|
Oakville, Washington
Oakville is a city in Grays Harbor County, Washington, United States. It was incorporated in 1905, with booming lumber, railway, and farming industries creating the early foundation of the community. The population was 715 at the 2020 census. History In 1818, the United States and Great Britain agreed to a treaty of joint occupancy in the Oregon Country, which included the land that would eventually become Oakville, Washington. Over the next several decades, citizens of the United States began to settle in the area. As traveling by boat was easier than moving through the dense forests, many used the river system, entering from the port of Grays Harbor and canoeing inland via the Chehalis River. The British government gave full ownership of the area to the United States in 1846. In 1850, the land now occupied by Oakville was mainly open prairie, maintained by yearly fires started deliberately by local tribes, which kept the forest from encroaching and which encouraged the bloom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
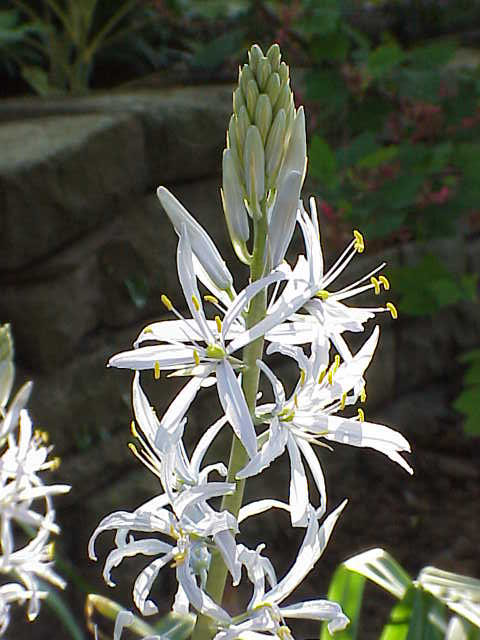
Camassia
''Camassia'' is a genus of plants in the asparagus family native to North America. Common names include camas, quamash, Indian hyacinth, camash, and wild hyacinth. It grows in the wild in great numbers in moist meadows. They are perennial plants with basal linear leaves measuring in length, which emerge early in the spring. They grow to a height of , with a multi-flowered stem rising above the main plant in summer. The six-petaled flowers vary in color from pale lilac or white to deep purple or blue-violet. Camas can appear to color entire meadows when in flower. Taxonomy and species Historically, the genus was placed in the lily family (Liliaceae), when this was very broadly defined to include most lilioid monocots., in When the Liliaceae was split, in some treatments ''Camassia'' was placed in a family called Hyacinthaceae (now the subfamily Scilloideae). DNA and biochemical studies have led the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group to reassign ''Camassia'' to the family Asparag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsters And Mysteries In America
''Monsters and Mysteries in America'' is an American documentary television series that premiered March 24, 2013 to April 1, 2015 on Destination America. Repeats air on the network's sister-station, the Discovery Channel. It also sometimes airs on Animal Planet, particularly during one of their "Monster weeks". In the United Kingdom, the series airs on the Sky-owned television channel Pick as ''Monsters and Mysteries''. Overview Unlike predecessors such as '' In Search Of...'' and ''MonsterQuest'', the series includes numerous legends in each episode and features first-person witness encounters. Each episode is split into three segments, all focusing on one particular monster, legend, or phenomenon. Ron Bowman has served as show runner and writer since the series' launch. In Season 1 episodes focused on a specific region in the United States; in later seasons, stories within episodes were based on a variety of towns all around the country. Lyle Blackburn of Rue-Morgue.com has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsolved Mysteries
''Unsolved Mysteries'' is an American mystery documentary television show, created by John Cosgrove and Terry Dunn Meurer. Documenting cold cases and paranormal phenomena, it began as a series of seven specials, presented by Raymond Burr, Karl Malden, and Robert Stack, beginning on NBC on January 20, 1987, becoming a full-fledged series on October 5, 1988, hosted by Stack. After nine seasons on NBC, the series moved to CBS for its 10th season on November 13, 1997. After adding Virginia Madsen as a co-host during season 11 failed to boost slipping ratings, CBS canceled the series after only a two-season, 12-episode run on June 11, 1999. The series was revived by Lifetime in 2000, with season 12 beginning on July 2, 2001. ''Unsolved Mysteries'' aired 103 episodes on Lifetime, before ending on September 20, 2002, an end that coincided with Stack's illness and eventual death. After a six-year absence, the series was resurrected by Spike in 2007, and began airing on October 13, 2008 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Free Lance-Star
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveling Library
A traveling library is a collection of books lent for stated periods by a central library to a branch library, club, or other organization or, in some instances, to an individual. The chief characteristics from which it derives its name are its temporary location in the place to which the collections of books is sent and the implication that any traveling library will or may be changed for another collection of books. A bookmobile is an example. History The date of the first traveling library is uncertain. Among its forerunners can be noted the itinerant chapman and ballad seller, the religious colporteur, and the camp library of Napoleon I listed in Bourrienne's ''Mémoires''. The traveling library can also be cited as a logical outgrowth of the "circulating schools" of Wales, promoted in 1730 by Griffith Jones, and the later similar extension schools of the General Assembly of the Kirk of Scotland in the Highlands and the Scottish islands. The first really practicable travelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhamnus Purshiana
''Frangula purshiana'' (cascara, cascara buckthorn, cascara sagrada, bearberry, and in the Chinook Jargon, chittem stick and chitticum stick; syn. ''Rhamnus purshiana'') is a species of plant in the family Rhamnaceae. It is native to western North America from southern British Columbia south to central California, and eastward to northwestern Montana. The dried bark of cascara was used as a laxative in folk medicine by the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest, and later worldwide in conventional medicines until 2002. Description Cascara is a large shrub or small tree tall, with a trunk 20–50 centimetres (8–20 in) in diameter. The buds have no scales, unique for the northwest region. The thin bark is brownish to silver-gray with light splotching (often, in part, from lichens); the inner bark is smooth and yellowish (turning dark brown with age and/or exposure to sunlight). Cascara bark has an intensely bitter flavor that will remain in the mouth for hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former President Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin. In addition, the NP had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber, and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land. The Northern Pacific was headquartered in Minnesota, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plat
In the United States, a plat ( or ) (plan) is a cadastral map, drawn to scale, showing the divisions of a piece of land. United States General Land Office surveyors drafted township plats of Public Lands Surveys to show the distance and bearing between section corners, sometimes including topographic or vegetation information. City, town or village plats show subdivisions broken into blocks with streets and alleys. Further refinement often splits blocks into individual lots, usually for the purpose of selling the described lots; this has become known as subdivision. After the filing of a plat, legal descriptions can refer to block and lot-numbers rather than portions of sections. In order for plats to become legally valid, a local governing body, such as a public works department, urban planning commission, or zoning board must normally review and approve them. In gardening history, in both varieties of English (and in French etc), a "plat" means a section of a formal par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
.png)