|
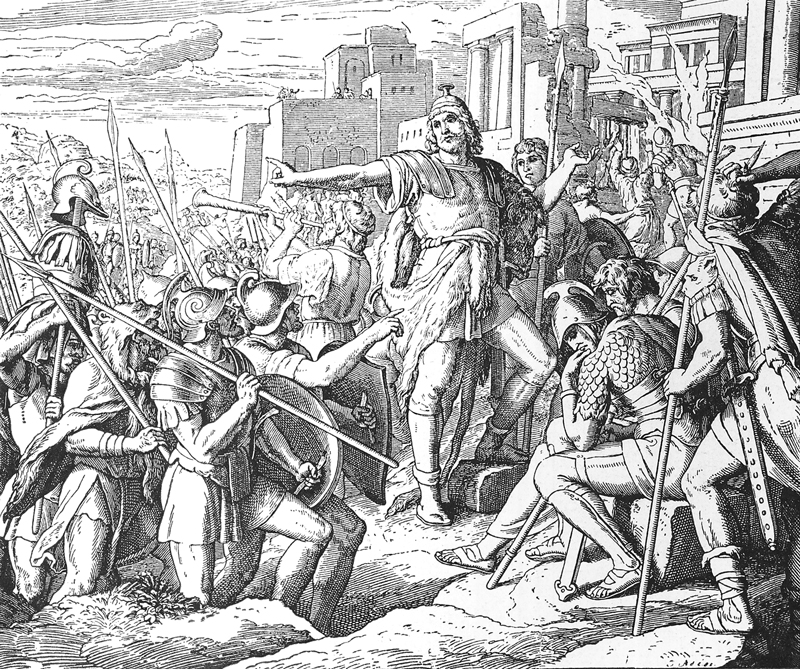
Nehemiah (band)
Nehemiah is the central figure of the Book of Nehemiah, which describes his work in rebuilding Jerusalem during the Second Temple period. He was governor of Persian Judea under Artaxerxes I of Persia (465–424 BC). The name is pronounced or in English. It is in Hebrew , ''Nəḥemyāh'', "Yah comforts". Most scholars believe Nehemiah was a real historical figure and that the Nehemiah Memoir, a name given by scholars to certain portions of the book written in the first person, is historically reliable.For confirmation that many scholars share this view, see For confirmation that most scholars share this view, see For an author who disagrees with the scholarly majority position on the historicity of Nehemiah and Ezra, but acknowledges the existence of that majority, see Nehemiah is venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic Church, where his feast day is July 13, the same as his contemporary, Ezra. He is also considered a saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church, where his feas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dung Gate
The Dung Gate ( he, שער האשפות ''Sha'ar Ha'ashpot'') or Silwan Gate, also known as the Mughrabi Gate ( ar, باب المغاربة ''Bab al-Maghariba''), is one of the Gates of the Old City of Jerusalem. It was built as a small postern gate in the 16th century by the Ottomans, first widened for vehicular traffic in 1952 by the Jordanians, and again in 1985 by the Israeli authorities. The gate is situated near the southeast corner of the Old City, southwest of the Temple Mount. Directly behind the gate lies the entrance to the Western Wall Plaza. The Dung Gate is a main passage for vehicles coming out of the Old City and for buses headed to the Western Wall. Names Built by the Ottomans in the 16th century, this small gate was then called Mughrabi Gate. In the 19th century, it started being called Dung Gate by Jews. It is also known as the Silwan Gate. The original ''Dung Gate'' ( he, שער האשפות ''Sha'ar Ha'ashpot'') was, in the Hebrew Bible (, the name of a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, divinities, objects, and binomial nomenclature. It can also be a descriptive title: for example, Pallas Athena, Phoebus Apollo, Alfred the Great, Suleiman the Magnificent, and Władysław I the Elbow-high. Many English monarchs have traditional epithets: some of the best known are Edward the Confessor, William the Conqueror, Richard the Lionheart, Æthelred the Unready, John Lackland and Bloody Mary. The word ''epithet'' can also refer to an abusive, defamatory, or derogatory phrase. This use as a euphemism is criticized by Martin Manser and other proponents of linguistic prescription. H. W. Fowler complained that "epithet is suffering a vulgarization that is giving it an abusive imputation." Linguistics Epithets are sometimes at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggadah
Aggadah ( he, ''ʾAggāḏā'' or ''Haggāḏā''; Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: אַגָּדְתָא ''ʾAggāḏəṯāʾ''; "tales, fairytale, lore") is the non-legalistic exegesis which appears in the classical rabbinic literature of Judaism, particularly the Talmud and Midrash. In general, Aggadah is a compendium of rabbinic texts that incorporates folklore, historical anecdotes, moral exhortations, and practical advice in various spheres, from business to medicine. Etymology The Hebrew word ''haggadah'' (הַגָּדָה) is derived from the Hebrew root נגד, meaning "declare, make known, expound", also known from the common Hebrew verb להגיד.Berachyahu Lifshitz, "Aggadah Versus Haggadah : Towards a More Precise Understanding of the Distinction", ''Diné Yisrael'' 24 (2007): page 23 (English section). The majority scholarly opinion is that the Hebrew word ''aggadah'' (אַגָּדָה) and corresponding Aramaic ''aggadta'' (אַגָּדְתָא) are variants of ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua The High Priest
Joshua ( ''Yəhōšūa‘'') or Yeshua ( ''Yēšūaʿ'') the High Priest was, according to the Bible, the first person chosen to be the High Priest for the reconstruction of the Jewish Temple after the return of the Jews from the Babylonian Captivity (See and in the Bible). Life Joshua son of Jozadak served as High Priest ca. 515–490 BCE in the common List of High Priests of Israel. This dating is based on the period of service at age 25–50 (per Numbers ) rather than age 30–50 (per ). The biblical text credits Joshua among the leaders that inspired a momentum towards the reconstruction of the temple, in Ezra . Later some of his sons and nephews are found guilty of intermarriage. Facts concerning the later part of Joshua's life are in part dependent upon whether Joshua was still alive at the time of his appearance in a vision seen by Zechariah. If the vision relates to Nehemiah's cleansing of the temple in then the engagement of Joshua's great-great-grandson to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zerubbabel
According to the biblical narrative, Zerubbabel, ; la, Zorobabel; Akkadian: 𒆰𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠 ''Zērubābili'' was a governor of the Achaemenid Empire's province Yehud Medinata and the grandson of Jeconiah, penultimate king of Judah. Zerubbabel led the first group of Jews, numbering 42,360, who returned from the Babylonian captivity in the first year of Cyrus the Great, the king of the Achaemenid Empire.' The date is generally thought to have been between 538 and 520 BC. Zerubbabel also laid the foundation of the Second Temple in Jerusalem soon after. In all of the accounts in the Hebrew Bible that mention Zerubbabel, he is always associated with the high priest who returned with him, Joshua (Jeshua) son of Jozadak (Jehozadak). Together, these two men led the first wave of Jewish returnees from exile and began to rebuild the Temple. Old Testament theologian John Kessler describes the region of Judah as a small province that contained land extending 25 km from Jerusalem a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirach
The Book of Sirach () or Ecclesiasticus (; abbreviated Ecclus.) is a Jewish work, originally in Hebrew, of ethical teachings, from approximately 200 to 175 BC, written by the Judahite scribe Ben Sira of Jerusalem, on the inspiration of his father Joshua son of Sirach, sometimes called Jesus son of Sirach or Yeshua ben Eliezer ben Sira. In Egypt, it was translated into Greek by the author's unnamed grandson, who added a prologue. This prologue is generally considered the earliest witness to a canon of the books of the prophets, and thus the date of the text is the subject of intense scrutiny. The book itself is the largest wisdom book from antiquity to have survived. Canonical status Sirach is accepted as part of the canon by Catholics, Eastern Orthodox, and most Oriental Orthodox Christians. The Anglican tradition considers Sirach (which was published with other Greek Jewish books in a separate section of the King James Bible) among the apocryphal books, and read them "f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judas Maccabeus
Judah Maccabee (or Judas Maccabeus, also spelled Machabeus, or Maccabæus, Hebrew: יהודה המכבי, ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') was a Jewish priest (''kohen'') and a son of the priest Mattathias. He led the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleucid Empire (167–160 BCE). The Jewish holiday of Hanukkah ("Dedication") commemorates the restoration of Jewish worship at the Second Temple in Jerusalem in 164 BCE, after Judah Maccabee removed all of the statues depicting Greek gods and goddesses and purified it. Life Early life Judah was the third son of Mattathias the Hasmonean, a Jewish priest from the village of Modi'in. In 167 BCE Mattathias, together with his sons Judah, Eleazar, Simon, John, and Jonathan, started a revolt against the Seleucid ruler Antiochus IV Epiphanes, who since 175 BCE had issued decrees that forbade Jewish religious practices. After Mattathias's death in 166 BCE, Judah assumed leadership of the revolt in accordance with the deathbed disposition of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Book Of Maccabees
2 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Β´, translit=Makkabaíōn 2 also known as the Second Book of Maccabees, Second Maccabees, and abbreviated as 2 Macc., is a deuterocanonical book which recounts the persecution of Jews under King Antiochus IV Epiphanes and the Maccabean Revolt against him. It concludes with the defeat of the Seleucid Empire general Nicanor in 161 BC by Judas Maccabeus, the leader of the Maccabees. 2 Maccabees was originally written in Koine Greek by an unknown diaspora Jew living in Hellenistic Egypt. It was likely written some time between 150 and 120 BC. Together with the book 1 Maccabees, it is one of the most important sources on the Maccabean Revolt. The work is not a sequel to 1 Maccabees but rather its own independent rendition of the historical events of the Maccabean Revolt. It both starts and ends its history earlier than 1 Maccabees, starting with an incident with the Seleucid official Heliodorus attempting to tax the Second Temple in 178 BC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo-Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ; he, שׁוּשָׁן ; grc-gre, Σοῦσα ; syr, ܫܘܫ ; pal, 𐭮𐭥𐭱𐭩 or ; peo, 𐏂𐎢𐏁𐎠 ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital of Elam and the Achaemenid Empire, and remained a strategic centre during the Parthian and Sasanian periods. The site currently consists of three archaeological mounds, covering an area of around one square kilometre. The modern Iranian town of Shush is located on the site of ancient Susa. Shush is identified as Shushan, mentioned in the Book of Esther and other Biblical books. Name The English name is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of People In The Hebrew Bible Called Shemaiah
Shemaiah is the name of several people in the Hebrew Bible (Hebrew: שמעיה ''shemayah'' "God Heard"): *a Levite in the time of David, who with 200 of his relatives took part in the bringing up of the ark from Obed-edom to Hebron (I Chronicles 15:8) *the eldest son of Obed-edom (I Chronicles 26:4-8) *Shemaiah son of Nethanel, a scribe mentioned as active at the death of David (I Chronicles 24:6) * Shemaiah, a prophet in the reign of Rehoboam (I Kings 12:22-24; II Chronicles 11:2-4; 12:5) *one of the Levites whom Jehoshaphat appointed to teach the law (II Chronicles 17:8) *Shemaiah, the father of Shimri, listed as a Simeonite five generations before the reign of Hezekiah (I Chronicles 4:37) *Shemaiah son of Jeduthun, a Levite in the time of Hezekiah (II Chronicles 29:14) *a Levite appointed to "distribute the oblations of the Lord" during the reign of Hezekiah (II Chronicles 31:15) *a Levite in the time of Josiah (II Chronicles 35:9) *the father of Urijah the prophet (Jeremiah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; Hebrew: ''Mīqrā''), is the Biblical canon, canonical collection of Hebrew language, Hebrew scriptures, including the Torah, the Nevi'im, and the Ketuvim. Different branches of Judaism and Samaritanism have maintained different versions of the canon, including the 3rd-century Septuagint text used by Second-Temple Judaism, the Syriac language Peshitta, the Samaritan Torah, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and most recently the 10th century medieval Masoretic Text, Masoretic text created by the Masoretes currently used in modern Rabbinic Judaism. The terms "Hebrew Bible" or "Hebrew Canon" are frequently confused with the Masoretic text, however, this is a medieval version and one of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)