|
Neolithic Decline
The Neolithic decline was a rapid collapse in populations between five and six thousand years ago (approximately 3000 BC) during the Neolithic period in western Eurasia. The specific causes of that broad population decline are still debated. While heavily-populated settlements were regularly created, abandoned, and resettled during the Neolithic, after around 5400 years ago, a great number of those settlements were permanently abandoned. The population decline is associated with worsening agricultural conditions and a decrease in cereal production. Other suggested causes include the emergence of communicable diseases spread from animals living in close quarters with humans. Conditions for the population increase that preceded the decline are generally ascribed to rapid population growth between 5950 and 5550 BP. That growth was catalysed by the introduction of agriculture, along with the spread of technologies such as pottery, the wheel, and animal husbandry. After the Neolithic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communicable Disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1 January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale. The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must now account for. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation RCYBP stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is sometimes used for dates established by means other than radiocarbon dating, such as stratigraphy. This usage differs from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
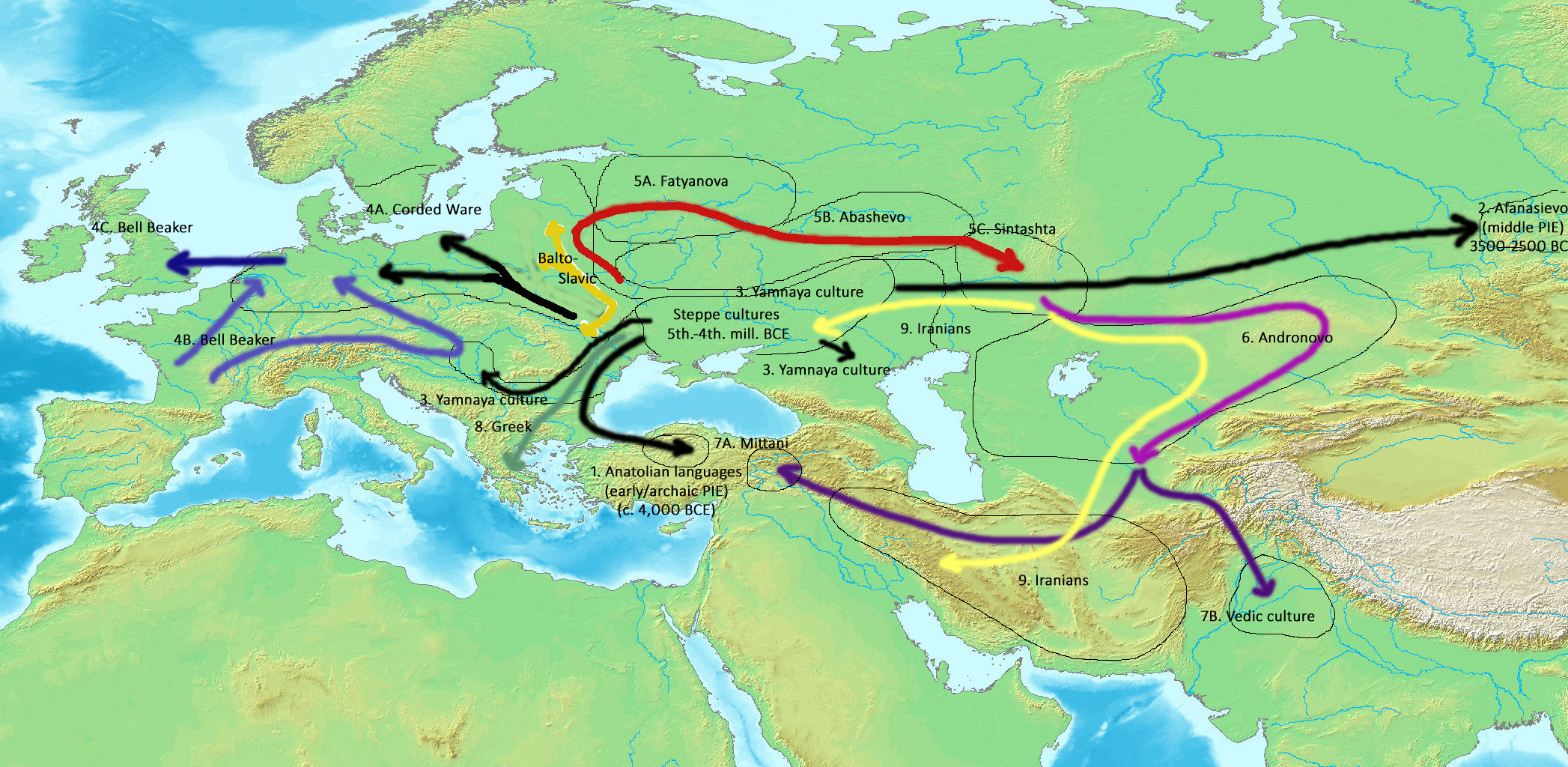
Indo-European Migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially explaining how these languages came to be spoken across a large area of Eurasia, from India and Iran, to Europe. While there can be no direct evidence of prehistoric languages, a synthesis of linguistics, archaeology, anthropology and genetics establish both the existence of Proto-Indo-European and the spread of its daughter dialects through migrations of large populations of its speakers, as well as the recruitment of new speakers through emulation of conquering elites. Comparative linguistics describes the similarities between various languages and the laws of systematic change, which allow the reconstruction of ancestral speech (see Indo-European studies). Archaeology traces the spread of artifacts, habitations, and burial sites presumed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontic–Caspian Steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extends from Dobruja in the northeastern corner of Bulgaria and southeastern Romania, through Moldova and southern and eastern Ukraine, across the Russian Northern Caucasus, the Southern and lower Volga regions to western Kazakhstan, adjacent to the Kazakh steppe to the east, both forming part of the larger Eurasian Steppe. It forms a part of the Palearctic realm and of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome. The area corresponds to Cimmeria, Scythia, and Sarmatia of classical antiquity. Across several millennia, numerous tribes of nomadic horsemen used the steppe; many of them went on to conquer lands in the settled regions of Europe, Western Asia, and Southern Asia. The term Ponto-Caspian region is used in biogeography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague (disease)
Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, weakness and headache. Usually this begins one to seven days after exposure. There are three forms of plague, each affecting a different part of the body and causing associated symptoms. Pneumonic plague infects the lungs, causing shortness of breath, coughing and chest pain; bubonic plague affects the lymph nodes, making them swell; and septicemic plague infects the blood and can cause tissues to turn black and die. The bubonic and septicemic forms are generally spread by flea bites or handling an infected animal, whereas pneumonic plague is generally spread between people through the air via infectious droplets. Diagnosis is typically by finding the bacterium in fluid from a lymph node, blood or sputum. Those at high risk may be vaccinated. Those exposed to a case of pneumonic plague may be treated with preventive medication. If infected, treatment is with antibiotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridgetunnel across the Öresund. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country, the third-largest country in the European Union, and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a total population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of , with around 87% of Swedes residing in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden has a nature dominated by forests and a large amount of lakes, including some of the largest in Europe. Many long rivers run from the Scandes range through the landscape, primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yersinia Pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly '' Pasteurella pestis'') is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores that is related to both ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' and ''Yersinia enterocolitica''. It is a facultative anaerobic organism that can infect humans via the Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''). It causes the disease plague, which caused the first plague pandemic and the Black Death, the deadliest pandemic in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic. ''Yersinia pestis'' is a parasite of its host, the rat flea, which is also a parasite of rats, hence ''Y. pestis'' is a hyperparasite. ''Y. pestis'' was discovered in 1894 by Alexandre Yersin, a Swiss/French physician and bacteriologist from the Pasteur Institute, during an epidemic of the plague in Hong Kong. Yersin was a member of the Pasteur school of thought. Kitasato Shibasaburō, a Japanese bacteriologist who practised Koch's me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasminogen Activator
Plasminogen activators are serine proteases that catalyze the activation of plasmin via proteolytic cleavage of its zymogen form plasminogen. Plasmin is an important factor in fibrinolysis, the breakdown of fibrin polymers formed during blood clotting. There are two main plasminogen activators: urokinase (uPA) and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). Tissue plasminogen activators are used to treat medical conditions related to blood clotting including embolic or thrombotic stroke, myocardial infarction, and pulmonary embolism. Plasminogen activators are inhibited by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-2, and protein C inhibitor. Function Produced mainly in the liver, plasminogen is the inactive zymogen form of plasmin, and circulates in plasma in a closed conformation that cannot be activated. Binding clots or cell surface causes its conformation to change, allowing it to be activated by plasminogen activators. Plasminogen activators do so by clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonic Plague
Pneumonic plague is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is one of three forms of plague, the other two being septicemic plague and bubonic plague. The pneumonic form may occur following an initial bubonic or septicemic plague infection. It may also result from breathing in airborne droplets from another person or animal infected with pneumonic plague. The difference between the forms of plague is the location of infection; in pneumonic plague the infection is in the lungs, in bubonic plague the lymph nodes, and in septicemic plague within the blood. Diagnosis is by testing the blood, sputum, or fluid from a lymph node. While vaccines are being developed, in most countries they are not yet commercially available. Prevention is by avoiding contact with infected rodents, people, or cats. It is recommen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamin Mangha
Cholent and other Sabbath stews ( yi, טשאָלנט, tsholnt ''or'' tshulnt) are traditional Jewish stews. It is usually simmered overnight for 10–12 hours or more, and eaten for lunch on Shabbat (the Sabbath). Shabbat stews were developed over the centuries to conform with Jewish laws that prohibit cooking on the Sabbath. The pot is brought to a boil on Friday before the Sabbath begins, and sometimes kept on a blech or hotplate, or left in a slow oven or electric slow cooker, until the following day. Cholent originated as a barley porridge in ancient Judea called "harisa" or "horisa",Gil Marks, Encyclopedia of Jewish Foods, 656 (Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons, 2010), 40. possibly as far back as the Second Temple period, and over the centuries various Jewish diaspora communities created their own variations of the dish based on local food resources and neighborhood influence. There are many variations of the dish, which is standard in both the Ashkenazi and Sephard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |