|
Neolectomycetes
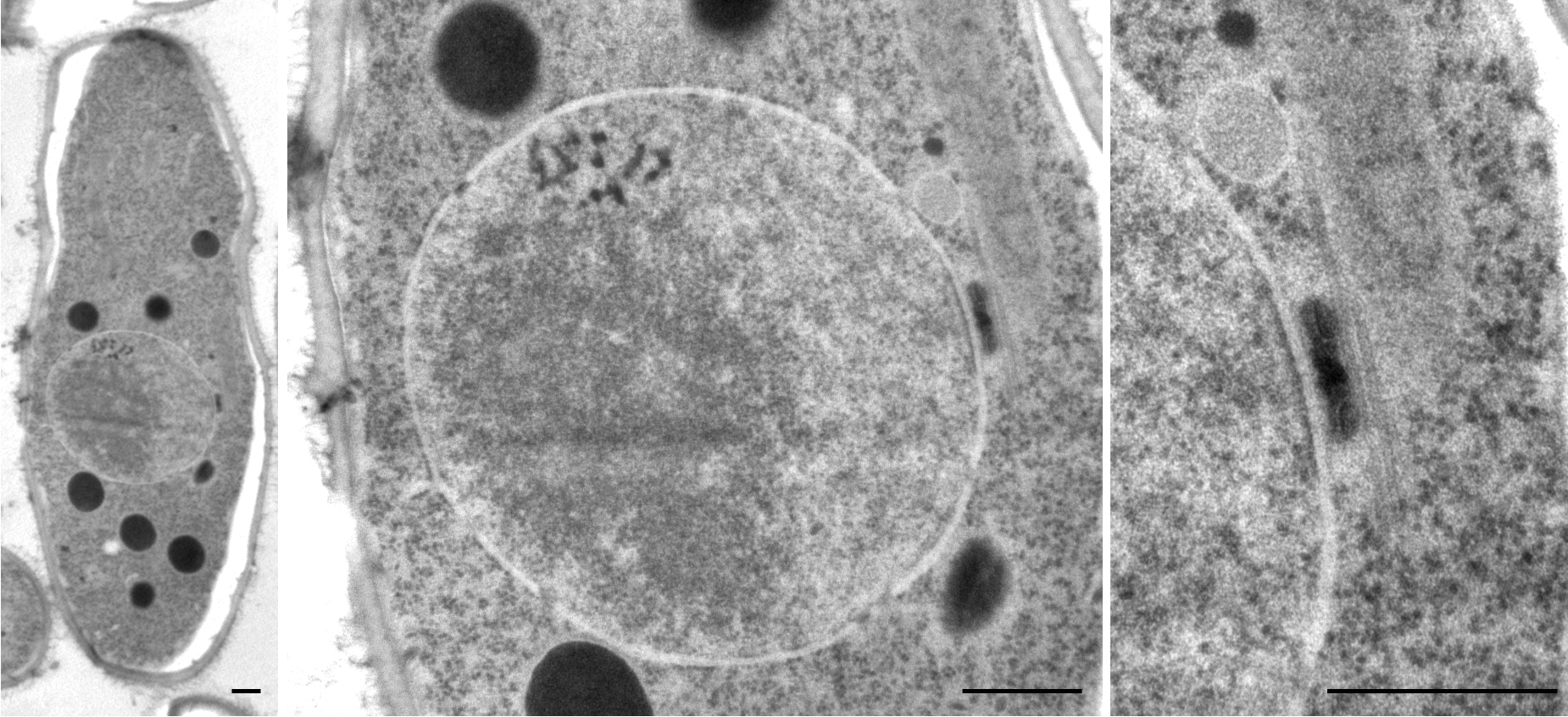
''Neolecta'' is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that have fruiting bodies in the shape of unbranched to lobed bright yellowish, orangish to pale yellow-green colored, club-shaped, smooth, fleshy columns up to about 7 cm tall. The species share the English designation "Earth tongues" along with some better-known fungi (e.g. ''Geoglossum'', ''Microglossum'') with a similar general form, but in fact they are only distantly related. ''Neolecta'' is the only genus belonging to the family Neolectaceae, which is the only family belonging to the order Neolectales. ''Neolectales'', in turn, is the only order belonging to the class Neolectomycetes, which belongs to the subdivision Taphrinomycotina of the Ascomycota. ''Neolecta'' is found in Asia, North America, Northern Europe and southern Brazil. The species all live in association with trees, and at least one, ''N. vitellina'', grows from rootlets of its host, but it is not known whether the fungus is parasitic, saprotrophic, or mutu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taphrinomycotina
The Taphrinomycotina are one of three subdivisions constituting the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ascus) and is more or less synonymous with the slightly older invalid name Archiascomycetes (sometimes spelled Archaeascomycetes; archea = ancient). Recent molecular studies suggest that the group is monophyletic and basal to the rest of the Ascomycota. The major taxa are Schizosaccharomycetes, Taphrinomycetes, Neolectomycetes, and Pneumocystis. The Schizosaccharomycetes are the yeasts (e.g. ''Schizosaccharomyces'') that reproduce by fission rather than budding, unlike most other yeasts, many of which are in the subdivision Saccharomycotina. The Taphrinomycetes are dimorphic plant parasites (e.g. ''Taphrina'') with both a yeast state and a filamentous (hyphal) state in infected plants. They characteristically infect leaves, catkins, and branches, not roots. Taphrinomycetes form asci but no ascomata. The Neolectomycetes are species in a single genus, ''N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolecta Flavovirescens
''Neolecta'' is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that have fruiting bodies in the shape of unbranched to lobed bright yellowish, orangish to pale yellow-green colored, club-shaped, smooth, fleshy columns up to about 7 cm tall. The species share the English designation "Earth tongues" along with some better-known fungi (e.g. ''Geoglossum'', ''Microglossum'') with a similar general form, but in fact they are only distantly related. ''Neolecta'' is the only genus belonging to the family Neolectaceae, which is the only family belonging to the order Neolectales. ''Neolectales'', in turn, is the only order belonging to the class Neolectomycetes, which belongs to the subdivision Taphrinomycotina of the Ascomycota. ''Neolecta'' is found in Asia, North America, Northern Europe and southern Brazil. The species all live in association with trees, and at least one, ''N. vitellina'', grows from rootlets of its host, but it is not known whether the fungus is parasitic, saprotrophic, or mutu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolecta Irregularis
''Neolecta'' is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that have fruiting bodies in the shape of unbranched to lobed bright yellowish, orangish to pale yellow-green colored, club-shaped, smooth, fleshy columns up to about 7 cm tall. The species share the English designation "Earth tongues" along with some better-known fungi (e.g. ''Geoglossum'', ''Microglossum'') with a similar general form, but in fact they are only distantly related. ''Neolecta'' is the only genus belonging to the family Neolectaceae, which is the only family belonging to the order Neolectales. ''Neolectales'', in turn, is the only order belonging to the class Neolectomycetes, which belongs to the subdivision Taphrinomycotina of the Ascomycota. ''Neolecta'' is found in Asia, North America, Northern Europe and southern Brazil. The species all live in association with trees, and at least one, ''N. vitellina'', grows from rootlets of its host, but it is not known whether the fungus is parasitic, saprotrophic, or mutu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myconet
''Myconet'' was a peer-reviewed mycological journal A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a ... intended for the documentation of selected mycosystematic files published on the Internet. The journal was published from 1997 to 2007. Publications established in 1997 Publications disestablished in 2007 Microbiology journals Mycology journals {{mycology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living Fossil
A living fossil is an extant taxon that cosmetically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living fossils commonly are of species-poor lineages, but they need not be. While the body plan of a living fossil remains superficially similar, it is never the same species as the remote relatives it resembles, because genetic drift would inevitably change its chromosomal structure. Living fossils exhibit stasis (also called "bradytely") over geologically long time scales. Popular literature may wrongly claim that a "living fossil" has undergone no significant evolution since fossil times, with practically no molecular evolution or morphological changes. Scientific investigations have repeatedly discredited such claims. The minimal superficial changes to living fossils are mistakenly declared as an absence of evolution, but they are examples of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conidia
A conidium ( ; ), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (), is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis. The two new haploid cells are genetically identical to the haploid parent, and can develop into new organisms if conditions are favorable, and serve in biological dispersal. Asexual reproduction in ascomycetes (the phylum Ascomycota) is by the formation of conidia, which are borne on specialized stalks called conidiophores. The morphology of these specialized conidiophores is often distinctive between species and, before the development of molecular techniques at the end of the 20th century, was widely used for identification of (''e.g.'' ''Metarhizium'') species. The terms microconidia and macroconidia are sometimes used. Conidiogenesis There are two main types of conidium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crozier (mycology)
A crozier is an anatomical feature of many fungi in the phylum Ascomycota that forms at the base of asci and looks like a hook-topped shepherd’s staff or stylized religious crosier. Croziers resemble and function similarly to clamp connections on the dikaryotic hyphae of Basidiomycota. During initial ascus formation in Ascomycota fruitbodies, the crozier helps to maintain the dikaryotic state of both the ascus itself and of the side branch that will continue propagation of the ascogenous hyphae. The tips of developing asci on these ascogenous hyphae curl over. One haploid nucleus migrates into the curved tip while the other compatible haploid nucleus remains in the penultimate space below the hook. The ascus itself forms as a radiating spur branch at the top of the hook. Each nucleus divides, resulting in the formation of a pair of compatible nuclei, i.e. a dikaryon, in the ascus. Two sister nuclei remain, one in the basal cell and the other in the crozier. The tip of the croz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
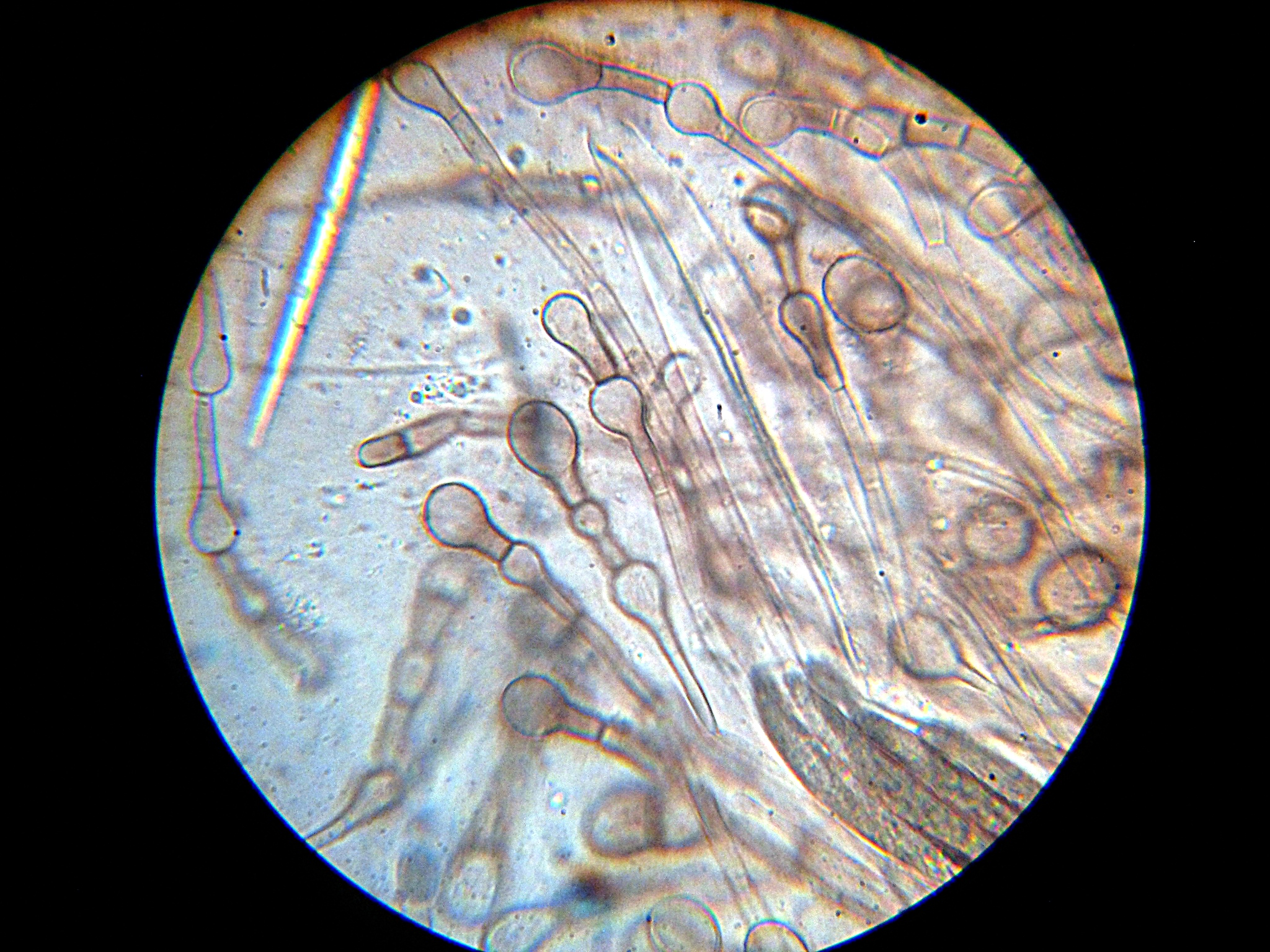
Ascus
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. ''Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. ''Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some ''Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the "bourrelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |