|
Nucleon Spin Structure
Nucleon spin structure describes the partonic structure of nucleon ( proton and neutron) intrinsic angular momentum ( spin). The key question is how the nucleon's spin, whose magnitude is 1/2ħ, is carried by its constituent partons ( quarks and gluons). It was originally expected before the 1980s that quarks carry all of the nucleon spin, but later experiments contradict this expectation. In the late 1980s, the European Muon Collaboration (EMC) conducted experiments that suggested the spin carried by quarks is not sufficient to account for the total spin of the nucleons. This finding astonished particle physicists at that time, and the problem of where the missing spin lies is sometimes referred to as the proton spin crisis. Experimental research on these topics has been continued by the Spin Muon Collaboration (SMC) and the COMPASS experiment at CERN, experiments E142, E143, E154 and E155 at SLAC, HERMES at DESY, experiments at JLab and RHIC, and others. Global analysis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark Spin Yellow
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons. Owing to a phenomenon known as '' color confinement'', quarks are never found in isolation; they can be found only within hadrons, which include baryons (such as protons and neutrons) and mesons, or in quark–gluon plasmas. There is also the theoretical possibility of more exotic phases of quark matter. For this reason, much of what is known about quarks has been drawn from observations of hadrons. Quarks have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, mass, color charge, and spin. They are the only elementary particles in the Standard Model of particle physics to experience all four fundamental interactions, also known as ''fundamental f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COMPASS Experiment
The NA58 experiment, or COMPASS (standing for "Common Muon and Proton Apparatus for Structure and Spectroscopy") is a 60-metre-long fixed-target experiment at the M2 beam line of the SPS at CERN. The experimental hall is located at the CERN North Area, close to the French village of Prévessin-Moëns. The experiment is a two-staged spectrometer with numerous tracking detectors, particle identification and calorimetry. The physics results are extracted by recording and analysing the final states of the scattering processes. The versatile set-up, the use of different targets and particle beams allow the investigation of various processes. The main physics goals are the investigation of the nucleon spin structure and hadron spectroscopy. The collaboration consists of 220 physicists from 13 different countries, involving 28 universities and research institutes. History and physics goals The COMPASS experiment was proposed in 1996 and approved by the CERN research committee. Betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deeply Virtual Compton Scattering
''Deeply'' is a 2000 film directed by Sheri Elwood, starring Julia Brendler, Lynn Redgrave and Kirsten Dunst. Synopsis Claire McKay ( Julia Brendler)—having suffered the death of her boyfriend—is brought by her mother to Ironbound Island in the hopes that time away from the city will allow her to recover emotionally. On the island where her mother was born, Claire meets an eccentric writer, Celia ( Lynn Redgrave), who in flashbacks, relates her own story as a grief-stricken teenager in 1949. Celia—Silly ( Kirsten Dunst) in the flashbacks—is the next chosen victim of a Viking curse which was placed on the island centuries ago when their longship sank in the bay. The nature of the curse is such that a "chosen one" is born every fifty years, and they are destined to die at sea in order for the fish the island depends on to continue to return. During the flashbacks Silly discovers a list of past victims, and that she is the next. However, in the end Silly is not claimed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Parton Distributions
In particle physics, the parton model is a model of hadrons, such as protons and neutrons, proposed by Richard Feynman. It is useful for interpreting the cascades of radiation (a parton shower) produced from quantum chromodynamics (QCD) processes and interactions in high-energy particle collisions. Model Parton showers are simulated extensively in Monte Carlo event generators, in order to calibrate and interpret (and thus understand) processes in collider experiments. As such, the name is also used to refer to algorithms that approximate or simulate the process. Motivation The parton model was proposed by Richard Feynman in 1969 as a way to analyze high-energy hadron collisions. Any hadron (for example, a proton) can be considered as a composition of a number of point-like constituents, termed "partons". The parton model was immediately applied to electron-proton deep inelastic scattering by Bjorken and Paschos. Component particles A hadron is composed of a number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
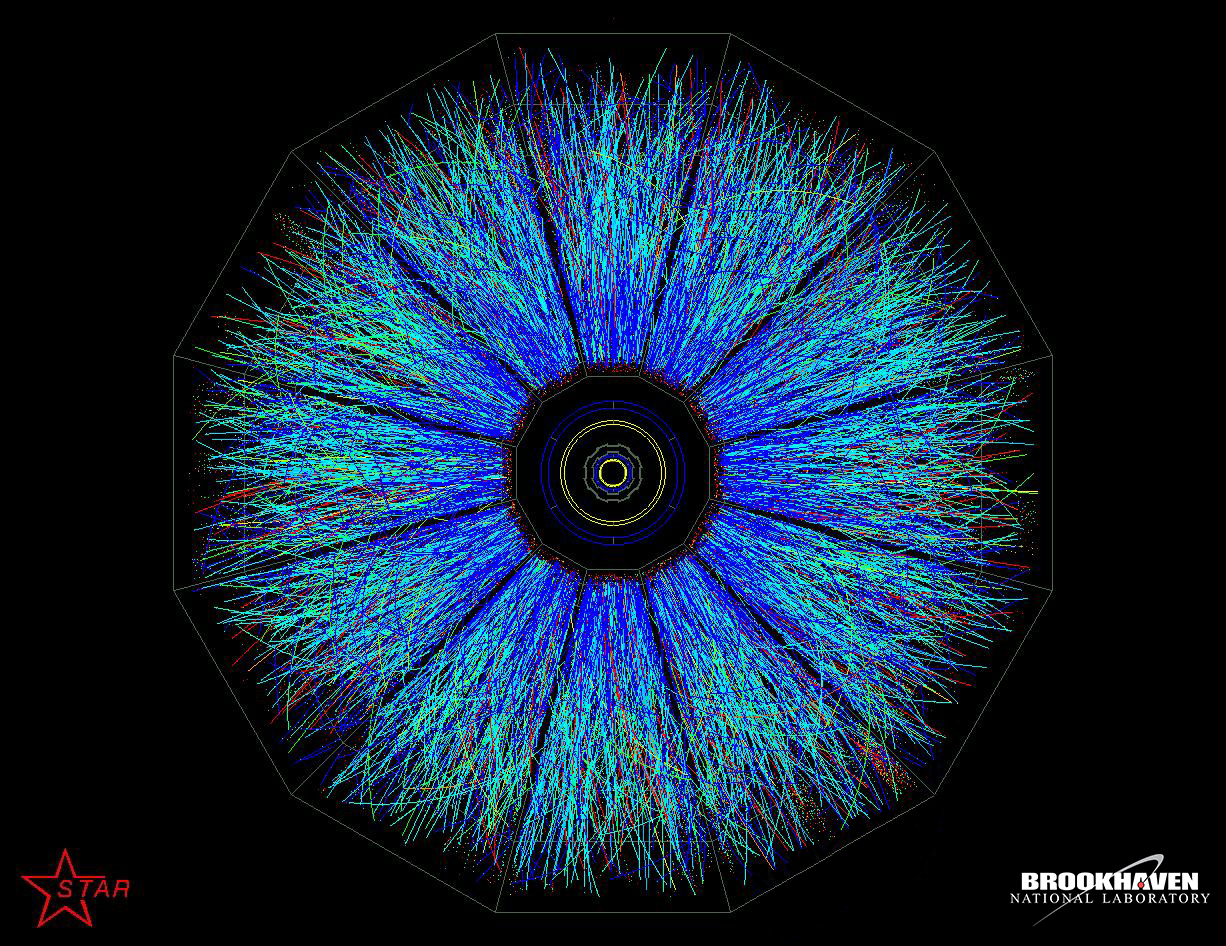
RHIC
The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC ) is the first and one of only two operating heavy- ion colliders, and the only spin-polarized proton collider ever built. Located at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) in Upton, New York, and used by an international team of researchers, it is the only operating particle collider in the US. By using RHIC to collide ions traveling at relativistic speeds, physicists study the primordial form of matter that existed in the universe shortly after the Big Bang. By colliding spin-polarized protons, the spin structure of the proton is explored. RHIC is as of 2019 the second-highest-energy heavy-ion collider in the world. As of November 7, 2010, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has collided heavy ions of lead at higher energies than RHIC. The LHC operating time for ions (lead–lead and lead–proton collisions) is limited to about one month per year. In 2010, RHIC physicists published results of temperature measurements from earlier exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), commonly called Jefferson Lab or JLab, is a US National Laboratory located in Newport News, Virginia. Its stated mission is "to provide forefront scientific facilities, opportunities and leadership essential for discovering the fundamental structure of nuclear matter; to partner in industry to apply its advanced technology; and to serve the nation and its communities through education and public outreach." Since June 1, 2006, it has been operated by Jefferson Science Associates, LLC, a limited liability company created by Southeastern Universities Research Association and PAE Applied Technologies. Until 1996 it was known as the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility (CEBAF); commonly, this name is still used for the main accelerator. Founded in 1984, Jefferson Lab employs more than 750 people, and more than 2,000 scientists from around the world have conducted research using the facility. History The facility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (English ''German Electron Synchrotron''), commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany. It operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter, and conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science, and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen. Functions DESY's function is to conduct fundamental research. It specializes in particle accelerator development, construction and operation, particle physics research to explore the fundamental characteristics of matter and forces, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a United States Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Stanford University under the programmatic direction of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science and located in Menlo Park, California. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 and shut down in the 2000s, that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, the facility is located on of Stanford University-owned land on Sand Hill Road in Menlo Park, Californi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Spin Crisis
The proton spin crisis (sometimes called the "proton spin puzzle") is a theoretical crisis precipitated by a 1987 experiment by the European Muon Collaboration (EMC), which tried to determine the distribution of spin within the proton. Physicists expected that the quarks carry all the protons' spin. However, not only was the total proton spin carried by quarks far smaller than 100%, these results were consistent with almost zero (4~24%) proton spin being carried by quarks. This surprising and puzzling result was termed the "proton spin crisis". The problem is considered one of the important unsolved problems in physics. Background A key question is how the nucleons' spins are distributed amongst their constituent parts ( "partons": quarks and gluons). Components of proton's spin are expectation values of individual sources of angular momentum. These values depend on the renormalization scale, because their operators are not separately conserved. Physicists originally expected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parton (particle Physics)
In particle physics, the parton model is a model of hadrons, such as protons and neutrons, proposed by Richard Feynman. It is useful for interpreting the cascades of radiation (a parton shower) produced from quantum chromodynamics (QCD) processes and interactions in high-energy particle collisions. Model Parton showers are simulated extensively in Monte Carlo event generators, in order to calibrate and interpret (and thus understand) processes in collider experiments. As such, the name is also used to refer to algorithms that approximate or simulate the process. Motivation The parton model was proposed by Richard Feynman in 1969 as a way to analyze high-energy hadron collisions. Any hadron (for example, a proton) can be considered as a composition of a number of point-like constituents, termed "partons". The parton model was immediately applied to electron- proton deep inelastic scattering by Bjorken and Paschos. Component particles A hadron is composed of a number of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Muon Collaboration
The European Muon Collaboration (EMC) was formed in 1973 to study the interactions of high energy muons at CERN. These experiments were motivated by the interest in determining the quark structure of the nucleon following the discovery of high levels of deep inelastic scattering at SLAC. In 1972 two muon beams were proposed for the then new Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) machine. One by Roger Clifft and Erwin Gabathuler and one by Friedhelm Brasse and Joerg Gayler. The two teams came together to design a high intensity muon beam of energy up to 280 GeV to do the experiments. The collaboration, which became known as the European Muon Collaboration (EMC), was formed around these people to carry out the experiments. A proposal for the beam and an apparatus to do the experiments was submitted to CERN in 1974 (the White Book). The experiments were approved and the apparatus was built between the years 1974–78. The collaboration grew in size to about 100 physicists. This was among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |