|
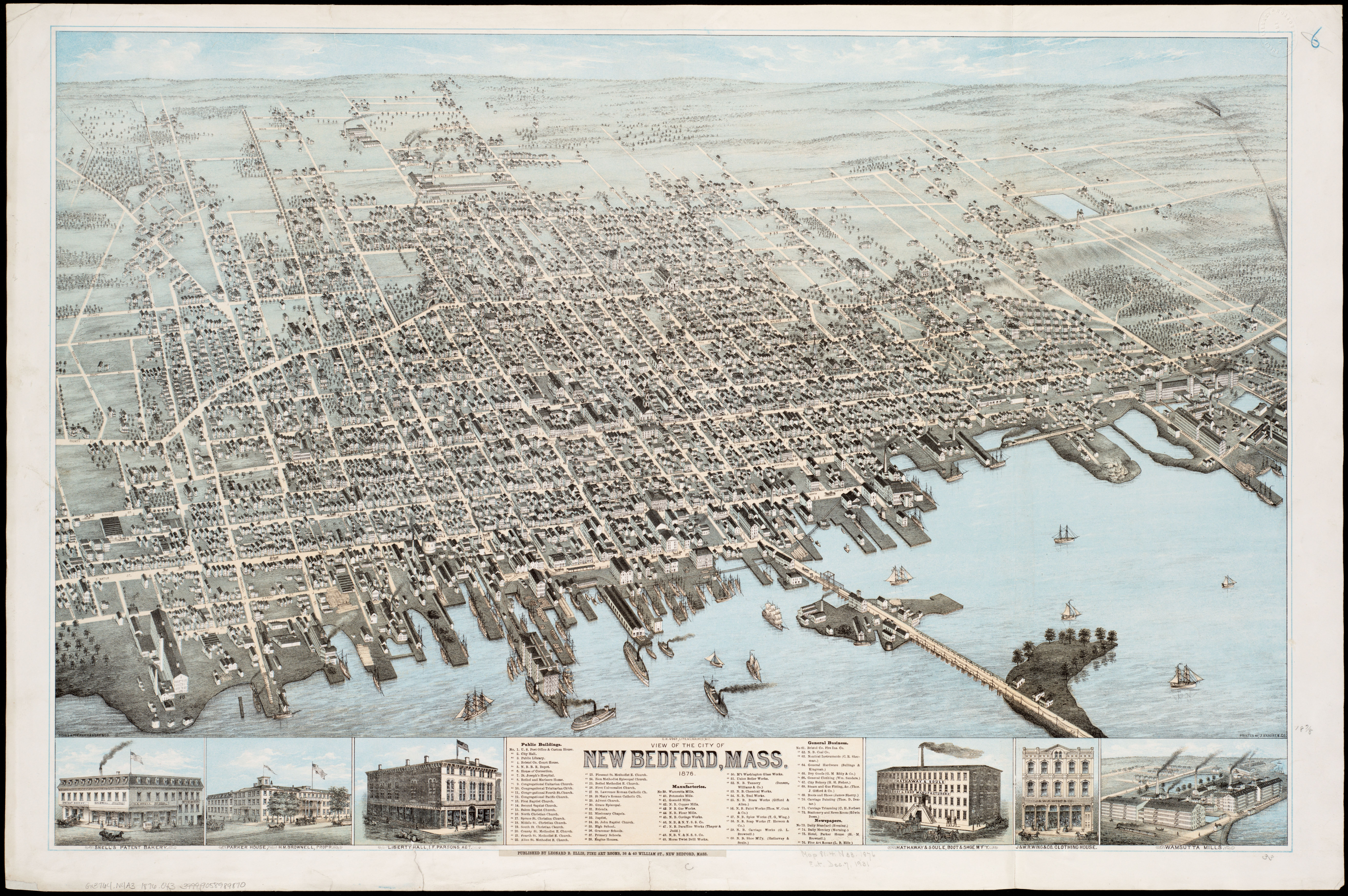
New Bedford, MA
New Bedford (Massachusett: ) is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts. It is located on the Acushnet River in what is known as the South Coast region. Up through the 17th century, the area was the territory of the Wampanoag Native American people. English colonists bought the land on which New Bedford would later be built from the Wampanoag in 1652, and the original colonial settlement that would later become the city was founded by English Quakers in the late 17th century. The town of New Bedford itself was officially incorporated in 1787. During the first half of the 19th century, New Bedford was one of the world's most important whaling ports. At its economic height during this period, New Bedford was the wealthiest city in the world per capita. New Bedford was also a center of abolitionism at this time. The city attracted many freed or escaped African-American slaves, including Frederick Douglass, who lived there from 1838 until 1841. The city also served as the primary s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut [Massachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət],'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east, Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York (state), New York to the west. The state's capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city, as well as its cultural and financial center, is Boston. Massachusetts is also home to the urban area, urban core of Greater Boston, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American History of the United States, history, academia, and the Economy of the United States, research economy. Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing, and trade. Massachusetts was transformed into a manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Bedford Whaling Museum
The New Bedford Whaling Museum is a museum in New Bedford, Massachusetts, United States that focuses on the history, science, art, and culture of the international whaling industry, and the "Old Dartmouth" region (now the city of New Bedford and towns of Acushnet, Massachusetts, Acushnet, Dartmouth, Massachusetts, Dartmouth, Fairhaven, Massachusetts, Fairhaven, and Westport, Massachusetts, Westport) in the South Coast (Massachusetts), South Coast of Massachusetts. The museum is governed by the Old Dartmouth Historical Society (ODHS), which was established in 1903 "to create and foster an interest in the history of Old Dartmouth." Since then, the museum has expanded its scope to include programming that addresses global issues "including the consequences of natural resource exhaustion, the diversification of industry, and tolerance in a multicultural society." Its collections include over 750,000 items, including 3,000 pieces of scrimshaw and 2,500 logbooks from whaling ships, both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Americans
Portuguese Americans ( pt, português-americanos), also known as Luso-Americans (''luso-americanos''), are citizens and residents of the United States who are connected to the country of Portugal by birth, ancestry, or citizenship. Americans and others who are not native Europeans from Portugal but originate from countries that were former colonies of Portugal do not necessarily self-identify as "Portuguese-American", but rather as their post-colonial nationalities, although many refugees (referred to as '' retornados'') from former Portuguese colonies, as well as many white Brazilians, are ethnically or ancestrally Portuguese. In 2017, an estimated 48,158 Portuguese nationals were living in the United States. Some Melungeon communities in rural Appalachia have historically self-identified as Portuguese. Given their complex ancestry, individual Melungeons may descend from Portuguese people, but not all do. History Bilateral ties date from the earliest years of the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast Guard Academy
The United States Coast Guard Academy (USCGA) is a service academy of the United States Coast Guard in New London, Connecticut. Founded in 1876, it is the smallest of the five U.S. service academies and provides education to future Coast Guard officers in one of nine major fields of study. Students are officers-in-training and are referred to as cadets, and upon graduation receive a Bachelor of Science degree and are commissioned as Coast Guard ensigns with a five-year active-duty service obligation, with additional years if the graduate attends flight school or subsequent government-funded graduate school. Out of approximately 250 cadets entering the academy each summer, around 200 graduate. Cadets can choose from among nine majors, with a curriculum that is graded according to their performance in a holistic program of academics, physical fitness, character, and leadership. Cadets are required to adhere to the academy's "Honor Concept," "''Who lives here reveres honor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Revenue Cutter Service
) , colors= , colors_label= , march= , mascot= , equipment= , equipment_label= , battles= , anniversaries=4 August , decorations= , battle_honours= , battle_honours_label= , disbanded=28 January 1915 , flying_hours= , website= , commander1= , commander1_label= , commander2= , commander2_label= , commander3= , commander3_label= , commander4= , commander4_label= , notable_commanders= , identification_symbol= , identification_symbol_label=Ensign (1799) , identification_symbol_2= , identification_symbol_2_label=Ensign (1815) , identification_symbol_3= , identification_symbol_3_label=Ensign (1836) , identification_symbol_4= , identification_symbol_4_label=Ensign (1841) , identification_symbol_5= , identification_symbol_5_label=Ensign (1867) , identification_symbol_6= , identification_symbol_6_label=Ensign (1868) The United States Revenue Cutter Service was established by an act of Congress () on 4 August 1790 as the Revenue-Marine upon the recommendation of Secretary of the Treasury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moby-Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is the sailor Ishmael's narrative of the obsessive quest of Ahab, captain of the whaling ship ''Pequod'', for revenge against Moby Dick, the giant white sperm whale that on the ship's previous voyage bit off Ahab's leg at the knee. A contribution to the literature of the American Renaissance, ''Moby-Dick'' was published to mixed reviews, was a commercial failure, and was out of print at the time of the author's death in 1891. Its reputation as a "Great American Novel" was established only in the 20th century, after the 1919 centennial of its author's birth. William Faulkner said he wished he had written the book himself, and D. H. Lawrence called it "one of the strangest and most wonderful books in the world" and "the greatest book of the sea ever written". Its opening sentence, "Call me Ishmael", is among world literature's most famous. Melville began writing ''Moby-Dick'' in February 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Melville
Herman Melville (born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are ''Moby-Dick'' (1851); '' Typee'' (1846), a romanticized account of his experiences in Polynesia; and ''Billy Budd, Sailor'', a posthumously published novella. Although his reputation was not high at the time of his death, the 1919 centennial of his birth was the starting point of a Melville revival, and ''Moby-Dick'' grew to be considered one of the great American novels. Melville was born in New York City, the third child of a prosperous merchant whose death in 1832 left the family in dire financial straits. He took to sea in 1839 as a common sailor on a merchant ship and then on the whaler ''Acushnet'', but he jumped ship in the Marquesas Islands. ''Typee'', his first book, and its sequel, ''Omoo'' (1847), were travel-adventures based on his encounters with the peoples of the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became a national leader of the abolitionist movement in Massachusetts and New York, becoming famous for his oratory and incisive antislavery writings. Accordingly, he was described by abolitionists in his time as a living counterexample to slaveholders' arguments that slaves lacked the intellectual capacity to function as independent American citizens. Northerners at the time found it hard to believe that such a great orator had once been a slave. It was in response to this disbelief that Douglass wrote his first autobiography. Douglass wrote three autobiographies, describing his experiences as a slave in his '' Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave'' (1845), which became a bestseller and was influential in promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolitionism In New Bedford, Massachusetts
Abolitionism in New Bedford, Massachusetts, began with the opposition to slavery voiced by Quakers during the late 1820s, followed by African Americans forming the antislavery group New Bedford Union Society in 1833, and an integrated group of abolitionists forming the New Bedford Anti-Slavery Society a year later. During the era New Bedford, Massachusetts, gained a reputation as a safe haven for fugitive slaves seeking freedom. Located on the East Coast of the United States, the town was becoming the "whaling capital of the world", where ships frequently returned to port, operated by crews of diverse backgrounds, languages, and ethnicity. This made it easy for fugitive slaves to "mix in" with crew members. The whaling and shipping industries were also uniquely open to people of color. Although only about 15% of the town supported abolition—and the town's abolitionists had different viewpoints about intermarriage, equal opportunity, and full integration—it provided opport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
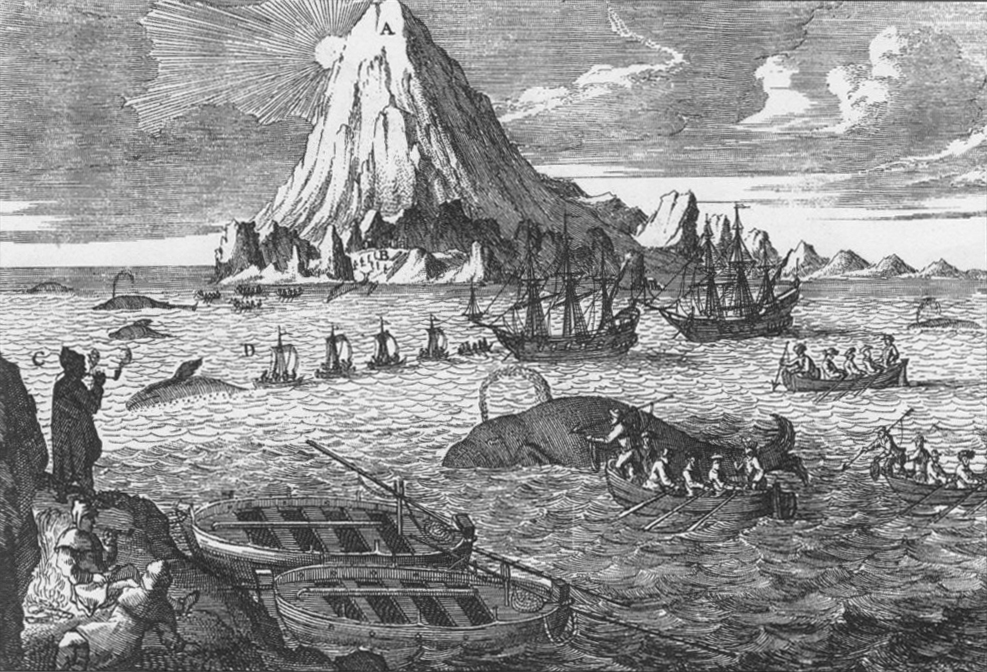
Whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution. It was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16th century, it had risen to be the principal industry in the Basque coastal regions of Spain and France. The industry spread throughout the world, and became increasingly profitable in terms of trade and resources. Some regions of the world's oceans, along the animals' migration routes, had a particularly dense whale population, and became the targets for large concentrations of whaling ships, and the industry continued to grow well into the 20th century. The depletion of some whale species to near extinction led to the banning of whaling in many countries by 1969, and to an international cessation of whaling as an industry in the late 1980s. The earliest known forms of whaling date to at least 3000 BC. Coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)