|
NBS1
Nibrin, also known as NBN or NBS1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NBN'' gene. Function Nibrin is a protein associated with the repair of double strand breaks (DSBs) which pose serious damage to a genome. It is a 754 amino acid protein identified as a member of the NBS1/hMre11/RAD50(N/M/R, more commonly referred to as MRN) double strand DNA break repair complex. This complex recognizes DNA damage and rapidly relocates to DSB sites and forms nuclear foci. It also has a role in regulation of N/M/R (MRN) protein complex activity which includes end-processing of both physiological and mutagenic DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). Cellular response to DSBs Cellular response is performed by damage sensors, effectors of lesion repair and signal transduction. The central role is carried out by ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) by activating the DSB signaling cascade, phosphorylating downstream substrates such as histone H2AX and NBS1. NBS1 relocates to DSB sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
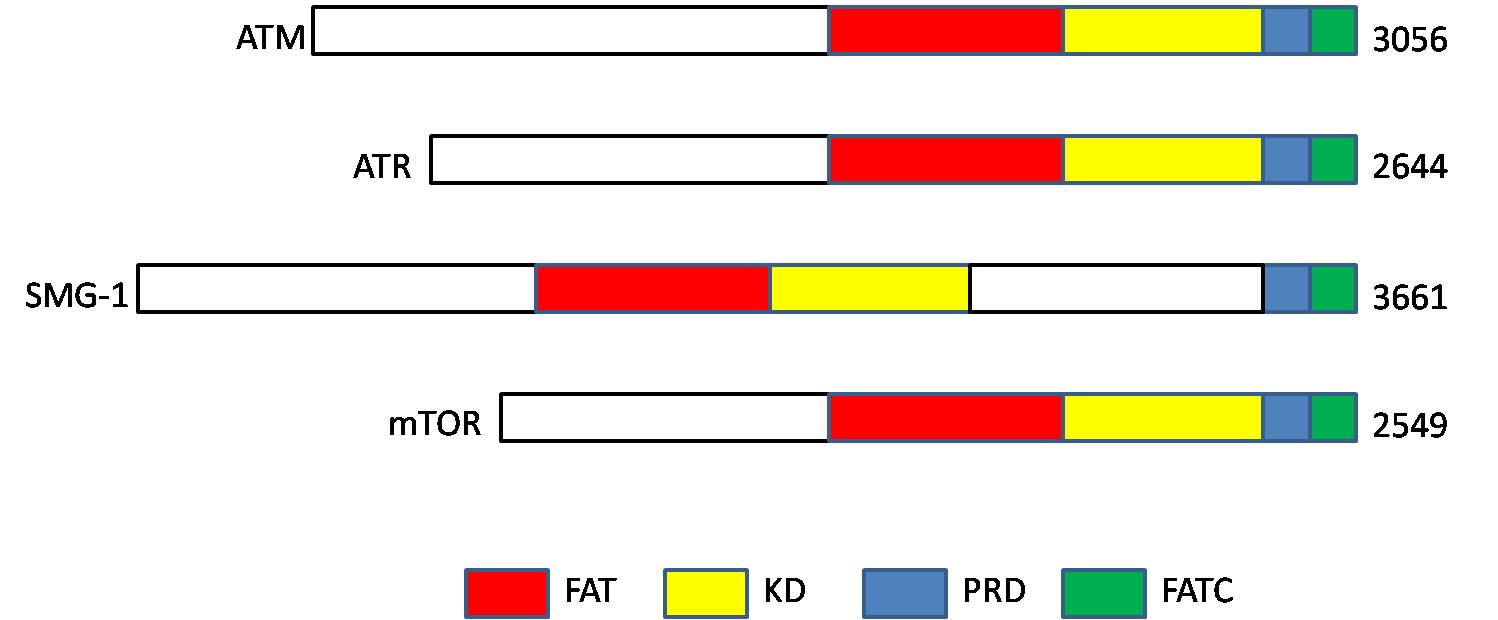
Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated
ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors. In 1995, the gene was discovered by Yosef Shiloh who named its product ATM since he found that its mutations are responsible for the disorder ataxia–telangiectasia#Cause, ataxia–telangiectasia. In 1998, the Shiloh and Michael B. Kastan, Kastan laboratories independently showed that ATM is a protein kinase whose activity is enhanced by DNA damage. Introduction Throughout the cell cycle DNA is monitored for damage. Damages result from errors during DNA replication, replication, by-products of metabolism, general toxic drugs or ionizing radiation. The cell cycle has diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1
The MRN complex (MRX complex in yeast) is a protein complex consisting of Mre11, Rad50 and Nbs1 (also known as Nibrin in humans and as Xrs2 in yeast). In eukaryotes, the MRN/X complex plays an important role in the initial processing of double-strand DNA breaks prior to repair by homologous recombination or non-homologous end joining. The MRN complex binds avidly to double-strand breaks both in vitro and in vivo and may serve to tether broken ends prior to repair by non-homologous end joining or to initiate DNA end resection prior to repair by homologous recombination. The MRN complex also participates in activating the checkpoint kinase ATM in response to DNA damage. Production of short single-strand oligonucleotides by Mre11 endonuclease activity has been implicated in ATM activation by the MRN complex. Evolutionary ancestry and biologic function The MRN complex has been mainly studied in eukaryotes. However, recent work shows that two of the three protein components of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rad50
DNA repair protein RAD50, also known as RAD50, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAD50'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' Rad50, a protein involved in DNA double-strand break repair. This protein forms a complex with MRE11 and NBS1 (also known as Xrs2 in yeast). This MRN complex (MRX complex in yeast) binds to broken DNA ends and displays numerous enzymatic activities that are required for double-strand break repair by nonhomologous end-joining or homologous recombination. Gene knockout studies of the mouse homolog of Rad50 suggest it is essential for cell growth and viability. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of Rad50, which encode distinct proteins, have been reported. Structure Rad50 is a member of the structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) family of proteins. Like other SMC proteins, Rad50 contains a long internal coiled-coil domain that folds back on itself, bringing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H2AX
H2A histone family member X (usually abbreviated as H2AX) is a type of histone protein from the H2A family encoded by the ''H2AFX'' gene. An important phosphorylated form is γH2AX (S139), which forms when double-strand breaks appear. In humans and other eukaryotes, the DNA is wrapped around histone octamers, consisting of core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4, to form chromatin. H2AX contributes to nucleosome-formation, chromatin-remodeling and DNA repair, and is also used ''in vitro'' as an assay for double-strand breaks in dsDNA. Formation of γH2AX H2AX becomes phosphorylated on serine 139, then called γH2AX, as a reaction on DNA double-strand breaks (DSB). The kinases of the PI3-family (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated, ATR and DNA-PKcs) are responsible for this phosphorylation, especially ATM. The modification can happen accidentally during replication fork collapse or in the response to ionizing radiation but also during controlled physiological processes such as V(D)J re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRE11A
Double-strand break repair protein MRE11 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MRE11'' gene. The gene has been designated ''MRE11A'' to distinguish it from the pseudogene ''MRE11B'' that is nowadays named ''MRE11P1''. Function This gene encodes a nuclear protein involved in homologous recombination, telomere length maintenance, and DNA double-strand break repair. By itself, the protein has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity and endonuclease activity. The protein forms a complex with the RAD50 homolog; this complex is required for nonhomologous joining of DNA ends and possesses increased single-stranded DNA endonuclease and 3' to 5' exonuclease activities. In conjunction with a DNA ligase, this protein promotes the joining of noncomplementary ends in vitro using short homologies near the ends of the DNA fragments. This gene has a pseudogene on chromosome 3. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Orthologs Mre11, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Syndrome
A cancer syndrome, or family cancer syndrome, is a genetic disorder in which inherited genetic mutations in one or more genes predispose the affected individuals to the development of cancers and may also cause the early onset of these cancers. Cancer syndromes often show not only a high lifetime risk of developing cancer, but also the development of multiple independent primary tumors. Many of these syndromes are caused by mutations in tumor suppressor genes, genes that are involved in protecting the cell from turning cancerous. Other genes that may be affected are DNA repair genes, oncogenes and genes involved in the production of blood vessels (angiogenesis). Common examples of inherited cancer syndromes are hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer (Lynch syndrome). Background Hereditary cancer syndromes underlie 5 to 10% of all cancers and there are over 50 identifiable hereditary forms of cancer. Scientific understanding of cancer su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses. Horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microhomology-mediated End Joining
Microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), also known as alternative nonhomologous end-joining (Alt-NHEJ) is one of the pathways for repairing double-strand breaks in DNA. As reviewed by McVey and Lee, the foremost distinguishing property of MMEJ is the use of microhomologous sequences during the alignment of broken ends before joining, thereby resulting in deletions flanking the original break. MMEJ is frequently associated with chromosome abnormalities such as deletions, translocations, inversions and other complex rearrangements. There are multiple pathways for repairing double strand breaks, mainly non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), homologous recombination (HR), and MMEJ. NHEJ directly joins both ends of the double strand break and is relatively accurate, although small (usually less than a few nucleotides) insertions or deletions sometimes occur. HR is highly accurate and uses the sister chromatid as a template for accurate repair of the DSB. MMEJ is distinguished from these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome Instability
Chromosomal instability (CIN) is a type of genomic instability in which chromosomes are unstable, such that either whole chromosomes or parts of chromosomes are duplicated or deleted. More specifically, CIN refers to the increase in rate of addition or loss of entire chromosomes or sections of them. The unequal distribution of DNA to daughter cells upon mitosis results in a failure to maintain euploidy (the correct number of chromosomes) leading to aneuploidy (incorrect number of chromosomes). In other words, the daughter cells do not have the same number of chromosomes as the cell they originated from. Chromosomal instability is the most common form of genetic instability and cause of aneuploidy. These changes have been studied in solid tumors (a tumor that usually doesn't contain liquid, pus, or air, compared to liquid tumor), which may or may not be cancerous. CIN is a common occurrence in solid and haematological cancers, especially colorectal cancer. Although many tumours sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity. In humans, infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner.Chowdhury SH, Cozma AI, Chowdhury JH. Infertility. Essentials for the Canadian Medical Licensing Exam: Review and Prep for MCCQE Part I. 2nd edition. Wolters Kluwer. Hong Kong. 2017. There are many causes of infertility, including some that medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryogenesis, embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cellular differentiation, cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |