|
Neiba
Neiba (also spelt ''Neyba'') is a city in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. It is the capital city of the Baoruco province, and is located 180 kilometres west of the national capital, Santo Domingo, close to the shore of Lake Enriquillo, the largest lake in the West Indies. History Before the conquest and colonization of Hispaniola, the place was a nitainato belonging to the Chiefdom of Jaragua. Founded in 1546 as a town from a cattle herd on the west side, years later it was depopulated together with the Villa de San Juan, being refounded in 1735 when it was repopulated and its neighbors enjoyed their lands that were from the Azua district. On March 13, 1844, a confrontation between Haitian and Dominican troops took place in the municipality in the so-called Battle of the Baptism of Blood, held in the now municipality of Galván, Bahoruco Province. The municipality was also the scene of the restoration struggles, where the first war day began with the assault on the Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neiba Dominican Republic
Neiba (also spelt ''Neyba'') is a city in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. It is the capital city of the Baoruco province, and is located 180 kilometres west of the national capital, Santo Domingo, close to the shore of Lake Enriquillo, the largest lake in the West Indies. History Before the conquest and colonization of Hispaniola, the place was a nitainato belonging to the Chiefdom of Jaragua. Founded in 1546 as a town from a cattle herd on the west side, years later it was depopulated together with the Villa de San Juan, being refounded in 1735 when it was repopulated and its neighbors enjoyed their lands that were from the Azua district. On March 13, 1844, a confrontation between Haitian and Dominican troops took place in the municipality in the so-called Battle of the Baptism of Blood, held in the now municipality of Galván, Bahoruco Province. The municipality was also the scene of the restoration struggles, where the first war day began with the assault on the Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neiba 2
Neiba (also spelt ''Neyba'') is a city in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. It is the capital city of the Baoruco province, and is located 180 kilometres west of the national capital, Santo Domingo, close to the shore of Lake Enriquillo, the largest lake in the West Indies. History Before the conquest and colonization of Hispaniola, the place was a nitainato belonging to the Chiefdom of Jaragua. Founded in 1546 as a town from a cattle herd on the west side, years later it was depopulated together with the Villa de San Juan, being refounded in 1735 when it was repopulated and its neighbors enjoyed their lands that were from the Azua district. On March 13, 1844, a confrontation between Haitian and Dominican troops took place in the municipality in the so-called Battle of the Baptism of Blood, held in the now municipality of Galván, Bahoruco Province. The municipality was also the scene of the restoration struggles, where the first war day began with the assault on the Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
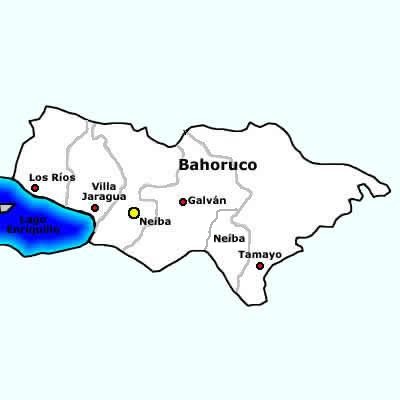
Baoruco Province
Baoruco, alternatively spelt Bahoruco (), is a province of the Dominican Republic located in the southwest of the country, part of the Enriquillo Region, along with the provinces of Barahona, Independencia and Pedernales. Before 1952 it included what is now Independencia Province. Important features are the Sierra de Neiba mountain range and Lake Enriquillo. Municipalities and municipal districts The province is divided into the following municipalities (''municipios'') and municipal districts (''distrito municipal'' - D.M.) within them: * Galván * Los Ríos ** Las Clavellinas city (D.M.) *Neiba ** El Palmar (D.M.) * Tamayo **Cabeza de Toro (D.M.) **Montserrat (D.M.) **Santana (D.M.) ** Uvilla (D.M.) *Villa Jaragua The following is a sortable table of the municipalities and municipal districts with population figures as of the 2014 estimate. Urban population are those living in the seats (''cabeceras'' literally heads) of municipalities or of municipal districts. Rural popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands, along with Saint Martin, that is shared by two sovereign states. The Dominican Republic is the second-largest nation in the Antilles by area (after Cuba) at , and third-largest by population, with approximately 10.7 million people (2022 est.), down from 10.8 million in 2020, of whom approximately 3.3 million live in the metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The official language of the country is Spanish. The native Taíno people had inhabited Hispaniola before the arrival of Europeans, dividing it into five chiefdoms. They had constructed an advanced farming and hunting society, and were in the process of becoming an organized civilization. The Taínos also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Enriquillo
Lake Enriquillo ( es, Lago Enriquillo) is a hypersaline lake in the Dominican Republic located in the southwestern region of the country. Its waters are shared between the provinces of Bahoruco and Independencia, the latter of which borders Haiti. Lake Enriquillo is the largest lake in both the Dominican Republic and Hispaniola, as well as the entire Caribbean. It is also the lowest point for an island country. Hydrology Lake Enriquillo covers an area of 145 mi2 (375 km2), and is the lowest point for an island country, falling below sea level. Its drainage basin includes 10 minor river systems. The rivers that rise in the Neiba Mountains to the north (lower center and lower right of the image) are perennial. Those rivers that rise in the Baoruco Mountains to the south are intermittent. Lake Enriquillo has no outlet. The lake's water level varies because of a combination of storm-driven precipitation events and the region's high evaporation rate. Salinity in the lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of The Dominican Republic
The municipalities of the Dominican Republic are, after the regions and the provinces, the third level of the political and administrative division of the Dominican Republic. The division of provinces into municipalities (''municipios'') is established in the Constitution and further regulated by Law 5220 on the Territorial Division of the Dominican Republic. It was enacted in 1959 and has been frequently amended to create new provinces, municipalities and lower-level administrative units. Municipalities may be further divided into ''secciones'' (literally: sections) and ''parajes'' (literally: places or neighborhoods). Municipal districts (''distritos municipales'') may be formed in the case of municipalities with several urban centres. Law 176-07 replaced ''Law Nº 3455 de Organización Municipal'' from January, 29, 1953; that had long served as the basis for municipal administration, see The provinces as the second level of political and administrative division contain at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, state, country, continent, planet, and beyond). Demonyms are used to designate all people (the general population) of a particular place, regardless of ethnic, linguistic, religious or other cultural differences that may exist within the population of that place. Examples of demonyms include ''Cochabambino'', for someone from the city of Cochabamba; French for a person from France; and '' Swahili'', for a person of the Swahili coast. As a sub-field of anthroponymy, the study of demonyms is called ''demonymy'' or ''demonymics''. Since they are referring to territorially defined groups of people, demonyms are semantically different from ethnonyms (names of ethnic groups). In the English language, there are many polysemic words that hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total , population_density_km2 = auto , timezone = AST (UTC −4) , area_code_type = Area codes , area_code = 809, 829, 849 , postal_code_type = Postal codes , postal_code = 10100–10699 (Distrito Nacional) , website Ayuntamiento del Distrito Nacional Santo Domingo ( meaning "Saint Dominic"), once known as Santo Domingo de Guzmán and Ciudad Trujillo, is the capital and largest city of the Dominican Republic and the largest metropolitan area in the Caribbean by population. As of 2022, the city and immediate surrounding area (the Distrito Nacional) had a population of 1,484,789, while the total population is 2,995,211 when including Greater Santo Domingo (the "metropolitan area"). The city is coterminous with the boundaries of the Distrito Nacional ("D.N.", "National District"), itself bordered on three sides by Santo Domingo Province. Founded by the Spanish in 1496, on the east bank of the Ozama River and then moved by Nicolás de Ovando in 1502 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Savanna Climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of precipitation and also less than 100-\left (\frac \right)mm of precipitation. This latter fact is in a direct contrast to a tropical monsoon climate, whose driest month sees less than of precipitation but has ''more'' than 100-\left (\frac \right) of precipitation. In essence, a tropical savanna climate tends to either see less overall rainfall than a tropical monsoon climate or have more pronounced dry season(s). In tropical savanna climates, the dry season can become severe, and often drought conditions prevail during the course of the year. Tropical savanna climates often feature tree-studded grasslands due to its dryness, rather than thick jungle. It is this widespread occurrence of tall, coarse grass (called savanna) which has led to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the North Atlantic Ocean. Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some Central and South American mainland nations which have Caribbean coastlines, such as Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic island nations of Barbados, Bermuda, and Trinidad and Tobago, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Origin and use of the term In 1492, Christopher Columbus became the first European to record his arri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |