|
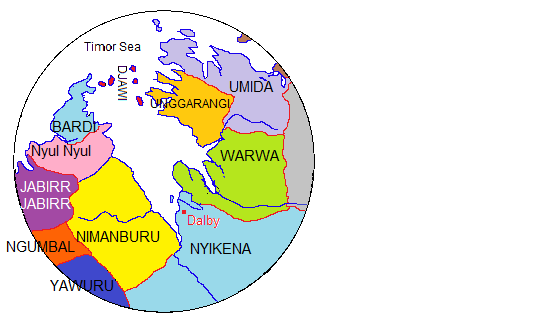
Nyul Nyul People
The Nyulnyul, also spelt Nyul Nyul, Njolnjol, Nyolnyol and other variants, are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Country According to Norman Tindale, the Nyulnyul held sway over some of tribal land. They were located on the western side of the Dampier Peninsula. Historically, the pressure of the Nimanburu led to them ceding ground on the King Sound, and by Tindale's time they were present from Cape Borda to Sandy Point, and at Carlyle Head and Goodenough Bay across the peninsula. Running clockwise, their northern neighbours were the Bardi people, the Nimanburu lay on their southeastern flank, while the Djaberadjabera were directly south on the adjacent coast. Language The Nyulnyul people spoke the Nyulnyul language Nyulnyul is an dormant Australian Aboriginal language, formerly spoken by the Nyulnyul people of Western Australia. Mary Carmel Charles is documented as the last fluent speaker of the Nyulnyul language of West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Lands Of Australian Aboriginal Tribes Around Derby
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years—the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is commonly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose, whether that be political or cultural, over short periods of time. Various academic disciplines also use the word in a variety of ways. The phrase "according to tradition", or "by tradition", usually means that whatever information follows is known only by oral tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Australian
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands. The term Indigenous Australians refers to Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders collectively. It is generally used when both groups are included in the topic being addressed. Torres Strait Islanders are ethnically and culturally distinct, despite extensive cultural exchange with some of the Aboriginal groups. The Torres Strait Islands are mostly part of Queensland but have a separate governmental status. Aboriginal Australians comprise many distinct peoples who have developed across Australia for over 50,000 years. These peoples have a broadly shared, though complex, genetic history, but only in the last 200 years have they been defined and started to self-identify as a single group. Australian Aboriginal identity has cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimberley (Western Australia)
The Kimberley is the northernmost of the nine regions of Western Australia. It is bordered on the west by the Indian Ocean, on the north by the Timor Sea, on the south by the Great Sandy Desert, Great Sandy and Tanami Desert, Tanami deserts in the region of the Pilbara, and on the east by the Northern Territory. The region was named in 1879 by government surveyor Alexander Forrest after Secretary of State for the Colonies John Wodehouse, 1st Earl of Kimberley. History The Kimberley was one of the earliest settled parts of Australia, with the first humans landing about 65,000 years ago. They created a complex culture that developed over thousands of years. Yam (vegetable), Yam (''Dioscorea hastifolia'') agriculture was developed, and rock art suggests that this was where some of the earliest boomerangs were invented. The worship of Wandjina deities was most common in this region, and a complex theology dealing with the transmigration of souls was part of the local people's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a total land area of . It is the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia's Sakha Republic. the state has 2.76 million inhabitants percent of the national total. The vast majority (92 percent) live in the south-west corner; 79 percent of the population lives in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated. The first Europeans to visit Western Australia belonged to the Dutch Dirk Hartog expedition, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first permanent European colony of Western Australia occurred following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Tindale
Norman Barnett Tindale AO (12 October 1900 – 19 November 1993) was an Australian anthropologist, archaeologist, entomologist and ethnologist. Life Tindale was born in Perth, Western Australia in 1900. His family moved to Tokyo and lived there from 1907 to 1915, where his father worked as an accountant at the Salvation Army mission in Japan. Norman attended the American School in Japan, where his closest friend was Gordon Bowles, a Quaker who, like him, later became an anthropologist. The family returned to Perth in August 1917, and soon after moved to Adelaide where Tindale took up a position as a library cadet at the Adelaide Public Library, together with another cadet, the future physicist, Mark Oliphant. In 1919 he began work as an entomologist at the South Australian Museum. From his early years, he had acquired the habit of taking notes on everything he observed, and cross-indexing them before going to sleep, a practice which he continued throughout his life, and which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dampier Peninsula
The Dampier Peninsula is a peninsula located north of Broome and Roebuck Bay in Western Australia. It is surrounded by the Indian Ocean to the west and north, and King Sound to the east. It is named after the mariner and explorer William Dampier who visited it. The northernmost part of the peninsula is Cape Leveque. It is sparsely inhabited, mostly by Indigenous Australian peoples, some of whom have been granted native title rights to some of their traditional lands. There are many coastal inlets, bays and other features, including Beagle Bay on its western side. Aboriginal heritage The peninsula is home to a rich heritage of Aboriginal culture, with the communities of Beagle Bay, Bobieding, Djarindjin, Ardyaloon (One Arm Point) and Ngardalargin, along with numerous other smaller communities, pearling camps, tourist resorts and Aboriginal outstations. The traditional owners of the areas around the peninsula are the Bardi, Nyunyul and Jabirr Jabirr (Djaberadjabera) peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimanburu
The Nimanburu were an Aboriginal Australian people of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Language The Nimanburu language was one of the Nyulnyulan languages. Their speech was described by other aboriginal informants as a 'heavy' dialect of the language spoken by the Warrwa. Country Norman Tindale estimate Nimanburu tribal lands to extend over roughly from the King Sound coast, around Repulse Point southwards to the swamp plain where the Fraser River debouches into the sea. Their inland extension ran as far as the headwaters of that river. People Despite being territorially a coastal people, the Nimanburu refrained from seafaring, and were not known to employ rafts as other contiguous groups in the King Sound did. Alternative names * ''Nimanboro, Nimanbur, Ninambur.'' * ''Wadiabulu.'' (Nyigina exonym An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Sound
King Sound is a large gulf in northern Western Australia. It expands from the mouth of the Fitzroy River, one of Australia's largest watercourses, and opens to the Indian Ocean. It is about long, and averages about in width. The port town of Derby lies near the mouth of the Fitzroy River on the eastern shore of King Sound. King Sound has the highest tides in Australia, and amongst the highest in the world, reaching a maximum tidal range of at Derby.Derby tides at derbytourism.com.au . Retrieved 7 January 2007 The tidal range and water dynamic were researched in 1997–1998. Waters within the sound are generally turbid. The turbidity is associated with the erosion of |
Bardi People
The Bardi people, also spelt Baada or Baardi and other variations, are an Aboriginal Australian people, living north of Broome and inhabiting parts of the Dampier Peninsula in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. They are ethnically close to the Jawi people, and several organisations refer to the Bardi Jawi grouping, such as the Bardi Jawi Niimidiman Aboriginal Corporation Registered Native Title Body (RNTBC) and the Bardi Jawi Rangers. Language The Bardi language is a non-Pama-Nyungan tongue, the most northerly variety of the Nyulnyulan language family. It is mutually intelligible with Jawi. It is the best known Nyulnyulan language, and a detailed grammar of the language exists, written by Claire Bowern. The Pallotine priest and linguist, Father Hermann Nekes, who worked with Ernst Alfred Worms in compiling dictionaries of Baardi and related languages, found his informants to be extremely linguistically astute. In an interview in 1938, a journalist writes of him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djaberadjabera
The Jabirr Jabbirr are an Indigenous Australian people of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Jabirr Jabirr, is also written as Jabirrjabirr and with other spellings such as DjaberrDjaberr, Djaberadjabera, Dyaberdyaber and Jabba Jabba. Their language is the Jabirr Jabirr language. Country The Djaberadjabera held, according to Norman Tindale's estimation, some of tribal land on the western side of the Dampier Peninsula. From the coastal area of Sandy Point at Beagle Bay, their territory went south as far as Cape Bertholet. Their inland extension was about 30 miles. Running clockwise, their neighbours were, to the north, the Nyulnyul, the Warrwa on their eastern flank, the Nimanburu southeast, and the Ngombal to their south. History of contact By 1953 only 5 members of the tribe were still known to survive, and in 1974 Tindale stated that they were virtually extinct. Alternative spellings * ''Djaberadjaber, Djaberdjaber'' * ''Dyaberdyaber'' * ''DjaberrDjaber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyulnyul Language
Nyulnyul is an dormant Australian Aboriginal language, formerly spoken by the Nyulnyul people of Western Australia. Mary Carmel Charles is documented as the last fluent speaker of the Nyulnyul language of Western Australia. Phonology Consonants Nyulnyul has seventeen consonant phonemes, with five distinct places of articulation. yulnyul is a morphologically complex language with both prefixing and suffixing. Vowels Nyulnyul uses a three vowel system, with contrastive length for all vowels. Classification Nyulnyul is very closely related to and was possibly mutually intelligible with Bardi, Jawi, Jabirrjabirr and Nimanburru. These are all members of the Western Nyulnyulan subgroup of Nyulnyulan, a non-Pama-Nyungan family of northern Australia. It is possible that Ngumbarl also belongs to this group, although Bowern makes arguments from the Daisy Bates/ Billingee records that Ngumbarl is an Eastern Nyulnyulan language.Bowern, C. 2010Two Missing Pieces in a Nyulnyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Aboriginal Kinship
Aboriginal Australian kinship comprises the systems of Aboriginal customary law governing social interaction relating to kinship in traditional Aboriginal cultures. It is an integral part of the culture of every Aboriginal group across Australia, and particularly important with regard to marriages between Aboriginal people. The subsection system Subsection systems are a unique social structure that divide all of Australian Aboriginal society into a number of groups, each of which combines particular sets of kin. In Central Australian Aboriginal English vernacular, subsections are widely known as "skins". Each subsection is given a name that can be used to refer to individual members of that group. Skin is passed down by a person's parents to their children. The name of the groups can vary. There are systems with two such groupings (these are known as ' moieties' in kinship studies), systems with four (sections), six and eight (subsection systems). Some language groups exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |