|
Nicholas Shackleton
Sir Nicholas John Shackleton (23 June 1937 – 24 January 2006) was an English geologist and paleoclimatologist who specialised in the Quaternary Period. He was the son of the distinguished field geologist Robert Millner Shackleton and great-nephew of the explorer Ernest Shackleton. Education and employment Educated at Cranbrook School, Kent (thanks to the generosity of a person he called his "fairy godmother" as she paid his school fees) Shackleton went on to read natural sciences at Clare College, Cambridge. He graduated with the Bachelor of Arts degree in 1961, promoted in 1964 to Master of Arts. In 1967 Cambridge awarded him a PhD degree, for a thesis entitled "The Measurement of Paleotemperatures in the Quaternary Era". Apart from periods abroad as Visiting Professor or Research Associate, Shackleton's entire scientific career was spent at Cambridge. He became Ad hominem Professor in 1991, in the Department of Earth Sciences, working in the Godwin Institute for Quate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today, although a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has been proposed but is not yet officially recognised by the ICS). The Quaternary Period is typically defined by the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four successive formations or "orders" ( it, quattro ordini). The term "quaternary" was introduced by Jules Desn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge Department Of Earth Sciences
The Department of Earth Sciences at Cambridge is the University of Cambridge's Earth Sciences department. First formed around 1731, the department incorporates the Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences. History The department's history can be traced back to 1731 when the 1st Woodwardian Professor of Geology was appointed, in accordance with the bequest of John Woodward. The present Department of Earth Sciences was formed by an amalgamation of the Department of Geology, Department of Geodesy and Geophysics and the Department of Mineralogy and Petrology in 1980. The main location of the department is at the Downing Site, Downing St. The Bullard Laboratories, located in West Cambridge on Madingley Rd is a satellite department of the main building. The department incorporates the Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences and the Godwin Laboratory. The department is the home of the Sedgwick Club, which was founded in memory of Adam Sedgwick in 1880, and is the oldest student run geological s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Innovation Award
The Science Innovation Award is an award bestowed annually by the European Association of Geochemistry on a scientist who has made "a particularly important and innovative breakthrough in geochemistry", and consists of a medal and certificate. The specific subject area of the award varies according to a five-year cycle: Former recipients of the Science Innovation Award are, in reverse chronological order: {, class="wikitable" align=center , +Science Innovation Award winners !Year!!Name(s)!!Medal , - , 2022 , , Lenny Winkel, ETH Zürich, Switzerland, , Heinz A. Lowenstam Medal , - , 2021 , , Fabrice Gaillard, Institute of Earth Sciences at Orléans, France , , Ted Ringwood Medal , - , 2020 , , Kevin Russo, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, United States , , Werner Stumm Medal , - , 2019 , , Ariel Anbar, Arizona State University, United States , , Samuel Epstein Medal , - , 2018 , , Jess Adkins, Caltech, United States , , Nicholas Shackleton Medal , - , 2017 , , Bo Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Association Of Geochemistry
The European Association of Geochemistry (EAG) is a pan-European organization founded to promotes geochemical research. The EAG organizes conferences, meetings and educational courses for geochemists in Europe, including the Goldschmidt Conference which it co-sponsors with the North American Geochemical Society. Awards The European Association of Geochemistry gives the following awards: * The Urey Medal (European Association of Geochemistry) for outstanding contributions advancing geochemistry over a career. * The Science Innovation Award for an important and innovative breakthrough in geochemistry. * The Houtermans Award for exceptional contributions to geochemistry made by scientists under 35 years old. * Geochemical Fellows – Awarded annually by the Geochemical Society and the European Association of Geochemistry to outstanding scientists who have, over some years, made a major contribution to the field of geochemistry. Publications The European Association of Geochemistry p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres, namely biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields. There are both reductionist and holistic approaches to Earth sciences. It is also the study of Earth and its neighbors in space. Some Earth scientists use their knowledge of the planet to locate and develop energy and mineral resources. Others study the impact of human activity on Earth's environment, and design methods to protect the planet. Some use their knowledge about Earth proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as The Royal Society and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the President are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Quaternary Research
The International Union for Quaternary Research (INQUA) was founded in 1928. It has members from a number of scientific disciplines who study the environmental changes that occurred during the glacial ages, the last 2.6 million years. One goal of these investigators is to document the timing and patterns in past climatic changes to help understand the causes of changing climates. INQUA is a Scientific Union member of the International Council for Science (ICSU). INQUA holds an international congress normally every four years. The congresses serve as an educational forum as well as the opportunity for the various commissions, committees, and working groups to conduct business in person. Past congresses have been held in Copenhagen (1928), Leningrad (Saint Petersburg) (1932), Vienna (1936), Rome (1953), Madrid (1957), Warsaw (1961), Boulder (1965), Paris (1969), Christchurch (1973), Birmingham (1977), Moscow (1982), Ottawa (1987), Beijing (1991), Berlin (1995), Durban (1999 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milankovitch Cycle
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he hypothesized that variations in eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession combined to result in cyclical variations in the intra-annual and latitudinal distribution of solar radiation at the Earth's surface, and that this orbital forcing strongly influenced the Earth's climatic patterns. Earth's movements The Earth's rotation around its axis, and revolution around the Sun, evolve over time due to gravitational interactions with other bodies in the Solar System. The variations are complex, but a few cycles are dominant. The Earth's orbit varies between nearly circular and mildly elliptical (its eccentricity varies). When the orbit is more elongated, there is more variation in the distance between the Earth and the Sun, and in the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
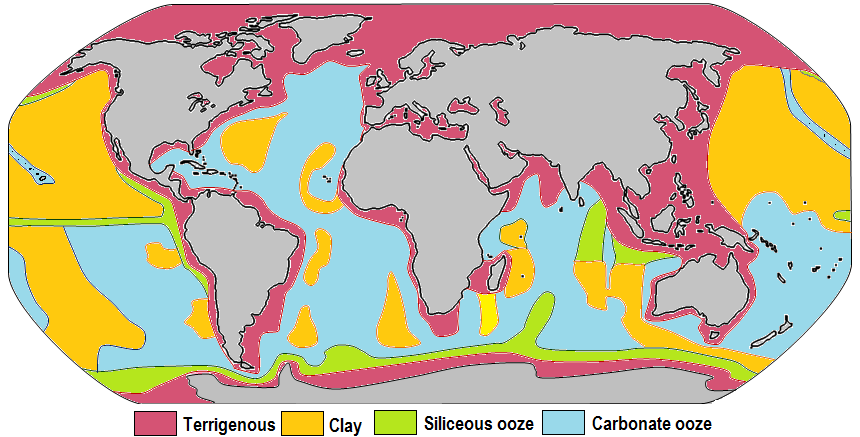
Ocean Sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea. Additional deposits come from marine organisms and chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris. Except within a few kilometres of a mid-ocean ridge, where the volcanic rock is still relatively young, most parts of the seafloor are covered in sediment. This material comes from several different sources and is highly variable in composition. Seafloor sediment can range in thickness from a few millimetres to several tens of kilometres. Near the surface seafloor sediment remains unconsolidated, but at depths of hundreds to thousands of metres the sediment becomes lithified (turned to rock). Rates of sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature'' cover the full r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Isotope
There are three known stable isotopes of oxygen (8O): , , and . Radioactive isotopes ranging from to have also been characterized, all short-lived. The longest-lived radioisotope is with a half-life of , while the shortest-lived isotope is with a half-life of (though the half-lives of the neutron-unbound and are still unknown). List of isotopes , - , , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" , 3 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , , (3/2−) , , , - , , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" , 4 , , , 2p , , 0+ , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 5 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β+ () , , rowspan=2, (3/2−) , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β+p () , , - , , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , , β+ , , 0+ , , , - , , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" , 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)