|
OASTH
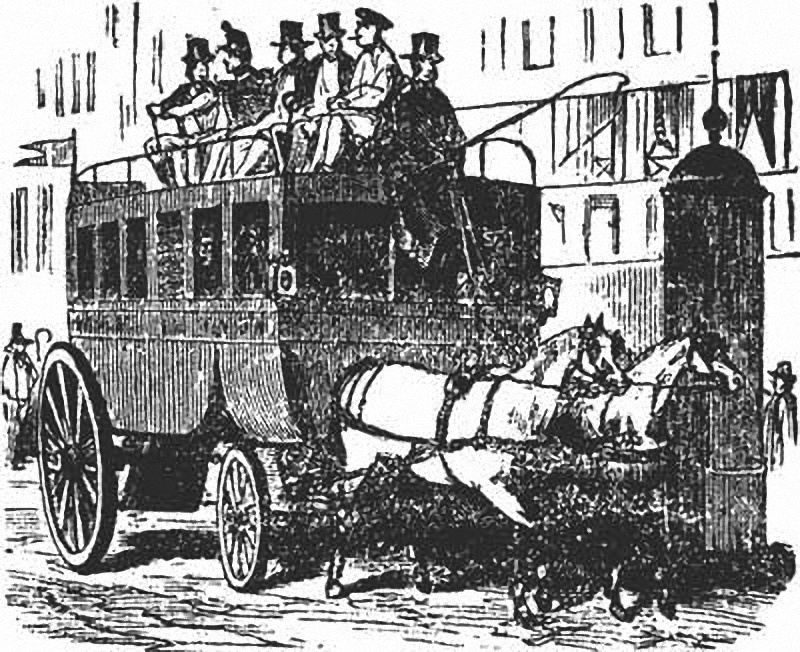
The Thessaloniki Urban Transport Organisation ( el, Οργανισμός Αστικών Συγκοινωνιών Θεσσαλονίκης), abbreviated OASTH ( el, ΟΑΣΘ), is a mass transport company operating in Thessaloniki, Greece. It was founded in 1957 and now covers a large area of the metropolitan area of Thessaloniki, the country's second-largest city. OASTH only includes bus transportation due to lack of other means of transport. History Before the creation of OASTH in 1957, public transport in Thessaloniki was initially covered by an extensive tram network opened in the late 19th century. Later a Belgian bus company started operating with horse-pulled carriages seating 4 to 5 people. OASTH was founded by Presidential Decree 3721 and aimed at replacing the city's tram network as sole provider of public transport. The initial fleet included 283 buses of 60 to 80 seats. In 1978, OASTH acquired the first articulated buses in Greece. In 1979 OASTH expands, taking o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OASTH2
The Thessaloniki Urban Transport Organisation ( el, Οργανισμός Αστικών Συγκοινωνιών Θεσσαλονίκης), abbreviated OASTH ( el, ΟΑΣΘ), is a mass transport company operating in Thessaloniki, Greece. It was founded in 1957 and now covers a large area of the metropolitan area of Thessaloniki, the country's second-largest city. OASTH only includes bus transportation due to lack of other means of transport. History Before the creation of OASTH in 1957, public transport in Thessaloniki was initially covered by an extensive tram network opened in the late 19th century. Later a Belgian bus company started operating with horse-pulled carriages seating 4 to 5 people. OASTH was founded by Presidential Decree 3721 and aimed at replacing the city's tram network as sole provider of public transport. The initial fleet included 283 buses of 60 to 80 seats. In 1978, OASTH acquired the first articulated buses in Greece. In 1979 OASTH expands, taking o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OASTH 1
The Thessaloniki Urban Transport Organisation ( el, Οργανισμός Αστικών Συγκοινωνιών Θεσσαλονίκης), abbreviated OASTH ( el, ΟΑΣΘ), is a mass transport company operating in Thessaloniki, Greece. It was founded in 1957 and now covers a large area of the metropolitan area of Thessaloniki, the country's second-largest city. OASTH only includes bus transportation due to lack of other means of transport. History Before the creation of OASTH in 1957, public transport in Thessaloniki was initially covered by an extensive tram network opened in the late 19th century. Later a Belgian bus company started operating with horse-pulled carriages seating 4 to 5 people. OASTH was founded by Presidential Decree 3721 and aimed at replacing the city's tram network as sole provider of public transport. The initial fleet included 283 buses of 60 to 80 seats. In 1978, OASTH acquired the first articulated buses in Greece. In 1979 OASTH expands, taking o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capital city, capital of the geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, the administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek language, Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Vardar, Axios. The Thessaloniki (municipality), municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of Macedonia, the administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Axios. The municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metropolitan area had 1,091,424 inhabitants in 2021. It is Greece's second major economic, industrial, commercial and political centre, and a major transportation hub for Greece and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki Metro
