical dorsal ramus) is the dorsal primary ramus of the first cervical nerve (C1). It exits the spinal cord between the skull and the first cervical vertebra In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sau ..., the Atlas (anatomy), atlas. It lies within the suboccipital triangle along with the vertebral artery, where the artery enters the foramen magnum. It supplies muscles of the suboccipital triangle, the rectus capitis posterior major, obliquus capitis superior, and obliquus capitis inferior. The suboccipital nerve also innervates rectus capitis posterior minor. See also * Vertebral artery Additional images File:Gray792.png, Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ. File:Suboccipital_triangle.P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis (anatomy)
In anatomy, the axis (from Latin ''axis'', "axle") or epistropheus is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The axis' defining feature is its strong odontoid process (bony protrusion) known as the dens, which rises dorsally from the rest of the bone. Structure The body is deeper in front or in the back and is prolonged downward anteriorly to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra. It presents a median longitudinal ridge in front, separating two lateral depressions for the attachment of the longus colli muscles. Odontoid Process of Axis (Dens) The dens, also called the odontoid process or the peg, is the most pronounced projecting feature of the axis. The dens exhibits a slight constriction where it joins the main body of the vertebra. The condition where the dens is separated from the body of the axis is called ''os odontoideum'' and may cause nerve and circulation compression syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the vertebral column, backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxon, taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The anterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semispinalis Capitis
The semispinalis muscles are a group of three muscles belonging to the transversospinales. These are the semispinalis capitis, the semispinalis cervicis and the semispinalis thoracis. The semispinalis capitis (''complexus'') is situated at the upper and back part of the neck, deep to the splenius, and medial to the longissimus cervicis and longissimus capitis. It arises by a series of tendons from the tips of the transverse processes of the upper six or seven thoracic and the seventh cervical vertebrae, and from the articular processes of the three cervical vertebrae above this ( C4-C6). The tendons, uniting, form a broad muscle, which passes upward, and is inserted between the superior and inferior nuchal lines of the occipital bone. It lies deep to the trapezius muscle and can be palpated as a firm round muscle mass just lateral to the cervical spinous processes. The semispinalis cervicis (or ''semispinalis colli''), arises by a series of tendinous and fleshy fibers from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
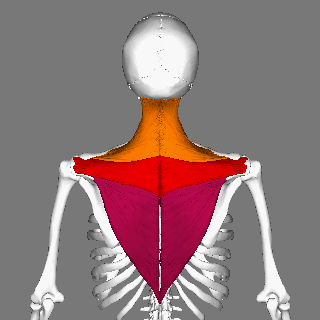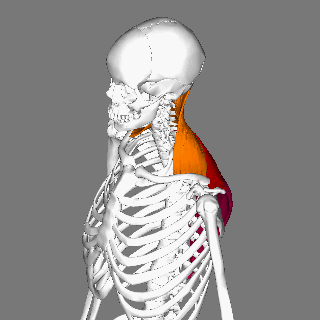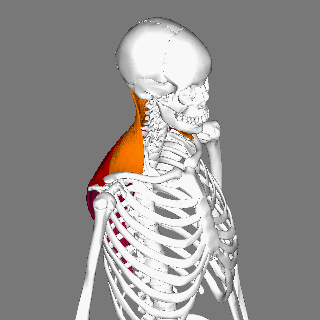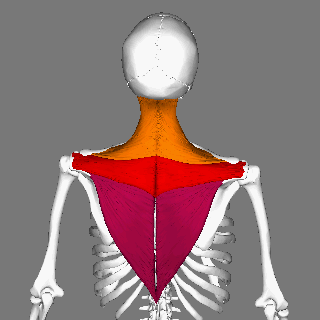
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebra
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, and inferio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlanto-axial Joint
The atlanto-axial joint is a joint in the upper part of the neck between the atlas bone and the axis bone, which are the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is a pivot joint. Structure The atlanto-axial joint is a joint between the atlas bone and the axis bone, which are the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is a pivot joint. There is a pivot articulation between the odontoid process of the axis and the ring formed by the anterior arch and the transverse ligament of the atlas. Lateral and median joints There are three atlanto-axial joints: one median and two lateral: * The median atlanto-axial joint is sometimes considered a triple joint: ** one between the posterior surface of the anterior arch of atlas and the front of the odontoid process ** one between the anterior surface of the ligament and the back of the odontoid process * The lateral atlantoaxial joint involves the lateral mass of atlas and axis. Between the articular processes of the two bones there is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |