|
Naratheinga Uzana
Naratheinga Uzana ( my, နရသိင်္ဃ ဥဇနာ, ; also known as Naratheinkha Uzana; 1190s–1235) was the regent of Pagan from c. 1231 to 1235. He was crown prince prior to his regency. He is regarded by some historians G.H. Luce and Than Tun as king between 1231 and 1235 but others Htin Aung and Michael Aung-Thwin Michael Aung-Thwin (1946 – August 14, 2021) was a Burmese American historian and emeritus professor at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, specializing in early Southeast Asian and Burmese history. Early life and education Aung-Thwin wa ... do not accept him as king.Htin Aung 1970: 43Than Tun 1964: 131–132Aung-Thwin and Aung-Thwin 2012: 99 One contemporary stone inscription identifies him as the crown prince, and another identifies him as the king. Neither inscription provides any regnal dates but they were conjecturally dated c. 1230 or c. 1231 by Luce. Luce and Than Tun accept that he was king. It is not universally accepted. Htin Aung d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Burmese Monarchs
This is a list of the monarchs of Burma (Myanmar), covering the monarchs of all the major kingdoms that existed in the present day Burma (Myanmar). Although Burmese chronicles, Burmese chronicle tradition maintains that various monarchies of Burma (Mon people, Mon, Bamar people, Burman, Rakhine people, Arakanese), began in the 9th century Common Era, BCE, historically verified data date back only to 1044 CE at the accession of Anawrahta of Pagan dynasty, Pagan. The farther away the data are from 1044, the less verifiable they are. For example, the founding of the city of Pagan (Bagan) in the 9th century is verifiable–although the accuracy of the actual date, given in the Chronicles as 849, remains in question–but the founding of early Pagan dynasty, given as the 2nd century, is not.Harvey 1925: 364 For early kingdoms, see List of early and legendary monarchs of Burma. The reign dates follow the latest available dates as discussed in each section. Early kingdoms * See List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
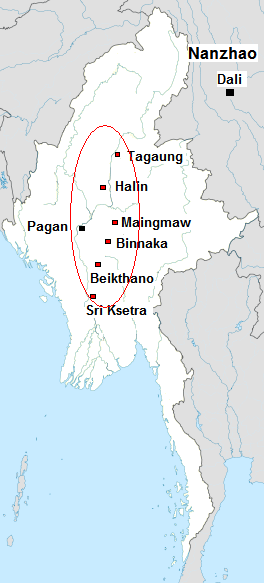
Pagan Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy River, Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and Burmese culture, culture, the spread of Bamar people, Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Bagan, Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Bamar, Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heirs Apparent Who Never Acceded
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officially bequeathing private property and/or debts can be performed by a testator via will, as attested by a notary or by other lawful means. Terminology In law, an ''heir'' is a person who is entitled to receive a share of the deceased's (the person who died) property, subject to the rules of inheritance in the jurisdiction of which the deceased was a citizen or where the deceased (decedent) died or owned property at the time of death. The inheritance may be either under the terms of a will or by intestate laws if the deceased had no will. However, the will must comply with the laws of the jurisdiction at the time it was created or it will be declared invalid (for example, some states do not recognise handwritten wills as valid, or only in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagan Dynasty
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Monarchs
This is a list of the monarchs of Burma (Myanmar), covering the monarchs of all the major kingdoms that existed in the present day Burma (Myanmar). Although Burmese chronicle tradition maintains that various monarchies of Burma ( Mon, Burman, Arakanese), began in the 9th century BCE, historically verified data date back only to 1044 CE at the accession of Anawrahta of Pagan. The farther away the data are from 1044, the less verifiable they are. For example, the founding of the city of Pagan ( Bagan) in the 9th century is verifiable–although the accuracy of the actual date, given in the Chronicles as 849, remains in question–but the founding of early Pagan dynasty, given as the 2nd century, is not.Harvey 1925: 364 For early kingdoms, see List of early and legendary monarchs of Burma. The reign dates follow the latest available dates as discussed in each section. Early kingdoms * See List of early and legendary monarchs of Burma. Pagan (849–1297) Early Pagan (to 1044 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Heirs To The Burmese Thrones
This is a list of the individuals who were, at any given time, considered the next in line to succeed the Burmese monarch to inherit the throne of various History of Burma, Burmese kingdoms (849–1885). Those who actually succeeded at any future time are shown in bold. Pagan Kingdom Pinya Kingdom Sagaing Kingdom Ava Kingdom Hanthawaddy Kingdom, Ramanya Prome Kingdom Toungoo Dynasty The dates after 1582 are according to the Gregorian calendar. Konbaung Dynasty Thibaw Min was deposed and exiled in 1885. He died in exile in India in 1916. He was succeeded as head of the family by his daughter Myat Phaya (1925–1956). From 1956 to 2019, the claimant to the throne was Taw Phaya, the second son of Princess Myat Phaya Galay. References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Heirs To The Burmese Thrones, List Of Lists of Burmese people, Burmese monarchs Lists of Burmese monarchs Heirs to the Burmese throne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Aung-Thwin
Michael Aung-Thwin (1946 – August 14, 2021) was a Burmese American historian and emeritus professor at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, specializing in early Southeast Asian and Burmese history. Early life and education Aung-Thwin was born in Rangoon, Burma (now Yangon, Myanmar) in 1946. Aung-Thwin's mother, Margaret Hope Aung-Thwin, of mixed Anglo-Burmese, Karen, and Arakanese descent, was a Fulbright scholar and lecturer. He attended Kodaikanal International School in South India, where his mother taught. He earned a bachelor of arts degree at Doane College in 1969, followed by a master of arts degree at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in 1971, and a PhD at the University of Michigan. Academic career Aung-Thwin held academic posts at Elmira College, Kyoto University, Northern Illinois University Northern Illinois University (NIU) is a public research university in DeKalb, Illinois. It was founded as Northern Illinois State Normal School on May 22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Htin Aung
Htin Aung ( my, ထင်အောင် ; also Maung Htin Aung; 18 May 1909 – 10 May 1978) was a writer and scholar of Burmese culture and history. Educated at Oxford and Cambridge, Htin Aung wrote several books on Burmese history and culture in both Burmese and English. His English-language works brought a much-needed Burmese perspective to the international study of Burmese history, previously written by British historians of the colonial era. His important works include ''A History of Burma'', ''Folk Elements in Burmese Buddhism'', ''Selections from Burmese Folk Tales'', ''Thirty Burmese Tales'' and '' Burmese Drama''. Htin Aung, as the rector of the University of Rangoon from 1946 to 1958, was the highest ranking academic in the Burmese education system, at the time. He was one of the founding fathers of the Association of Southeast Asian Institutions of Higher Learning (ASAIHL). Early life and education Htin Aung was born to a Burmese aristocratic family on 18 May 1909 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Than Tun
Than Tun ( my, သန်းထွန်း, ; 6 April 1923 – 30 November 2005) was an influential Burma, Burmese historian as well as an outspoken critic of the State Peace and Development Council, military junta of Burma. For his lifelong contributions to the development of worldwide study of Burmese history and culture, Professor Than Tun was awarded the Fukuoka Asian Culture Prize in 2000. Overview A native of Daunggyi village, Ngathaingchaung/Yekyi Township, Irrawaddy Division, Than Tun entered Rangoon University in 1939, and received bachelor's degrees in history and law in 1946 and 1948, respectively and an MA in history in 1950. In 1956, he received his PhD in history with a paper named “Buddhism in Burma: (1000-1300)" from University of London, School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS). Dr. Than Tun became a lecturer in University of Rangoon’s Department of History and Political Science in 1959. In 1965, he was promoted to the Professor and Head of Departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed Theravādins, have preserved their version of Gautama Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhism), Buddha Dhamma'' in the Pāli Canon for over two millennia. The Pāli Canon is the most complete Buddhist canon surviving in a Indo-Aryan languages, classical Indian language, Pali, Pāli, which serves as the school's sacred language and ''lingua franca''.Crosby, Kate (2013), ''Theravada Buddhism: Continuity, Diversity, and Identity'', p. 2. In contrast to ''Mahāyāna'' and ''Vajrayāna'', Theravāda tends to be conservative in matters of doctrine (''pariyatti'') and monastic discipline (''vinaya''). One element of this conservatism is the fact that Theravāda rejects the authenticity of the Mahayana sutras (which appeared c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Htilominlo
Htilominlo ( my, ထီးလိုမင်းလို, ; also called Nadaungmya or Zeya Theinkha Uzana; 1175 – 1235) was king of Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1211 to 1235. His 24-year reign marked the beginning of the gradual decline of Pagan dynasty. It was the first to see the impact of over a century of continuous growth of tax-free religious wealth, which had greatly reduced the potential tax base. Htilominlo was the last of the temple builders although most of his temples were in remote lands not in the Pagan region, reflecting the deteriorating state of royal treasury.Htin Aung 1967: 50–54 All the royal chronicles say he was succeeded by his son Kyaswa. But two contemporary inscriptions indicate that another son of his Naratheinga Uzana was at least acting as the regent towards the end of his reign.Htin Aung 1970: 43Than Tun 1964: 131–132 Early life Htilominlo was born to King Sithu II and his queen Saw Mya Kan. Chronicles do not agree on the birth, dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
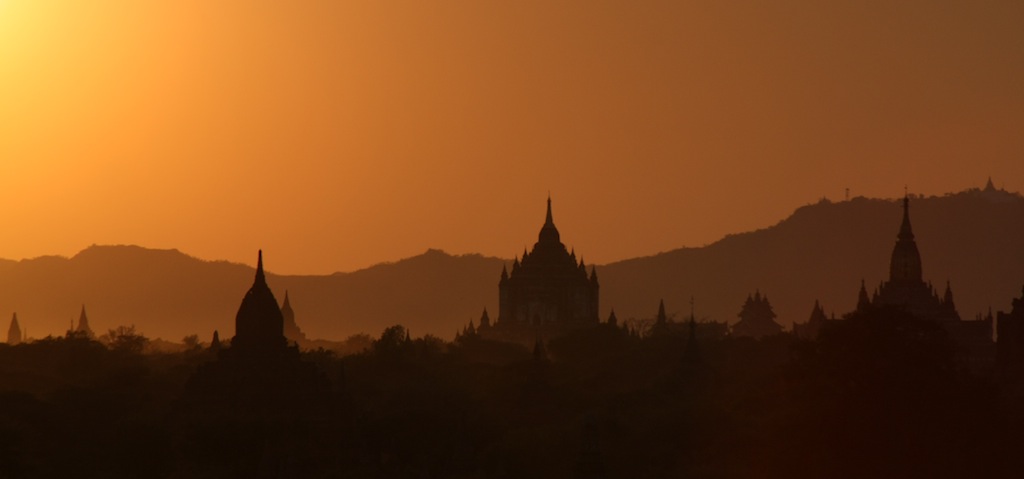
Bagan
Bagan (, ; formerly Pagan) is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Bagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that would later constitute Myanmar. During the kingdom's height between the 11th and 13th centuries, more than 10,000 Buddhist temples, pagodas and monasteries were constructed in the Bagan plains alone, of which the remains of over 2200 temples and pagodas survive. The Bagan Archaeological Zone is a main attraction for the country's nascent tourism industry. Etymology Bagan is the present-day standard Burmese pronunciation of the Burmese word ''Pugan'' ( my-Mymr, ပုဂံ), derived from Old Burmese ''Pukam'' ( my-Mymr, ပုကမ်). Its classical Pali name is ''Arimaddanapura'' ( my-Mymr, အရိမဒ္ဒနာပူရ, lit. "the City that Tramples on Enemies"). Its other names in Pali are in reference to its extreme dry zone cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |