|
Negative Bias Temperature Instability
Negative-bias temperature instability (NBTI) is a key reliability issue in MOSFETs, a type of transistor aging. NBTI manifests as an increase in the threshold voltage and consequent decrease in drain current and transconductance of a MOSFET. The degradation is often approximated by a power-law dependence on time. It is of immediate concern in p-channel MOS devices (pMOS), since they almost always operate with negative gate-to-source voltage; however, the very same mechanism also affects nMOS transistors when biased in the accumulation regime, i.e. with a negative bias applied to the gate. More specifically, over time positive charges become trapped at the oxide-semiconductor boundary underneath the gate of a MOSFET. These positive charges partially cancel the negative gate voltage ''without'' contributing to conduction through the channel as electron holes in the semiconductor are supposed to. When the gate voltage is removed, the trapped charges dissipate over a time scale of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) "Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents" upright=1.6, Two power MOSFETs in V_in_the_''off''_state,_and_can_conduct_a_continuous_current_of_30 surface-mount_packages._Operating_as_switches,_each_of_these_components_can_su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronics, electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of Photolithography, photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar process, planar diffusion and p–n junction isolation, junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Defects
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
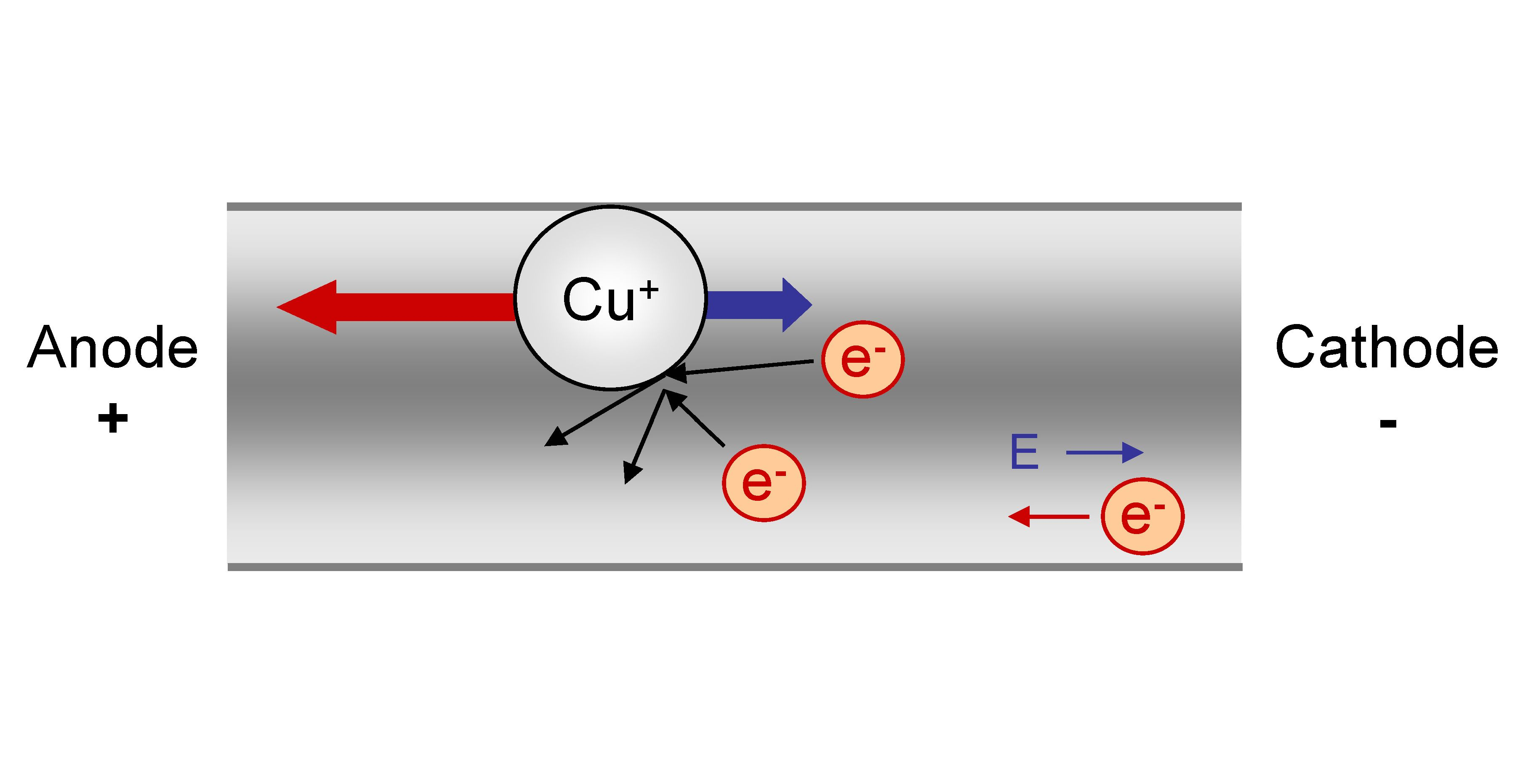
Electromigration
Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in microelectronics and related structures. As the structure size in electronics such as integrated circuits (ICs) decreases, the practical significance of this effect increases. History The phenomenon of electromigration has been known for over 100 years, having been discovered by the French scientist Gerardin. The topic first became of practical interest during the late 1960s when packaged ICs first appeared. The earliest commercially available ICs failed in a mere three weeks of use from runaway electromigration, which led to a major industry effort to correct this problem. The first observation of electromigration in thin films was made by I. Blech.I. Blech: ''Electromigration in Thin Aluminum Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Carrier Injection
Hot carrier injection (HCI) is a phenomenon in solid-state electronic devices where an electron or a “hole” gains sufficient kinetic energy to overcome a potential barrier necessary to break an interface state. The term "hot" refers to the effective temperature used to model carrier density, not to the overall temperature of the device. Since the charge carriers can become trapped in the gate dielectric of a MOS transistor, the switching characteristics of the transistor can be permanently changed. Hot-carrier injection is one of the mechanisms that adversely affects the reliability of semiconductors of solid-state devices. Physics The term “hot carrier injection” usually refers to the effect in MOSFETs, where a carrier is injected from the conducting channel in the silicon substrate to the gate dielectric, which usually is made of silicon dioxide (SiO2). To become “hot” and enter the conduction band of SiO2, an electron must gain a kinetic energy of ~3.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, though it was not identified until 1923, by Dirk Coster and George de Hevesy, making it the penultimate stable element to be discovered (the last being rhenium in 1925). Hafnium is named after , the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Hafnium is used in filaments and electrodes. Some semiconductor fabrication processes use its oxide for integrated circuits at 45 nanometers and smaller feature lengths. Some superalloys used for special applications contain hafnium in combination with niobium, titanium, or tungsten. Hafnium's large neutron capture cross section makes it a good material for neutron absorption in control rods in nuclear power plants, but at the same time requires that it be removed from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Oxide
The gate oxide is the dielectric layer that separates the gate terminal of a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) from the underlying source and drain terminals as well as the conductive channel that connects source and drain when the transistor is turned on. Gate oxide is formed by thermal oxidation of the silicon of the channel to form a thin (5 - 200 nm) insulating layer of silicon dioxide. The insulating silicon dioxide layer is formed through a process of self-limiting oxidation, which is described by the Deal–Grove model. A conductive gate material is subsequently deposited over the gate oxide to form the transistor. The gate oxide serves as the dielectric layer so that the gate can sustain as high as 1 to 5 MV/cm transverse electric field in order to strongly modulate the conductance of the channel. Above the gate oxide is a thin electrode layer made of a conductor which can be aluminium, a highly doped silicon, a refractory metal such as tungste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor Aging
Transistor aging (sometimes called silicon aging) is the process of silicon transistors developing flaws over time as they are used, degrading performance and reliability, and eventually failing altogether. Despite the name, similar mechanisms may affect transistors made of any kind of semiconductor. Manufacturers compensate for this (as well as manufacturing defects) by running chips at slower speeds than they are initially capable of. Causes The main causes of transistor aging in MOSFETs are ''electromigration'' and ''charge trapping''. Electromigration is the movement of ions caused by momentum from the transfer of electrons in the conductor. This results in degradation of the material, causing intermittent glitches that are very difficult to diagnose, and eventual failure. Charge trapping is related to time-dependent gate oxide breakdown, and manifests as an increase in resistance and threshold voltage (the voltage needed for the transistor to conduct), and a decrease in dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle which is the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or crystal lattice the negative charge of the electrons is balanced by the positive charge of the atomic nuclei, the absence of an electron leaves a net positive charge at the hole's location. Holes in a metal or semiconductor crystal lattice can move through the lattice as electrons can, and act similarly to positively-charged particles. They play an important role in the operation of semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits. If an electron is excited into a higher state it leaves a hole in its old state. This meaning is used in Auger electron spectroscopy (and other x-ray techniques), in computational chemistry, and to explain the low electron-electron scattering-rate in crystals (metals, semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |