|
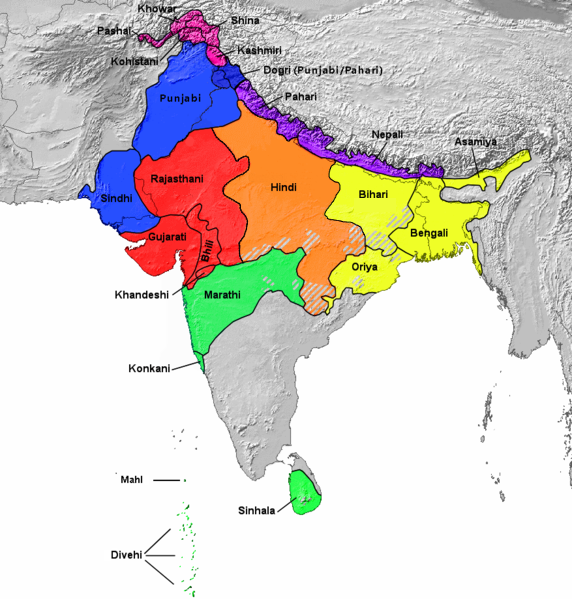
Northern Indo-Aryan Languages
The Northern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Pahāṛi languages, are a proposed group of Indo-Aryan languages spoken in the lower ranges of the Himalayas, from Nepal in the east, through the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Punjab(not to be confused with the various other languages with that name) was coined by G. A. Grierson. Classification The Pahari languages fall into three groups. Eastern Pahari *Nepali is spoken by an estimated 11,100,000 people in Nepal, 265,000 people in Bhutan, and 2,500,000 people in India. It is an official language in Nepal and India. * Jumli is spoken by an estimated 40,000 people in the Karnali zone of Nepal. * Doteli spoken by an estimated 1 million people in far west Nepal. It is considered by many to be a dialect of Nepali, according to some scholars (e.g., Rahul Sankrityayan), a dialect of Kumaoni, but the Nepalese Language Commission considers it a separate language. Central Pahari * Kumaoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China China–Nepal border, to the north, and India India–Nepal border, in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a Geography of Nepal, diverse geography, including Terai, fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten List of highest mountains#List, tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rahul Sankrityayan
Rahul Sankrityayan (born Kedarnath Pandey; 9 April 1893 – 14 April 1963) was an Indian writer and a polyglot who wrote in Hindi. He played a pivotal role in giving travelogue a 'literary form'. He was one of the most widely travelled scholars of India, spending forty-five years of his life on travels away from his home. He became a Buddhist monk (''Bhikkhu'') and eventually became a Marxist. Sankrityayan was an Indian patriot, having been arrested and jailed for three years for his anti-British writings and speeches. He is referred to as the 'Greatest Scholar' for his scholarship. He was a polymath and polyglot. The Government of India awarded him the civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan in 1963. Childhood He was born as Kedarnath Pandey to a Brahmin, brahmin family on 9 April 1893 in Pandaha village. His ancestral village was Kanaila Chakrapanpur, Azamgarh district, in Eastern Uttar Pradesh. Philosophy Initially, he was a keen follower of Arya Samaj of Swami Dayananda Saras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhadarwahi Language
Bhadarwahi is an Indo-Aryan language of the Western Pahari group spoken in the Bhaderwah region of Jammu and Kashmir, India. The name Bhadarwahi can be understood either in a narrow sense as referring to the dialect, locally known as Bhiḍlāi, native to the Bhadarwah valley, or in a broader sense to cover the group of related dialects spoken in the wider region where Bhadarwahi proper is used as a lingua franca. In addition to Bhadarwahi proper, this group also includes Padri, Bhalesi, and Khasali (Khashali) dialect. The Churahi language is closely related. The name of the language is spelt in the Takri as . Variants include ''Bhaderwahi'' (), ''Baderwali'' (), ''Bhadri'' (), Badrohi (), ''Bhadlayi'' (), and ''Bhadlai'' (). Phonology According to Masica (1991) there are a set of lateral retroflex affricates /ʈ͡ꞎ ɖ͡ɭ ɖ͡ɭʱ/ from old /Cr/ clusters. Status The language is commonly called Pahari. Some speaker may even call it a dialect of Dogri D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandeali Language
Mandeali (Takri: ) is a language spoken in northern India, predominantly in the Mandi district of Himachal Pradesh by the people of the Mandi Valley and particularly in the major city of Mandi. Other spellings for the name are Mandiyali and Mandiali. UNESCO reports it is one of the highly endangered languages of India. Speakers of the dialect have decreased by 21% from 1961 to 2001. The language is closely related to Kangri. The Chambealic varieties are often considered separate languages, but at least some are 90–95% intelligible with Mandeali proper. Dialects Preliminary survey suggests speakers have functional intelligibility of Kangri. People in southeast Mandi district may have more difficulty understanding Kangri. Standard Mandeali is spoken throughout the broad valley running north and south from Jogindernagar to Sundarnagar. Mandeali Pahari is spoken north around Barot, east of Uhl River. Intelligible with difficulty to standard Mandeali. May be intermediate variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirmauri Language
Sirmauri is a Western Pahari language spoken in the Sirmaur district in the northern Indian state of Himachal Pradesh Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks .... Its two main varieties are Dharthi (also called Giriwari) and Giripari. Grammar Postpositions Script The native script of the language is called Sirmauri script. This script is under proposal to be encoded in the Unicode. It is locally known as Dhankari. Pabuuchi was a script used by a class of astrologers. Status The language is commonly called Pahari or Himachali. The language has no official status and is recorded as a dialect of Hindi. According to the United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO), the language is in the critically endangered category, i.e. the youngest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahasu Pahari Language
Mahasu Pahari (Takri script, Takri: ) is a Western Pahari (Himachali, Takri script, Takri: ) language spoken in Himachal Pradesh. It is also known as Mahasui or Mahasuvi. The speaking population is about 1,000,000 (2001). It is more commonly spoken in the Himachal Pradesh, Shimla district, Shimla (Simla) and Solan district, Solan districts. It is to be known that Shimla and Solan were parts of the old Mahasu district. Himachal Pradesh State on 1 September, 1972 reorganised the districts dissolving Mahasu district. The Solan district was carved out of Solan and Arki, India, Arki tehsils of the then Mahasu district and tehsils of Kandaghat and Nalagarh of the then Shimla District of Punjab. Area According to different locations, the language has developed several dialects. Lower Mahasu Pahari (Baghati, Baghliani, Keonthal, Kiunthali), Upper Mahasu Pahari (Rampur, Himachal Pradesh, Rampuri, Rohru, Rohruri, Nawar Valley, Nawari, Jubbal, Jubbali, Shimla Siraji, Sodochi). The Kiunthal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kullu Pahari Language
Kului (, also known as Kulvi, Takri: ) is a Western Pahari language spoken in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. Phonology Consonants For the stops and affricates there is a four-way distinction in phonation between tenuis , voiced , aspirated and breathy voiced series. lists as separate phonemes aspirated correlates of , , , , , , and , but describes the aspiration as a voiceless pharyngeal friction. is dental, but becomes alveolar if the next syllable contains a retroflex consonant. and are rare, but contrast with the other nasals word-medially between vowels. , and , together with their aspirated correlates, don't occur in the beginning of words. The glottal stop occurs only between a vowel and , , or , e.g. "a trumpet", which contrasts with "famine". The pharyngeal fricative historically derives from and occurs word-finally, e.g. "grass", "twenty". Script The native script of the language is a variety of Takri The Tākri script (Takri (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pahari Kinnauri Language
Pahari Kinnauri, or Kinnauri Pahari ( Takri: ), also known as Oras Boli ( Takri: ), is a Western Pahari of northern India. It is spoken by different tribal groups in Kinnaur District Kinnaur is one of the twelve administrative districts of the state of Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The district is divided into three administrative areas (Kalpa, Nichar (Bhabanagar), and Pooh) and has six tehsils. The administrative h ...; the language used to be commonly known as ‘Kinnauri Tribal language’, but this is now considered a derogatory term. It is not clear how distinct it is from other varieties of Himachali. Script The native script of the language is a variety of Takri script. Status The language is also commonly called Pahari or Himachali. The language has no official status and is recorded under Kinnauri or Pahari. According to the United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO), the language is of definitely endangered category, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduri Language
Hinduri (or Handuri) is a Western Pahari language of northern India. It was classified as a dialect under the Kiunthali Group Script Status The language is commonly called Pahari or Himachali. Some speakers may even call it a dialect of Punjabi or Dogri Dogri ( Name Dogra Akkhar: ; Devanagari: डोगरी; Nastaliq: ; ) is an Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, India, with smaller groups of speakers in adjoining regions of western Himachal Prad .... The language has no official status. According to the United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO), the language is of critically endangered category, i.e. the youngest speakers of Handuri are generally grandparents or older and they too speak it infrequently or partially. The demand for the inclusion of 'Pahari (Himachali)' under the Eight Schedule of the Constitution, which is supposed to represent multiple Pahari languages of Himachal Prade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaunsari Language
Jaunsari () is a Western Pahari language of northern India spoken by the Jaunsari people in the Chakrata and Kalsi blocks of Dehradun district in the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand state. The dialects of Jaunsari share about 60% of their basic vocabulary with each of the neighbouring varieties of Bangani, Jaunpuri, Nagpuriya and Sirmauri Sirmauri is a Western Pahari language spoken in the Sirmaur district in the northern Indian state of Himachal Pradesh Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western H .... Script Jaunsari was historically written in Jaunsari Script . The Devanagari script is being used these days in certain works. Status The language has no official status. According to the United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO), the language is of definitely endangered category, i.e. many Jaunsari children are not learning Jaunsari as their mother tong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwal Division
Garhwal (IPA: /ɡəɽʋːɔɭ/) is one of the two administrative divisions of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Lying in the Himalayas, it is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Kumaon, on the south by Uttar Pradesh state, and on the northwest by Himachal Pradesh state. It includes the districts of Chamoli, Dehradun, Haridwar, Pauri Garhwal, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal, and Uttarkashi. The people of Garhwal are known as Garhwali and speak the Garhwali language. The administrative center for Garhwal division is the town of Pauri. The Divisional Commissioner is the administrative head of the Division, and is a senior Indian Administrative Service officer. As the administrative head of the division, the Commissioner is overall incharge of the 7 districts in the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand, and is aided in his duties by an additional commissioner and the district magistrates. Sushil Kumar is the divisional commissioner of the Garhwal Division since December 2021. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwali Language
Garhwali (, , in native pronunciation) is an Indo-Aryan language of the Central Pahari subgroup. It is primarily spoken by over 2.5 million Garhwali people in the Garhwal region of the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand in the Indian Himalayas. Garhwali has a number of regional dialects. It is not an endangered language ('' Ethnologue'' lists it as "vigorous"), it is nonetheless designated as "vulnerable" in UNESCO's '' Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'', which indicates that the language requires consistent conservation efforts. Geographical distribution Garhwali is spoken primarily by people in Tehri Garhwal, Pauri Garhwal, Uttarkashi, Chamoli, Rudraprayag and Dehradun districts of Garhwal division in the state of Uttarakhand. Garhwali is also spoken by Garhwali migrants to other parts of India including Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh. According to various estimates, there are at least 3.5 million Garhwali migrants living in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |