|
Naval Base Trinidad
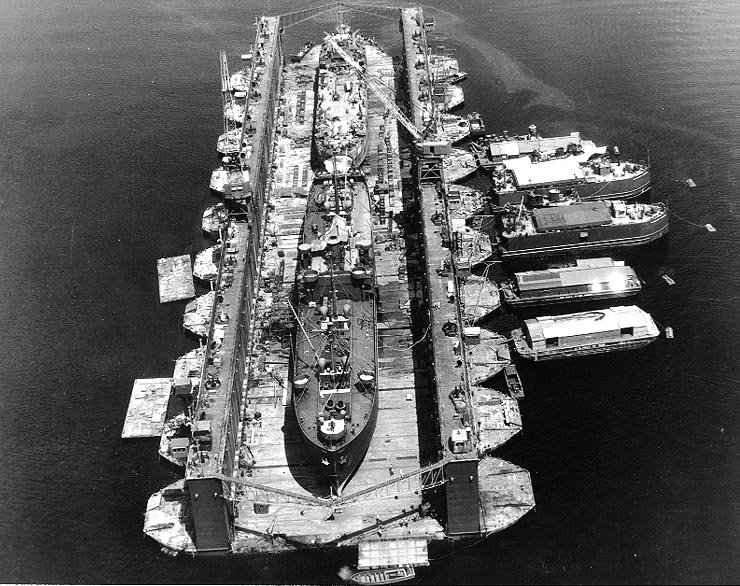
Naval Base Trinidad, also called NAS Trinidad, NAS Port-of-Spain, was a large United States Navy Naval base built during World War II to support the many naval ships fighting and patrolling the Battle of the Atlantic. The fighting in the area became known as the Battle of the Caribbean. Naval Base Trinidad was located on the Island of Trinidad in West Indies of the Caribbean Sea. The base also supported the United States Army Air Forces, United States Coast Guard, US Marine Corps and US Army. Naval Base Trinidad was a US Naval Advance Base built to protect the shipping lanes to and from the Panama Canal from U-boats attacks, by sea and air. The base did fueling, loading and unloading of cargo ships. The base also became a repair depot, with auxiliary floating drydocks that were able to repair boats and ships in the field. Naval Base Trinidad was commissioned on June 1, 1941, and at its peak it had 135,000 troops on the island. History After Adolf Hitler’s declaration of war ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African American Seabees Of The 80th CB Erecting An Airship Hangar At Carlsen Field Trinidad
African or Africans may refer to: * Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa: ** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa *** Ethnic groups of Africa *** Demographics of Africa *** African diaspora ** African, an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the African Union ** Citizenship of the African Union ** Demographics of the African Union **Africanfuturism ** African art ** *** African jazz (other) ** African cuisine ** African culture ** African languages ** African music ** African Union ** African lion, a lion population in Africa Books and radio * ''The African'' (essay), a story by French author J. M. G. Le Clézio * ''The African'' (Conton novel), a novel by William Farquhar Conton * ''The African'' (Courlander novel), a novel by Harold Courlander * ''The Africans'' (radio program) Music * "African", a song by Peter Tosh f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Floating Drydock
An auxiliary floating drydock is a type of US Navy floating dry dock. Floating dry docks are able to submerge underwater and to be placed under a ship in need of repair below the water line. Water is then pumped out of the floating dry dock, raising the ship out of the water. The ship becomes blocked on the deck of the floating dry dock for repair. Most floating dry docks have no engine and are towed by tugboats to their destinations. Floating dry docks come in different sizes to accommodate varying ship sizes, while large floating dry docks come in sections and can be combined to increase their size and lift power. Ballast pontoon tanks are flooded with water to submerge or pumped dry to raise the ship. World War II At the start of World War II, the US Navy had only three steel auxiliary floating dry docks: To reduce travel time for repair work, over 150 auxiliary floating dry docks of different sizes were built during World War II between 1942 and 1945. These newly built f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaplane Base
A seaplane base is a type of airport that is located in a body of water, usually a river, bay, harbor, or lake, where seaplanes and amphibious aircraft take-off and land. History Initially following the invention of the seaplane, traditional boat docks were typically used as there was little need for purpose-built facilities. This would later change, however, as commercial seaplane operations proved financially viable, leading many companies, most notably Pan American Airways, to push for the construction of seaplane bases that were optimized for such use. These new seaplane bases often featured terminal buildings for passengers and cargo, concrete ramps for amphibious aircraft, and floating docks that connected to land. Seaplane bases would end up becoming very heavily utilized for commercial air traffic for a number of years, but they eventually fell out of favor as land based aircraft rose in prominence. Advances in aircraft technology following World War II resulted in the deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaguaramas, Trinidad And Tobago
Chaguaramas (pronounced, in the local English dialect, "shag-gah-rah-muss") lies in the Northwest Peninsula of Trinidad west of Port of Spain; the name is often applied to the entire peninsula, but is sometimes used to refer to its most developed area. The developed area in Chaguaramas starts at ALCOA and ends at the Army and Coast Guard camps on the mainland. In the description or context of "developed area" one excludes the five islands which are in various stages of development or redevelopment as of 2016. Most of the roadway in Chaguaramas lies close to the coastline and one can view the sea from the winding road. Chaguaramas is about 14 km from Port of Spain. Leasing of Chaguaramas to the United States The entire peninsula was leased to the United States in 1940 for the construction of a naval base, Naval Base Trinidad, under the ''Destroyers for Bases Agreement''. The base was also used during the early 1960s as a BMEWS early warning radar site, as well as a missile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carenage
Carenage is a town in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located in northwestern Trinidad, and is administered by the Diego Martin Regional Corporation. Located close to Chaguaramas, it is more of a residential area than a commercial or industrial locale. The name is derived from the practice of careening Careening (also known as "heaving down") is a method of gaining access to the hull of a sailing vessel without the use of a dry dock. It is used for cleaning or repairing the hull. Before ship's hulls were protected from marine growth by fasteni ... (i.e., beaching, "carénage" in French) sailing vessels for maintenance, which had been done in the area for many years. References External links Local Government Corporations from Nalis, the National Library and Information Service of Trinidad and Tobago. Populated places in Trinidad and Tobago {{trinidad-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
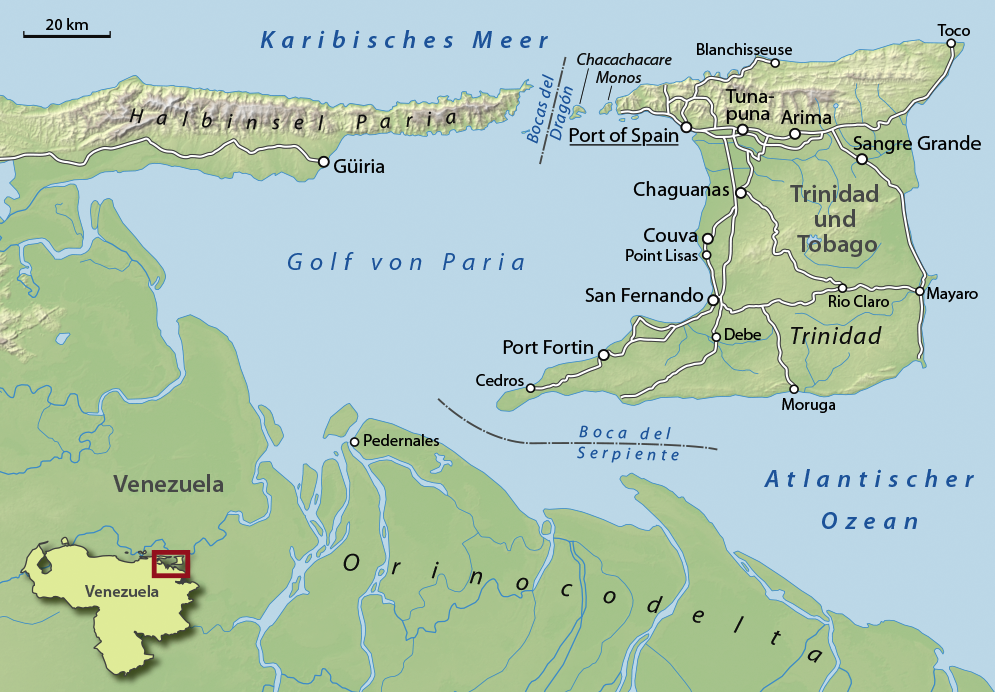
Gulf Of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries by as little as 15 km at its narrowest and 120 km at its widest points. The tides within the Gulf are semi-diurnal in nature with a range of approximately 1m. The Gulf of Paria is considered to be one of the best natural harbors on the Atlantic coast of the Americas. The jurisdiction of the Gulf of Paria is split between Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela with Trinidad and Tobago having control over approximately (37.7%) and Venezuela the remainder (62.3%). It was originally named the Gulf of the Whale ( es, Golfo de la Ballena) by Christopher Columbus, but the 19th-century whaling industry eliminated whales from the area and populations have never recovered. Cartographic sources of the late 18th century repeatedly refer to it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyers-for-bases Deal
The destroyers-for-bases deal was an agreement between the United States and the United Kingdom on September 2, 1940, according to which 50 , , and US Navy destroyers were transferred to the Royal Navy from the US Navy in exchange for land rights on British possessions. Generally referred to as the "twelve hundred-ton type" (also known as "flush-deck", or "four-pipers" after their four funnels), the destroyers became the British and were named after towns common to both countries. US President Franklin Roosevelt used an executive agreement, which does not require congressional approval. However, he came under heavy attack from antiwar Americans, who pointed out that the agreement violated the Neutrality Acts. Background By late June 1940, France had surrendered to Germany and Italy. The British and their Commonwealth and empire stood alone in warfare against Hitler and Mussolini. The British Chiefs of Staff Committee concluded in May that if France collapsed, "we do not thin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana. The first European to encounter Guiana was Sir Walter Raleigh, an English explorer. The Dutch were the first Europeans to settle there, starting in the early 17th century, when they founded the colonies of Essequibo and Berbice, adding Demerara in the mid-18th century. In 1796, Great Britain took over these three colonies during hostilities with the French, who had occupied the Netherlands. Britain returned control to the Batavian Republic in 1802 but captured the colonies a year later during the Napoleonic Wars. The colonies were officially ceded to the United Kingdom in 1815 and consolidated into a single colony in 1831. The colony's capital was at Georgetown (known as Stabroek prior to 1812). The economy has become more diversified since the late 19th century but has relied on r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabees
United States Naval Construction Battalions, better known as the Navy Seabees, form the U.S. Naval Construction Force (NCF). The Seabee nickname is a heterograph of the initial letters "CB" from the words "Construction Battalion". Depending upon context, "Seabee" can refer to all enlisted personnel in the USN's occupational field 7 (OF-7), all personnel in the Naval Construction Force (NCF), or Construction Battalion. Seabees serve both in and outside the NCF. During World War II they were plankowner, plank-holders of both the Naval Combat Demolition Units and the Underwater Demolition Teams (UDTs). The men in the NCF considered these units to be "Seabee". In addition, Seabees served as elements of Cubs, Lions, Acorns and the United States Marine Corps. They also provided the manpower for the top secret CWS Chemical Warfare Service: Flame Tank Group Seabees, Flame Tank Group. Today the Seabees have many special task assignments starting with Camp David and the Naval Support Unit at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |