|
Not Knot
''Not Knot'' is a 16-minute film on the mathematics of knot theory and low-dimensional topology, centered on and titled after the concept of a knot complement. It was produced in 1991 by mathematicians at the Geometry Center at the University of Minnesota, directed by Charlie Gunn and Delle Maxwell, and distributed on videotape with a 48-page paperback booklet of supplementary material by A K Peters. Topics The video is structured into three parts. It begins by introducing knots, links, and their classification, using the trefoil knot, figure-eight knot, and Borromean rings as examples. It then describes the construction of two-dimensional surfaces such as cones and cylinders by gluing together the edges of flat sheets of paper, the internal geometry of the resulting manifolds or orbifolds, and the behavior of light rays within them. Finally, it uses a three-dimensional version of the same construction method to focus in more depth on the link complement of the Borromean rings an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Theory
In the mathematical field of topology, knot theory is the study of knot (mathematics), mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, Unknot, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3 (in topology, a circle is not bound to the classical geometric concept, but to all of its homeomorphisms). Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbifold
In the mathematical disciplines of topology and geometry, an orbifold (for "orbit-manifold") is a generalization of a manifold. Roughly speaking, an orbifold is a topological space which is locally a finite group quotient of a Euclidean space. Definitions of orbifold have been given several times: by Ichirô Satake in the context of automorphic forms in the 1950s under the name ''V-manifold''; by William Thurston in the context of the geometry of 3-manifolds in the 1970s when he coined the name ''orbifold'', after a vote by his students; and by André Haefliger in the 1980s in the context of Mikhail Gromov's programme on CAT(k) spaces under the name ''orbihedron''. Historically, orbifolds arose first as surfaces with singular points long before they were formally defined. One of the first classical examples arose in the theory of modular forms with the action of the modular group \mathrm(2,\Z) on the upper half-plane: a version of the Riemann–Roch theorem holds after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Films About Mathematics
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere through the use of moving images. These images are generally accompanied by sound and, more rarely, other sensory stimulations. The word "cinema", short for cinematography, is often used to refer to filmmaking and the film industry, and to the art form that is the result of it. Recording and transmission of film The moving images of a film are created by photographing actual scenes with a motion-picture camera, by photographing drawings or miniature models using traditional animation techniques, by means of CGI and computer animation, or by a combination of some or all of these techniques, and other visual effects. Before the introduction of digital production, series of still images were recorded on a strip of chemically sensitiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo (journal)
''Leonardo'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by the MIT Press covering the application of contemporary science and technology to the arts and music. History ''Leonardo'' journal was established in 1968 by artist and scientist Frank Malina in Paris, France. ''Leonardo'' has published writings by artists who work with science- and technology-based art media for 50 years. Journal operations were moved to the San Francisco Bay Area by Frank's son Roger Malina, an astronomer and space scientist, who took over operations of the journal upon Frank Malina's death in 1981. In 1982, the International Society for the Arts Sciences and Technology (Leonardo/ISAST) was founded to further the aims of ''Leonardo'' by providing avenues of communication for artists working in contemporary media. The society also publishes ''Leonardo Music Journal'', the ''Leonardo Electronic Almanac'', ''Leonardo Reviews'', and the ''Leonardo Book Series''. All publications are produced in collabor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mathematical Gazette
''The Mathematical Gazette'' is an academic journal of mathematics education, published three times yearly, that publishes "articles about the teaching and learning of mathematics with a focus on the 15–20 age range and expositions of attractive areas of mathematics." It was established in 1894 by Edward Mann Langley as the successor to the Reports of the Association for the Improvement of Geometrical Teaching. Its publisher is the Mathematical Association. William John Greenstreet was its editor for more than thirty years (1897–1930). Since 2000, the editor is Gerry Leversha. Editors * Edward Mann Langley: 1894-1896 * Francis Sowerby Macaulay: 1896-1897 * William John Greenstreet: 1897-1930 * Alan Broadbent: 1930-1955 * Reuben Goodstein: 1956-1962 * Edwin A. Maxwell: 1962-1971 * Douglas Quadling Douglas Arthur Quadling (1926–2015) was an English mathematician, school master and educationalist who was one of the four drivers behind the School Mathematics Project (SMP) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Polyhedron
In geometry, a uniform polyhedron has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive (i.e., there is an isometry mapping any vertex onto any other). It follows that all vertices are congruent. Uniform polyhedra may be regular (if also face- and edge-transitive), quasi-regular (if also edge-transitive but not face-transitive), or semi-regular (if neither edge- nor face-transitive). The faces and vertices need not be convex, so many of the uniform polyhedra are also star polyhedra. There are two infinite classes of uniform polyhedra, together with 75 other polyhedra: *Infinite classes: ** prisms, **antiprisms. * Convex exceptional: ** 5 Platonic solids: regular convex polyhedra, ** 13 Archimedean solids: 2 quasiregular and 11 semiregular convex polyhedra. * Star (nonconvex) exceptional: ** 4 Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra: regular nonconvex polyhedra, ** 53 uniform star polyhedra: 14 quasiregular and 39 semiregular. Hence 5 + 13 + 4 + 53 = 75. There are also many degen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Geometry
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai– Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with: :For any given line ''R'' and point ''P'' not on ''R'', in the plane containing both line ''R'' and point ''P'' there are at least two distinct lines through ''P'' that do not intersect ''R''. (Compare the above with Playfair's axiom, the modern version of Euclid's parallel postulate.) Hyperbolic plane geometry is also the geometry of pseudospherical surfaces, surfaces with a constant negative Gaussian curvature. Saddle surfaces have negative Gaussian curvature in at least some regions, where they locally resemble the hyperbolic plane. A modern use of hyperbolic geometry is in the theory of special relativity, particularly the Minkowski model. When geometers first realised they were working with something other than the standard Euclidean geometry, they described their geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Complement
In mathematics, the knot complement of a tame knot ''K'' is the space where the knot is not. If a knot is embedded in the 3-sphere, then the complement is the 3-sphere minus the space near the knot. To make this precise, suppose that ''K'' is a knot in a three-manifold ''M'' (most often, ''M'' is the 3-sphere). Let ''N'' be a tubular neighborhood of ''K''; so ''N'' is a solid torus. The knot complement is then the complement of ''N'', :X_K = M - \mbox(N). The knot complement ''XK'' is a compact 3-manifold; the boundary of ''XK'' and the boundary of the neighborhood ''N'' are homeomorphic to a two-torus. Sometimes the ambient manifold ''M'' is understood to be 3-sphere. Context is needed to determine the usage. There are analogous definitions of link complement. Many knot invariants, such as the knot group, are really invariants of the complement of the knot. When the ambient space is the three-sphere no information is lost: the Gordon–Luecke theorem states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a neighborhood that is homeomorphic to an open subset of n-dimensional Euclidean space. One-dimensional manifolds include lines and circles, but not lemniscates. Two-dimensional manifolds are also called surfaces. Examples include the plane, the sphere, and the torus, and also the Klein bottle and real projective plane. The concept of a manifold is central to many parts of geometry and modern mathematical physics because it allows complicated structures to be described in terms of well-understood topological properties of simpler spaces. Manifolds naturally arise as solution sets of systems of equations and as graphs of functions. The concept has applications in computer-graphics given the need to associate pictures with coordinates (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-dimensional Topology
In mathematics, low-dimensional topology is the branch of topology that studies manifolds, or more generally topological spaces, of four or fewer dimensions. Representative topics are the structure theory of 3-manifolds and 4-manifolds, knot theory, and braid groups. This can be regarded as a part of geometric topology. It may also be used to refer to the study of topological spaces of dimension 1, though this is more typically considered part of continuum theory. History A number of advances starting in the 1960s had the effect of emphasising low dimensions in topology. The solution by Stephen Smale, in 1961, of the Poincaré conjecture in five or more dimensions made dimensions three and four seem the hardest; and indeed they required new methods, while the freedom of higher dimensions meant that questions could be reduced to computational methods available in surgery theory. Thurston's geometrization conjecture, formulated in the late 1970s, offered a framework that sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
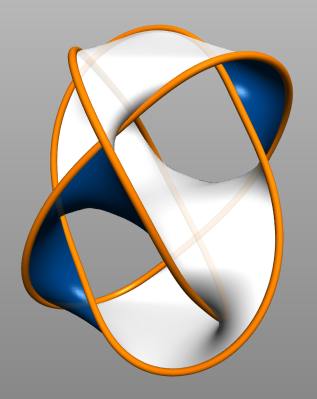
Borromean Rings
In mathematics, the Borromean rings are three simple closed curves in three-dimensional space that are topologically linked and cannot be separated from each other, but that break apart into two unknotted and unlinked loops when any one of the three is cut or removed. Most commonly, these rings are drawn as three circles in the plane, in the pattern of a Venn diagram, alternatingly crossing over and under each other at the points where they cross. Other triples of curves are said to form the Borromean rings as long as they are topologically equivalent to the curves depicted in this drawing. The Borromean rings are named after the Italian House of Borromeo, who used the circular form of these rings as a coat of arms, but designs based on the Borromean rings have been used in many cultures, including by the Norsemen and in Japan. They have been used in Christian symbolism as a sign of the Trinity, and in modern commerce as the logo of Ballantine beer, giving them the alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |