|
Nankai Trough
The is a submarine trough located south of the Nankaidō region of Japan's island of Honshu, extending approximately offshore. The underlying fault, the ''Nankai megathrust,'' is the source of the devastating Nankai megathrust earthquakes, while the trough itself is potentially a major source of hydrocarbon fuel, in the form of methane clathrate. In plate tectonics, the Nankai Trough marks a subduction zone that is caused by subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath Japan, part of the Eurasian plate (Kanda et al., 2004). This plate boundary would be an oceanic trench except for a high flux of sediments that fills the trench. Within the Nankai Trough there is a large amount of deformed trench sediments (Ike, 2004), making one of Earth's best examples of accretionary prism. Furthermore, seismic reflection studies have revealed the presence of basement highs that are interpreted as seamounts that are covered in sediments (Ike, 2004). The northern part of the trough is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nankai Trough Location Map
Nankai () is a family of schools in China founded by Yan Xiu (严范孙) (1860–1920) and Zhang Boling (张伯苓) (1876–1951). The schools include: * Nankai High School in Tianjin (天津南开中学) (1904). * Nankai University in Tianjin (南开大学) (1919). * The Nankai Women's High School (1923), Tianjin Second Nankai High School (天津第二南开中学) (present). * The Nankai Elementary School in Tianjin (天津南开小学) (1928, ruined in WW2). * Nanyu High School (1935), Chongqing Nankai Secondary School (重庆南开中学) (1936). * Chongqing Nankai Elementary School (重庆南开小学) (1937). * Shuguang Middle School in Zigong (自贡蜀光中学) (1937). * Nankai University Affiliated High School (南开大学附中) (1954). Nankai District (南开区, Nán-kāi Qū) in the city of Tianjin Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagami Trough
The also Sagami Trench, Sagami Megathrust, or Sagami Subduction Zone is a long trough, which is the surface expression of the convergent plate boundary where the Philippine Sea Plate is being subducted under the Okhotsk Plate. It stretches from the Boso Triple Junction in the east, where it meets the Japan Trench, to Sagami Bay in the west, where it meets the Nankai Trough. It runs north of the Izu Islands chain and the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc (IBM). Megathrust earthquakes associated with the Sagami Trough, known as Kantō earthquakes, are a major threat to Tokyo and the Kantō Region because of the proximity to a population center (with over 36 million living in Tokyo's metro area, with a total of 43 million living in the Kanto Region) and the magnitude the Sagami Trough can create. Earthquakes The Sagami Trough megathrust generated the 1703 Genroku earthquake, which was the greatest rupture along the trough in the last thousand years, and the 1855 (Ansei) and 1923 (Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismicity
Seismicity is a measure encompassing earthquake occurrences, mechanisms, and magnitude at a given geographical location. As such, it summarizes a region's seismic activity. The term was coined by Beno Gutenberg and Charles Francis Richter in 1941. Seismicity is studied by geophysicists. Calculation of seismicity Seismicity is quantitatively computed. Generally, the region under study is divided in equally sized areas defined by latitude and longitude, and the Earth's interior is divided into various depth intervals on account of Earth's layering: Up to depth, , and > . The usual formula to calculate seismicity is: S = \frac where : _i: is the energy of a single seismic event (i.e., earthquake); : _0: interval of latitude; : _0: interval of longitude : _0: interval of the hypocenter; : _0: interval of the time of the seismic event. : The result is seismicity as energy per cubic unit. See also * Moment magnitude scale * Plate tectonics * Seismology * Wadati–Benioff zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Ocean Drilling Program
The Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) was an international marine research program. The program used heavy drilling equipment mounted aboard ships to monitor and sample sub-seafloor environments. With this research, the IODP documented environmental change, Earth processes and effects, the biosphere, solid earth cycles, and geodynamics. The program began a new 10-year phase with the International Ocean Discovery Program, from the end of 2013. Navigating the route to discovery Scientific ocean drilling represented the longest running and most successful international collaboration among the Earth sciences. Scientific ocean drilling began in 1961 with the first sample of oceanic crust recovered aboard the ''CUSS 1'', a modified U.S. Navy barge. American author John Steinbeck, also an amateur oceanographer, documented Project Mohole for LIFE Magazine. Legacy programs The Deep Sea Drilling Project (DSDP), established in June 1966, operated the ''Glomar Challenger'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Ocean Discovery Program
The International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) is an international marine research collaboration dedicated to advancing scientific understanding of the Earth through drilling, coring, and monitoring the subseafloor. The research enabled by IODP samples and data improves scientific understanding of changing climate and ocean conditions, the origins of ancient life, risks posed by geohazards, and the structure and processes of Earth's tectonic plates and uppermost mantle. IODP began in 2013 and builds on the research of four previous scientific ocean drilling programs: Project Mohole, Deep Sea Drilling Project, Ocean Drilling Program, and Integrated Ocean Drilling Program. Together, these programs represent the longest running and most successful international Earth science collaboration. Scientific scope The scientific scope of IODP is laid out in the program's science plan, ''Illuminating Earth's Past, Present, and Future''. The science plan covers a 10-year period of operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smectite
A smectite (from ancient Greek ''σμηκτός'' smektos 'lubricated'; ''σμηκτρίς'' smektris 'walker's earth', 'fuller's earth'; rubbing earth; earth that has the property of cleaning) is a mineral mixtures of various swelling sheet silicates (phyllosilicates), which have a three-layer 2:1 (TOT) structure and belong to the clay minerals. Smectites mainly consist of montmorillonite, but can often contain secondary minerals such as quartz and calcite. Terminology In clay mineralogy, smectite is synonym of montmorillonite (also the name of a pure clay mineral phase) to indicate a class of swelling clays. The term smectite is commonly used in Europe and in the UK while the term montmorillonite is preferred in North America, but both terms are equivalent and can be used interchangeably. For industrial and commercial applications, the term bentonite is mostly used in place of smectite or montmorillonite. Mineralogical structure The 2:1 layer (TOT) structure consists of tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
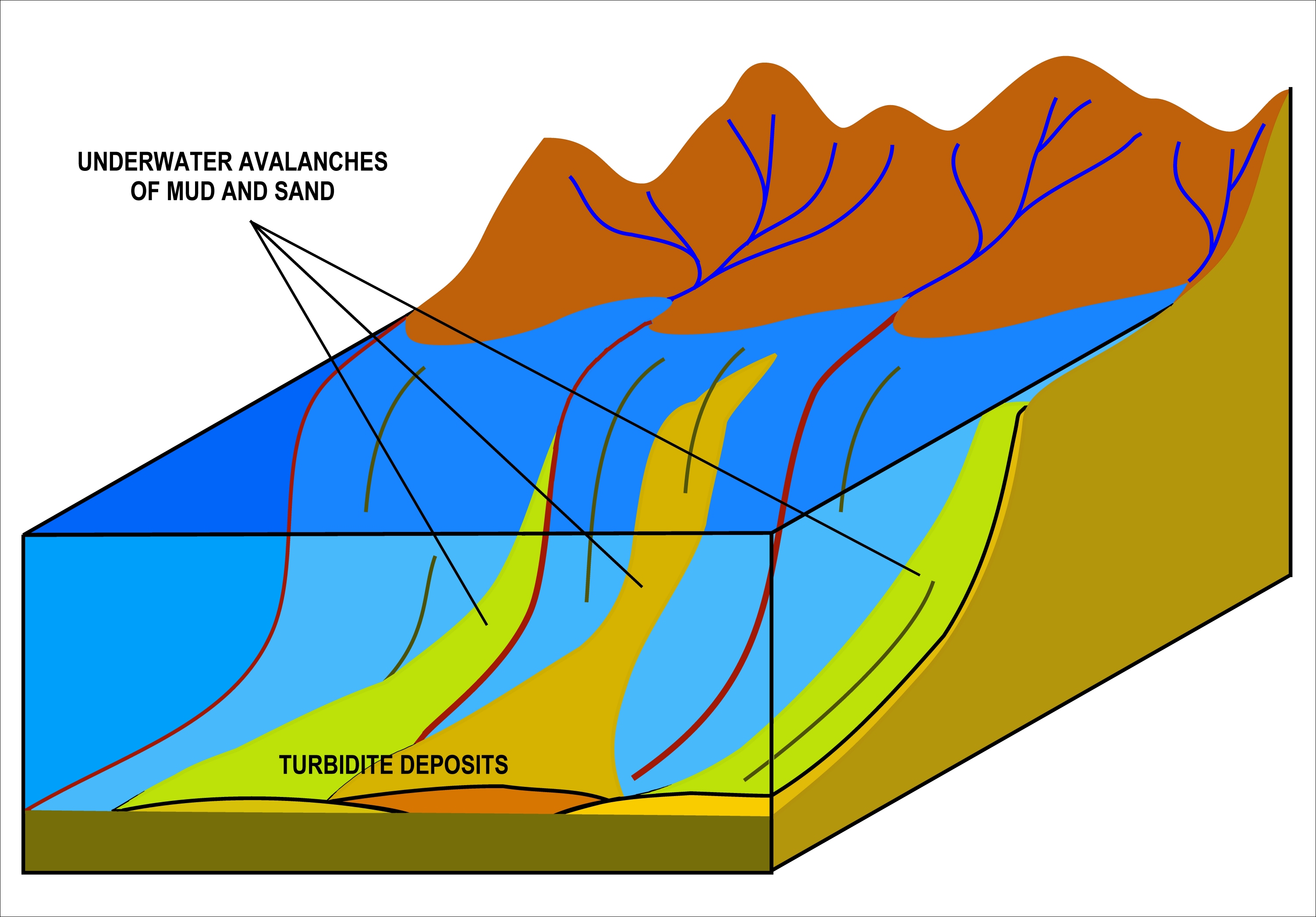
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit). In geology, trenches result from erosion by rivers or by geological movement of tectonic plates. In civil engineering, trenches are often created to install underground utilities such as gas, water, power and communication lines. In construction, trenches are dug for foundations of buildings, retaining walls and dams, and for cut-and-cover construction of tunnels. In archaeology, the "trench method" is used for searching and excavating ancient ruins or to dig into strata of sedimented material. In geotechnical engineering, trenches serve for locating faults and investigating deep soil properties. In trench warfare, soldiers occupy trenches to protect them against weapons fire. Trenches are dug by use of manual tools such as shovels and pickaxes, or by heavy equipment such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia (a landmass consisting of the traditional continents of Europe and Asia), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent and the area east of the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. It also includes oceanic crust extending westward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and northward to the Gakkel Ridge. The eastern edge is a boundary with the North American Plate to the north and a boundary with the Philippine Sea Plate to the south and possibly with the Okhotsk Plate and the Amurian Plate. The southern edge is a boundary with the African Plate to the west, the Arabian Plate in the middle and the Indo-Australian Plate to the east. The western edge is a divergent boundary with the North American Plate forming the northernmost part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is straddled by Iceland. All volcanic eruptions in Iceland, such as the 1973 eruption of Eldfell, the 1783 eruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |