|
Nabedes
Naved, Nabed, Nahbed, or Nabedes (Greek: ''Nabédēs'') was a Sasanian military commander during the reign of Khosrow I. He is first recorded as the commander of Nisibis, engaging the Romans in a battle during Belisarius invasion of Mesopotamia in 541. Procopius quotes Belisarius as describing Nabedes to be the "first among the Persians in glory and in every other sort of honour" after Khosrow I himself. In 543, Nabedes and his outnumbered forces defeated a major Byzantine invasion of Armenia in an ambush at Anglon. During the Lazic War, he performed an invasion in 550, reaching Abasgia Abasgia may refer to: *Region inhabited by ancient Abasgoi tribes *Kingdom of Abkhazia, 778–1008 *Kingdom of Georgia The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, wa ... and taking hostages, including the wife of Opsites of Lazica. References Lazic War 6th-century Iranian people Sasanian Armenia Nusaybin G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Anglon (543)
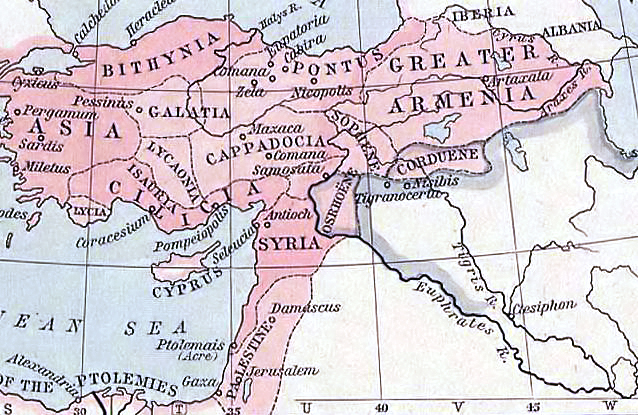
The Battle of Anglon took place in 543 AD, during the Byzantine (East Roman) invasion of Sasanian-ruled Armenia ("Persarmenia"). After receiving the news of a rebellion in Persia and an epidemic in King Khosrow I's army, the Roman armies in the East under the orders of Emperor Justinian I initiated a hasty invasion of Persarmenia. The outnumbered Persian forces in the region performed a meticulous ambush at the mountainous fortress of Anglon, decisively defeating the Roman forces in a siege-like confrontation. Background The Sasanian ruler Khosrow I began an Khosrow I's invasion of Commagene (542), invasion of Commagene in 542, but retreated to Adurbadagan and halted at Adhur Gushnasp, intending to begin a campaign against Byzantine Armenia. The Romans had been negotiating with Khosrow I, until they received information about the epidemic of the so-called Plague of Justinian in Khosrow I's force and a rebellion in Persia by the prince Anoshazad. Seeing this as an opportunity, Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nisibis (541)
The Battle of Nisibis was fought between Byzantine forces under Belisarius and Peter and the Sassanian garrison of the frontier fortress of Nisibis that was under Nabedes. It took place while the Sassanian king Khosrow I was Lazic War, invading the Roman base in Lazica. It was part of a Byzantine offensive led by Belisarius into Persian land. Upon arriving in the area, Belisarius stationed his troops a significant distance away from the fortified city. He hoped to drag the Sasanian garrison into a battle far from the city walls, and after defeating them, capture the undefended city, which seemed impregnable otherwise. The Byzantine commander Peter stationed his forces, together with those of John Troglita who was associated with him, closer to the city. Belisarius warned Peter that since the Byzantines did not normally eat until midday the garrison would sally out then so the Byzantines would have to fight while hungry. Peter ignored this and at midday, his man dispersed to eat. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazic War
The Lazic War, also known as the Colchidian War or in Georgian historiography as the Great War of Egrisi was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire for control of the ancient Georgian region of Lazica. The Lazic War lasted for twenty years, from 541 to 562, with varying success and ended in a victory for the Persians, who obtained an annual tribute in exchange for ending the war. The Lazic War is narrated in detail in the works of Procopius of Caesarea and Agathias. Lazica Lazica, situated on the eastern shore of the Black Sea, and controlling important mountain passes across the Caucasus and to the Caspian Sea, had a key strategic importance for both empires. For Byzantines, it was a barrier against a Persian advance through Iberia to the coasts of the Black Sea. Persians on the other side hoped to gain access to the sea, and control a territory from which Iberia, which was by now under their firm domination, could be threatened. Lazica featured a difficult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the Sasanian dynasty, House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived List of monarchs of Persia, Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
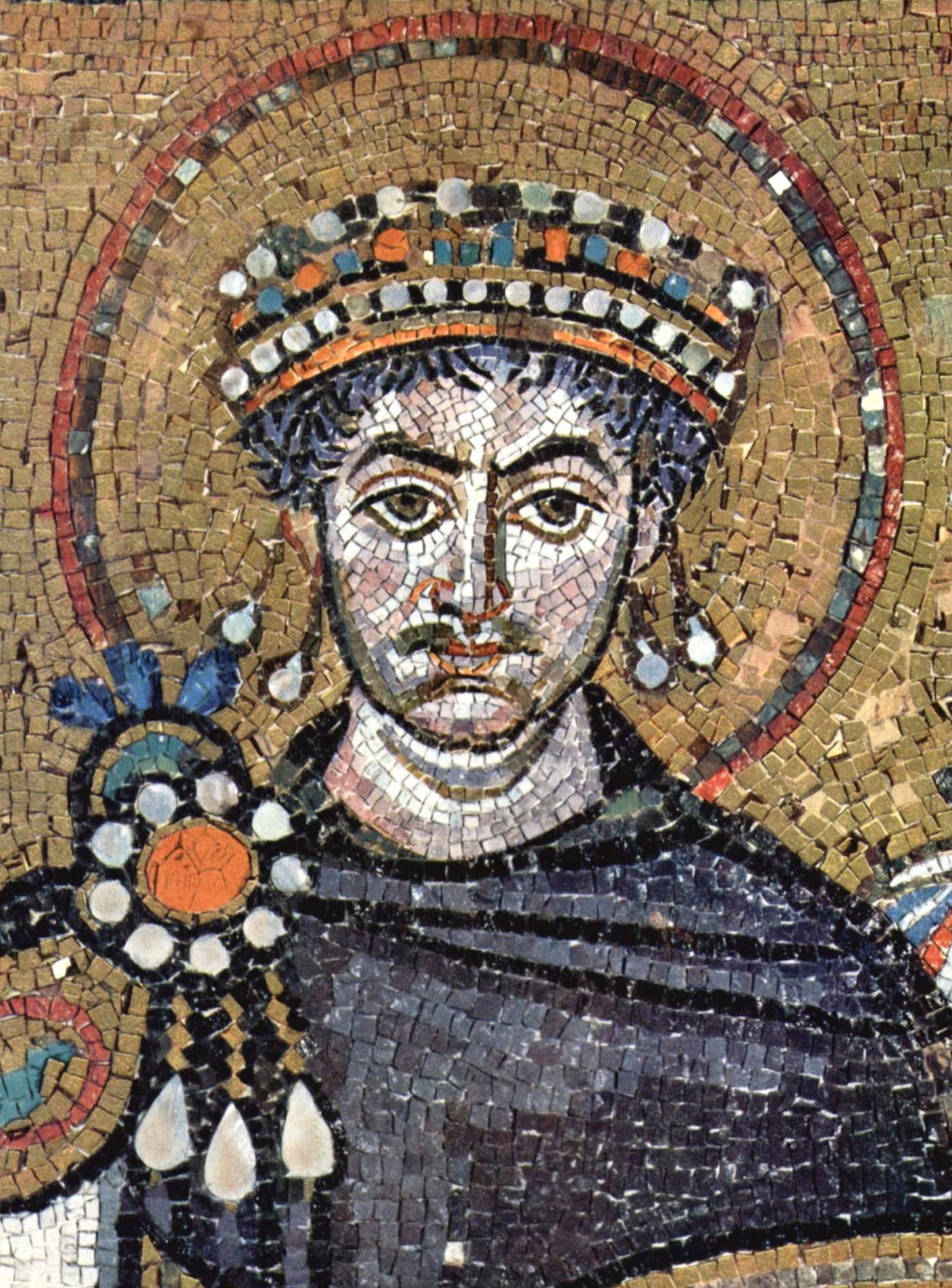
Khosrow I
Khosrow I (also spelled Khosrau, Khusro or Chosroes; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩; New Persian: []), traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan ( [] "the Immortal Soul"), was the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 531 to 579. He was the son and successor of Kavad I (). Inheriting a reinvigorated empire at war with the Byzantines, Khosrow I made a peace treaty with them in 532, known as the Perpetual Peace, in which the Byzantine emperor Justinian I paid 11,000 pounds of gold to the Sasanians. Khosrow then focused on consolidating his power, executing conspirators, including his uncle Bawi. Dissatisfied with the actions of the Byzantine clients and vassals, the Ghassanids, and encouraged by the Ostrogoth envoys from Italy, Khosrow violated the peace treaty and declared war against the Byzantines in 540. He sacked the city of Antioch, bathed in the Mediterranean Sea at Seleucia Pieria, and held chariot races at Apamea where he made the Blue Factio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisibis
Nusaybin (; '; ar, نُصَيْبِيْن, translit=Nuṣaybīn; syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, translit=Nṣībīn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is predominantly Kurdish. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius ( grc, Μυγδόνιος). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac-speaking, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean territory belonging to the former Western Roman Empire, which had been lost less than a century prior. One of the defining features of Belisarius' career was his success despite varying levels of available resources. His name is frequently given as one of the so-called "Last of the Romans". He conquered the Vandal Kingdom of North Africa in the Vandalic War in nine months and conquered much of Italy during the Gothic War. He also defeated the Vandal armies in the battle of Ad Decimum and played an important role at Tricamarum, compelling the Vandal king, Gelimer, to surrender. During the Gothic War, despite being significantly outnumbered, he and his troops recaptured the city of Rome and then held out against great odds during the siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Emperor Justinian's wars, Procopius became the principal Roman historian of the 6th century, writing the ''History of the Wars'', the ''Buildings'', and the ''Secret History''. Life Apart from his own writings the main source for Procopius's life was an entry in the ''Suda'',Suda pi.2479. See under 'Procopius' oSuda On Line a Byzantine Greek encyclopaedia written sometime after 975 which discusses his early life. He was a native of Caesarea in the province of ''Palaestina Prima''. He would have received a conventional upper class education in the Greek classics and rhetoric, perhaps at the famous school at Gaza. He may have attended law school, possibly at Berytus (present-day Beirut) or Constantinople (now Istanbul), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abasgia
Abasgia may refer to: *Region inhabited by ancient Abasgoi tribes *Kingdom of Abkhazia, 778–1008 *Kingdom of Georgia The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ..., 1008 to 1490/91, also referred to as Abasgia Former countries in Europe {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Iranian People
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Armenia
Sasanian Armenia, also known as Persian Armenia and Persarmenia ( hy, Պարսկահայաստան – ''Parskahayastan''), may either refer to the periods in which Armenia ( pal, 𐭠𐭫𐭬𐭭𐭩 – ''Armin'') was under the suzerainty of the Sasanian Empire or specifically to the parts of Armenia under its control such as after the partition of 387 when parts of western Armenia were incorporated into the Eastern Roman Empire while the rest of Armenia came under Sasanian suzerainty but maintained its existing kingdom until 428. In 428, Armenian nobles petitioned Bahram V to depose Artaxias IV (r. 422);''Introduction to Christian Caucasian History:II: States and Dynasties of the Formative Period'', Cyril Toumanoff, Traditio, Vol. 17, 1961, Fordham University, 6. Bahram V (r. 420–438) abolished the Kingdom of Armenia and appointed Veh Mihr Shapur as ''marzban'' (governor of a frontier province, "margrave") of the country, which marked the start of a new era known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)