|
North American Atlantic Region
North American Atlantic Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom identified by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne, spanning from the Atlantic and Gulf coasts to the Great Plains and comprising a major part of the United States and southeastern portions of Canada. It is bordered by the Circumboreal floristic region in the north, by the Rocky Mountain and Madrean floristic regions in the west and by the Caribbean floristic region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south of Florida. The flora of the region comprises two endemic monotypic families, Hydrastidaceae and Leitneriaceae, and is characterized by about a hundred of endemic genera (such as ''Sanguinaria'', ''Leavenworthia'', ''Gillenia'', '' Neviusia'', '' Dionaea'', '' Yeatesia'', '' Pleea''). The degree of species endemism is very high, many species are Tertiary relicts, which survived the Wisconsin glaciation and are now concentrated in the Appalachians (esp. Blue Ridge Mountains) and the Ozarks. A number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craggy Gardens-27527
Crag may refer to: * Crag (climbing), a cliff or group of cliffs, in any location, which is or may be suitable for climbing * Crag (dice game), a dice game played with three dice * Crag, Arizona, US * Crag, West Virginia, US * Crag and tail, a geological formation caused by the passage of a glacier over an area of hard rock * Crag Group, a geological group outcropping in East Anglia, UK ** Coralline Crag Formation ** Norwich Crag Formation ** Red Crag Formation ** Wroxham Crag Formation, see Cromer Forest Bed * Crag Hotel, Penang, Malaysia * Crag Jones (born 1962), Welsh climber * USS Crag (AM-214), USS ''Crag'' (AM-214), a 1943 US Navy ''Admirable''-class minesweeper * The Crag, the final event in the Nickelodeon Guts#The Crag, Nickelodeon Guts action sports program * Club de Radioaficionados de Guatemala, an amateur radio organization in Guatemala * Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010, concerning United Kingdom constitutional law See also * * Cragg (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
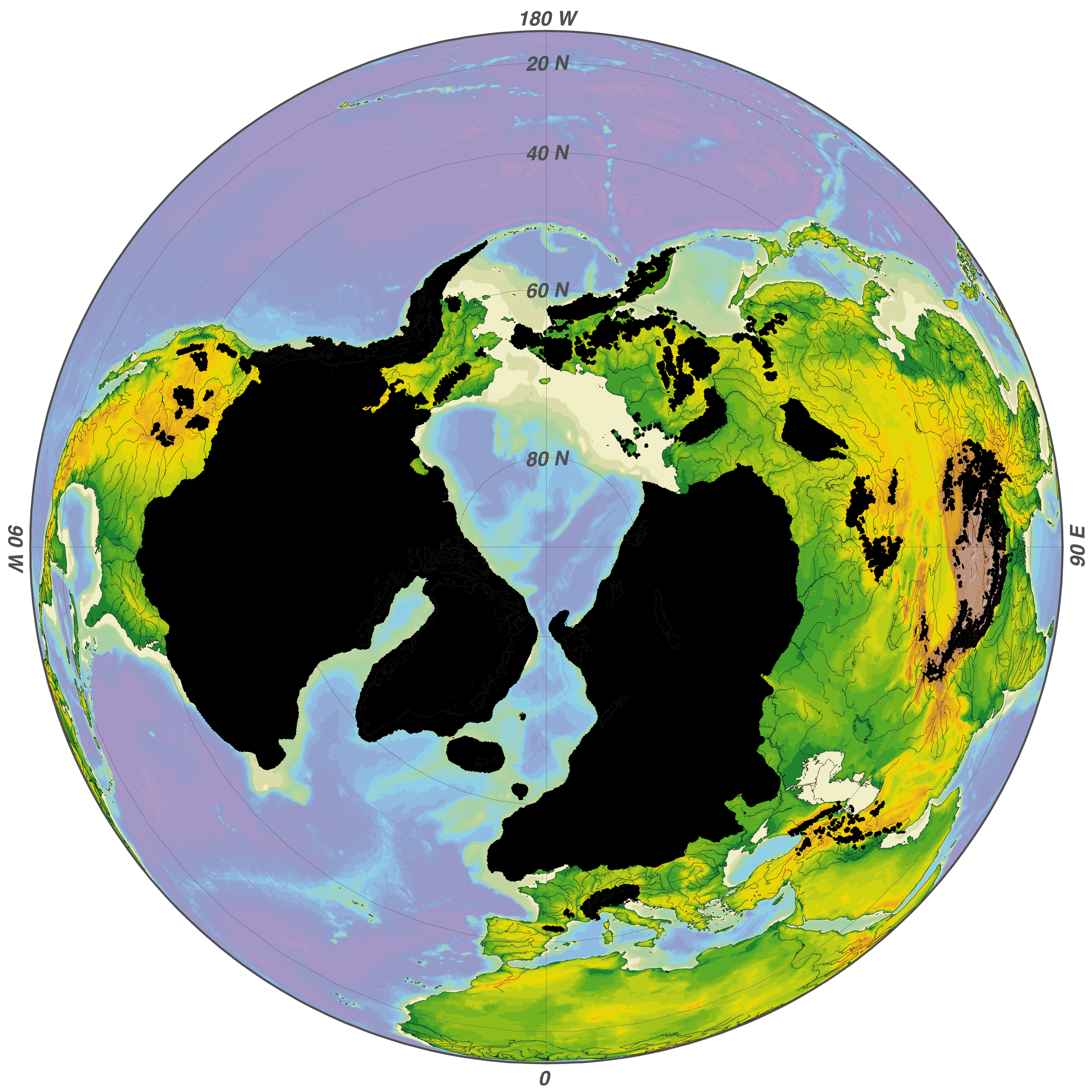
Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the ''Late Wisconsin'' in North America. This glaciation radically altered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relict (biology)
In biogeography and paleontology, a relict is a population or taxon of organisms that was more widespread or more diverse in the past. A relictual population is a population currently inhabiting a restricted area whose range was far wider during a previous geologic epoch. Similarly, a relictual taxon is a taxon (e.g. species or other lineage) which is the sole surviving representative of a formerly diverse group. Definition A relict (or relic) plant or animal is a taxon that persists as a remnant of what was once a diverse and widespread population. Relictualism occurs when a widespread habitat or range changes and a small area becomes cut off from the whole. A subset of the population is then confined to the available hospitable area, and survives there while the broader population either shrinks or evolves divergently. This phenomenon differs from endemism in that the range of the population was not always restricted to the local region. In other words, the species or group did n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the merged Paleogene and Neogene periods, which are informally called the Early Tertiary and the Late Tertiary, respectively. The Tertiary established the Antarctic as an icy island continent. Historical use of the term The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied. In the early d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleea
''Pleea'' is a small genus of flowering plants described as a genus in 1803. There is only one known species, ''Pleea tenuifolia'', the rush featherling, native to the southeastern United States (Florida, Alabama, North Carolina, and South Carolina )''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no) , anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind" , Former = Province of South Carolina , seat = Columbia , LargestCity = Charleston , LargestMetro = ...). Image References Tofieldiaceae[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeatesia
''Yeatesia'' is a putative genus of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae Acanthaceae is a family (the acanthus family) of dicotyledonous flowering plants containing almost 250 genera and about 2500 species. Most are tropical herbs, shrubs, or twining vines; some are epiphytes. Only a few species are distributed in te ..., found in northeast Mexico and the southeast United States, from Texas to Florida. Each of its species grows in very different habitats; ''Yeatesia mabryi'' is found in hardwood forests in Mexico, ''Y. platystegia'' prefers semiarid scrublands in Mexico and Texas, and ''Y. viridiflora'' grows in wetter forest bluffs and along water courses in US Gulf Coast states. Molecular evidence shows that ''Yeatesia'' is not a monophyletic genus. Species Currently accepted species include: *'' Yeatesia mabryi'' Hilsenb. *'' Yeatesia platystegia'' (Torr.) Hilsenb. *'' Yeatesia viridiflora'' (Nees) Small References {{Taxonbar, from=Q9096965 Acanthaceae Acantha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionaea Muscipula
The Venus flytrap (''Dionaea muscipula'') is a carnivorous plant native to subtropical wetlands on the East Coast of the United States in North Carolina and South Carolina. It catches its prey—chiefly insects and arachnids—with a trapping structure formed by the terminal portion of each of the plant's leaves, which is triggered by tiny hairs (called "trigger hairs" or "sensitive hairs") on their inner surfaces. When an insect or spider crawling along the leaves contacts a hair, the trap prepares to close, snapping shut only if another contact occurs within approximately twenty seconds of the first strike. Triggers may occur with a tenth of a second of contact. The requirement of redundant triggering in this mechanism serves as a safeguard against wasting energy by trapping objects with no nutritional value, and the plant will only begin digestion after five more stimuli to ensure it has caught a live bug worthy of consumption. ''Dionaea'' is a monotypic genus closely relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neviusia
''Neviusia'', the snow-wreaths, is a genus of ornamental plants, which are native to the United States, containing two extant species and one extinct species known from fossil leaves. This genus is a rare example of a disjunct range occurring in North America. The type species, ''Neviusia alabamensis'', occurs in several southeastern states, while second extant species, ''Neviusia cliftonii'', is endemic to the Mt Shasta region of California, and the extinct species ''Neviusia dunthornei'' is found in shale deposits in the Okanagan Highlands of Washington and British Columbia. It is named for Episcopal priest and botanist Reuben Nevius Reuben Denton Nevius (1827 – 14 December 1913) was an American botanist and Episcopal priest, missionary, and the first registrar of the Diocese of Olympia, Washington. Born in Ovid, New York, the Rev. Reuben Denton Nevius received in 1849 his D. .... References * * * * Kerrieae Rosaceae genera Flora of the United States {{a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gillenia
''Gillenia'' ( syn. ''Porteranthus'') is a genus of two species of perennial herbs in the family Rosaceae, '' Gillenia stipulata'' and '' Gillenia trifoliata''. Common names for plants in this genus include: Bowman's root, Indian-physic, American ipecac. This genus is endemic to dry open woods with acidic soils in eastern North America. Both plants are subshrubs with exposed semi-woody branches and serrated leaves; the larger lower leaves are divided into palmately arranged leaflets. Plants bloom in May, June, or July; blooms are composed of five slender white petals which are loosely arranged and typically appear slightly twisted and limp as if they were wilted. The flowers mature into small capsules. ''G. stipulata'' and ''G. trifoliata'' are often planted as ornamentals and used in herbal medicine. Classification and name Traditionally this genus is considered to be related to Spiraea, but it became apparent that it comes from the lineage which leads to tribe Maleae (w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leavenworthia
''Leavenworthia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Brassicaceae. It includes about eight species native to the southern and southeastern United States.''Leavenworthia''. Flora of North America. They are known generally as gladecresses.''Leavenworthia''. USDA PLANTS.''Leavenworthia''. Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Description [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |