Wisconsin glaciation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
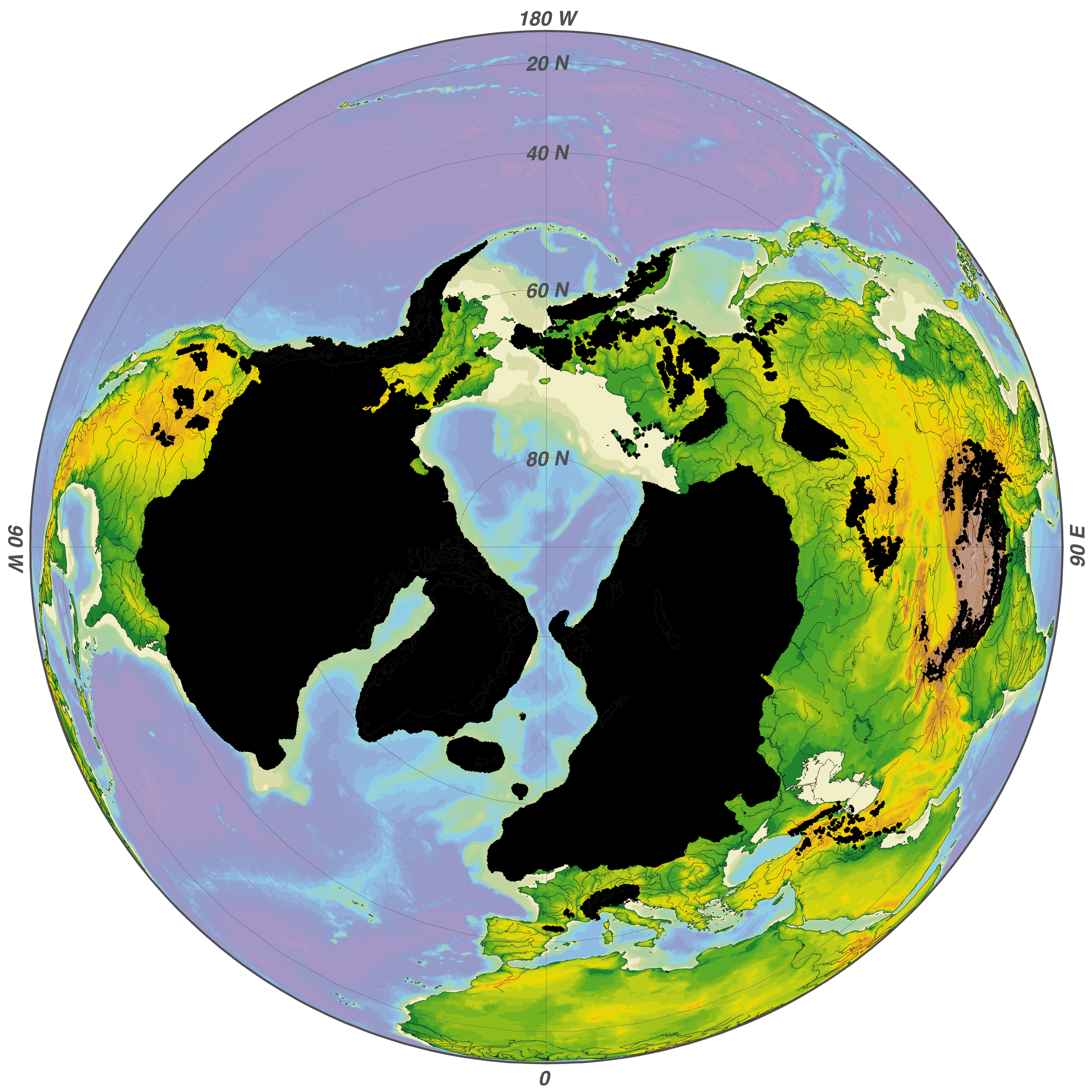 The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the
 Whenever the ice sheet melted from the north at a
Whenever the ice sheet melted from the north at a
 The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark).
Situated in the northern extremity of No ...
; the Greenland ice sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equ ...
; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eu ...
, also known as the ''Late Wisconsin'' in North America.
This glaciation radically altered the geography north of the Ohio River. At the height of the Wisconsin Episode glaciation, the ice sheet covered most of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
, the Upper Midwest
The Upper Midwest is a region in the northern portion of the U.S. Census Bureau's Midwestern United States. It is largely a sub-region of the Midwest. Although the exact boundaries are not uniformly agreed-upon, the region is defined as referrin ...
, and New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
, as well as parts of Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and W ...
, Montana
Montana () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West List of regions of the United States#Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions, division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North ...
, and Washington. On Kelleys Island in Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
, northern New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York (state), New York; on the ea ...
and in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
's Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
,SERC Media; Glacial Grooves, Central Park; Image 14884 is a 208 by 173 pixel JPEG; Uploaded: Apr5 09; Wayne Powell, CUNY Brooklyn College; http://serc.carleton.edu/details/images/14884.html the grooves left in rock by these glaciers can be easily observed. In southwestern Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North ...
and southeastern Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
a suture zone between the Laurentide and Cordilleran ice sheets formed the Cypress Hills, North America's northernmost point that remained south of the continental ice sheets. During much of the glaciation, sea level was low enough to permit land animals, including humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, to occupy Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
(the Bering Land Bridge) and move between North America and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
. As the glaciers retreated, glacial lakes were breached in great floods of water such as the Kankakee Torrent, which reshaped the landscape south of modern Chicago as far as the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers.
Times
Two related movements have been termed Wisconsin: Early Wisconsin and Late Wisconsin.Chapter II. Glacial History of the Huron-Erie Basin; Geological Report on Wayne County; W.H. Sherzer; Michigan Geological and Biological Survey, Publication 12, Geological Series 9; Lansing, Michigan; Wynkoop Hallenbeck Crawford Co., State Printers; 1913 The Early Wisconsin was the bigger of the two and extend farther west and south. It retreated an unknown distance before halting. During this period of quiet, the glacial deposits were eroded and weathered. This first Wisconsin period erased all the Illinoian glacial topography that extended over. The Late Wisconsin ice sheet extended more towards the west than the earlier movements. This may have been due to changes in the accumulation center of the ice sheet, topographic changes introduced by the Early phase or by pressure changes in the ice mass in the north.Continental ice sheets
Ice caps
Labrador Ice Sheet
The Labrador Ice Sheet centered east of Hudson Bay. Expanding towards the southwest, it reached into the eastern edge ofManitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Win ...
and across the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
to the Ohio River, upwards of from its source. Its eastern lobes covered New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
and reached south to Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of mainland Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer mon ...
and Long Island, New York
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18t ...
.Chamberlin, Thomas C. and Salisbury, Rollin T., Geology, 3 Vols. 1906, Vol III., pp. 330-333.
Ice lobes
Keewatin Ice Sheet
The Keewatin Ice Sheet began west of Hudson Bay in the Canadian Territory of Keewatin. The ice moved south some into Kansas and Missouri. To the west, it reached to the foothills of theRocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
.
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran Ice Sheet has left remnants throughout the Northern Rocky Mountains. Unlike the other two ice sheets, this one is mountain based coveringBritish Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
and reaching into northern Washington State and Montana
Montana () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West List of regions of the United States#Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions, division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North ...
. The Cordilleran Ice Sheet has more of an Alpine style of many glaciers merged into a whole. The striations made by the ice field in moving over the bedrock show that it moved principally to the west through the passes of the coast range.
Formation of proglacial and prehistoric lakes
moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris ( regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sh ...
, water would begin to pond in the divide between a moraine and the ice front. The ice would act as a dam as water could not drain through the ice sheet, which in the Wisconsin period covered most of the proglacial river valleys. Numerous small, isolated water bodies formed between the moraine and the ice front. As the ice sheet would continue to melt and recede northward, these ponds combined into proglacial lakes. In areas without an available outlet, the water levels would either continue to rise until reaching one or more low spots along the rim of a moraine, or the ice sheet would retreat, opening access to a lower portion of the moraine. Multiple outlets could form through low spots too until one would become dominant after erosion lowered both the outlet and lake surface.
Running water
Ice melt and rainfall carried large quantities ofclay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
, sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a soil t