The Thessaloniki Metro ( el, Μετρό Θεσσαλονίκης, ', ) is an underground rapid-transit system under construction in Thessaloniki, Greece's second largest city. Estimates for the cost of the megaproject are €1.62 billion ( $ billion) for the main line and €640 million ($ million) for the Kalamaria extension, for a total of €2.26 billion ($ billion). The project is primarily funded with loans from the European Investment Bank (EIB) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and funds from the Greek government. Construction by a Greek-Italian consortium is overseen by Attiko Metro S.A., the Greek state-owned company which oversaw construction of the Athens Metro and Athens Tram. Proposed during the 1910s and first seriously planned in the 1980s, construction of the main line began in 2006 and on the Kalamaria extension in 2013. Although the initial proposal included three extensions to the main line, the latest Attiko Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Greece
Transport in Greece has undergone significant changes in the past two decades, vastly modernizing the country's infrastructure and transportation. Although ferry transport between islands remains the prominent method of transport between the nation's islands, improvements to the road infrastructure, rail, urban transport, and airports have all led to a vast improvement in transportation. These upgrades have played a key role in supporting Greece's economy, which in the past decade has come to rely heavily on the construction industry. Cable transport *Lycabettus Funicular *Parnitha Funitel * Santorini cable car Rail transport Railways *total: , ( are, or will be, electrified) * standard gauge: gauge *narrow gauge: gauge; gauge * dual gauge: combined and gauges (three rail system) (2004) The state-owned company that owns and maintains Greece's railway network is OSE, while TrainOSE is the company responsible for operating all passenger and freight trains. Metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irisbus Citelis
The Irisbus Citelis is a low-floor city bus produced by Irisbus from 2005 to 2013 when it was replaced in production by Iveco Bus Urbanway. Production and operation It was introduced in 2005 to replace the Agora. It comes in three varieties: Citelis 10 and Citelis 12, which are standard buses with respectively and length, and Citelis 18, which is articulated and has a length of . Citelis models use Euro 4, Euro 5 & EEV engines. The buses can also be built as trolleybuses, utilising overhead electrical wires for their power supply instead of fuel. Trolleybus version of Citelis is also known as Škoda 24Tr Irisbus (12m) or Škoda 25Tr Irisbus (18m), especially in Eastern Europe. Transport Citelis vehicles were introduced in 2007 on Bucharest's trolleybus network run by STB and in 2006 or 2007 in Riga, capital of Latvia, in which they are owned by Rīgas Satiksme. They are also used by the RATP in Paris, Germany's VER, in Brno and Prague, Czech Republic, by ATM in Milan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo B9L
The Volvo B9L (also known as the Volvo 7500, Volvo 7700 or Volvo 7900 for integral models) was a fully low-floor single-decker bus chassis constructed by Volvo Buses from 2005 until 2013, replacing the Volvo B7L and Volvo B10L. An articulated model, known as the Volvo B9LA, is also available. It was superseded by the Volvo B5LH in Europe. The engine is mounted vertically on the rear left overhang of the chassis similarly to with the B7L, allowing B9Ls to be low-floor throughout the whole length of the bus due to a lack of underfloor equipment. The Volvo B9L is available as an integral bus bodied by Volvo (7500/7700/7900) or as a chassis only, with bodies by other manufacturers. Additionally, the B9L reintroduced CNG engines, an option unavailable in its predecessor, the B7L. These versions replaced much older predecessor, the B10L. It was the last low-floor bus chassis from Volvo to be available with such option. Large orders for B9Ls were placed in Malmö, where they form th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo B7L
The Volvo B7L is a fully low floor single-decker bus, double-decker bus and articulated bus chassis with a rear engine mounted vertically on the left of the rear overhang. It was built as a replacement for the Volvo B10L, and the Volvo Olympian. It was used as both a single-decker bus and a double-decker bus chassis largely in Continental Europe. The B7L was also available as an integrally-constructed Volvo bus - the Volvo 5000 (later replaced by 7500, with aluminium structure) and Volvo 7000 (later renumbered 7700, with stainless steel structure). Whilst similar to the B10L in design, both featuring a side-mounted engine, the B7L's engine was a Volvo D7C unit mounted vertically, as opposed to the horizontally mounted Volvo DH10/GH10 engine of the B10L; the radiator was mounted above the engine instead of the right-hand side, allowing the floor to be lower behind the rear axle. As with the B10L, B7L was also available in its articulated form named the B7LA. Unlike B10L, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo B10M
The Volvo B10M was a mid-engined city bus and coach chassis manufactured by Volvo between 1978 and 2003. It succeeded the B58 and was equipped with the same 9.6-litre horizontally mounted Volvo diesel engine mounted under the floor behind the front axle. An articulated version under the model name Volvo B10MA was also offered, as was a semi-integral version known as the C10M, with the engine in the middle of the chassis. History Designed as a successor to the Volvo B58, a large portion of B10M chassis were built in Sweden, but some were built in other countries, like the United Kingdom and Brazil.Evolução do Produto - Ônibus Volvo Buses Brasil The B10M was one of the best-sellin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iveco Bus
IVECO Bus (formerly Irisbus) is a bus manufacturer with headquarters in Turin. IVECO Bus is now only a brand division of IVECO which is a company incorporated under Dutch law and listed on Borsa Italiana. History IVECO (1975 - 1999) In 1975 Fiat Bus created the brand IVECO (Industrial Vehicle Corporation) which gradually was recognized by Officine Meccaniche (OM), Orlandi in Italy Berliet, Renault, Chausson, Saviem in France, Karosa in the Czech Republic, Magirus-Deutz in Germany e Pegaso in Spain with the integration of Renault Bus in 1999 became later Irisbus. Irisbus (1999 - 2013) The French-Italian company was created in January 1999 by the merger of the coach and bus divisions of Renault Véhicules Industriels and the bus and coach divisions of Fiat Industrial and IVECO with Ikarus Bus added in late 1999. The Ikarus Bus division was sold off in 2006 to Hungary's Műszertechnika Group acquiring the property of Heuliez and Karosa which was transformed in Iveco Czech Republ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus Companies Of Greece
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for charter#Other usages, charter purposes, or through private ownership. Although the average bus carries between 30 and 100 passengers, some buses have a capacity of up to 300 passengers. The most common type is the single-deck bus, single-deck rigid bus, with double-decker bus, double-decker and articulated buses carrying larger loads, and midibuses and minibuses carrying smaller loads. coach (vehicle), Coaches are used for longer-distance services. Many types of buses, such as city transit buses and inter-city coaches, charge a fare. Other types, such as elementary or secondary school buses or shuttle buses within a post-secondary education campus, are free. In many jurisdictions, bus drivers require a special commercial driver's license, larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |