|
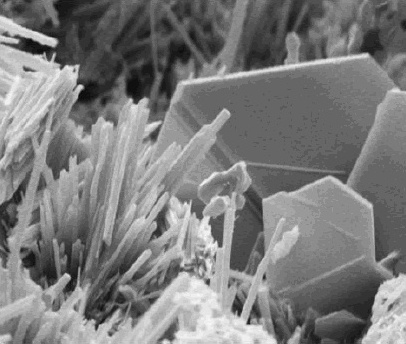
Norwegian Saltpeter
Calcium nitrate, also called ''Norgessalpeter'' (Norwegian salpeter), is an inorganic compound with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhydrous and hydrated forms are colourless salts. Calcium nitrate is mainly used as a component in fertilizers, but it has other applications. Nitrocalcite is the name for a mineral which is a hydrated calcium nitrate that forms as an efflorescence where manure contacts concrete or limestone in a dry environment as in stables or caverns. A variety of related salts are known including calcium ammonium nitrate decahydrate and calcium potassium nitrate decahydrate. Production and reactivity Norgessalpeter was synthesized at Notodden, Norway in 1905 by the Birkeland–Eyde process. Most of the world's calcium nitrate is now made in Porsgrunn. It is produced by treating limestone with nitric acid, followed by neutralization with ammonia: :CaCO3 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caverns
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the Earth#Surface, ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called Caving, ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
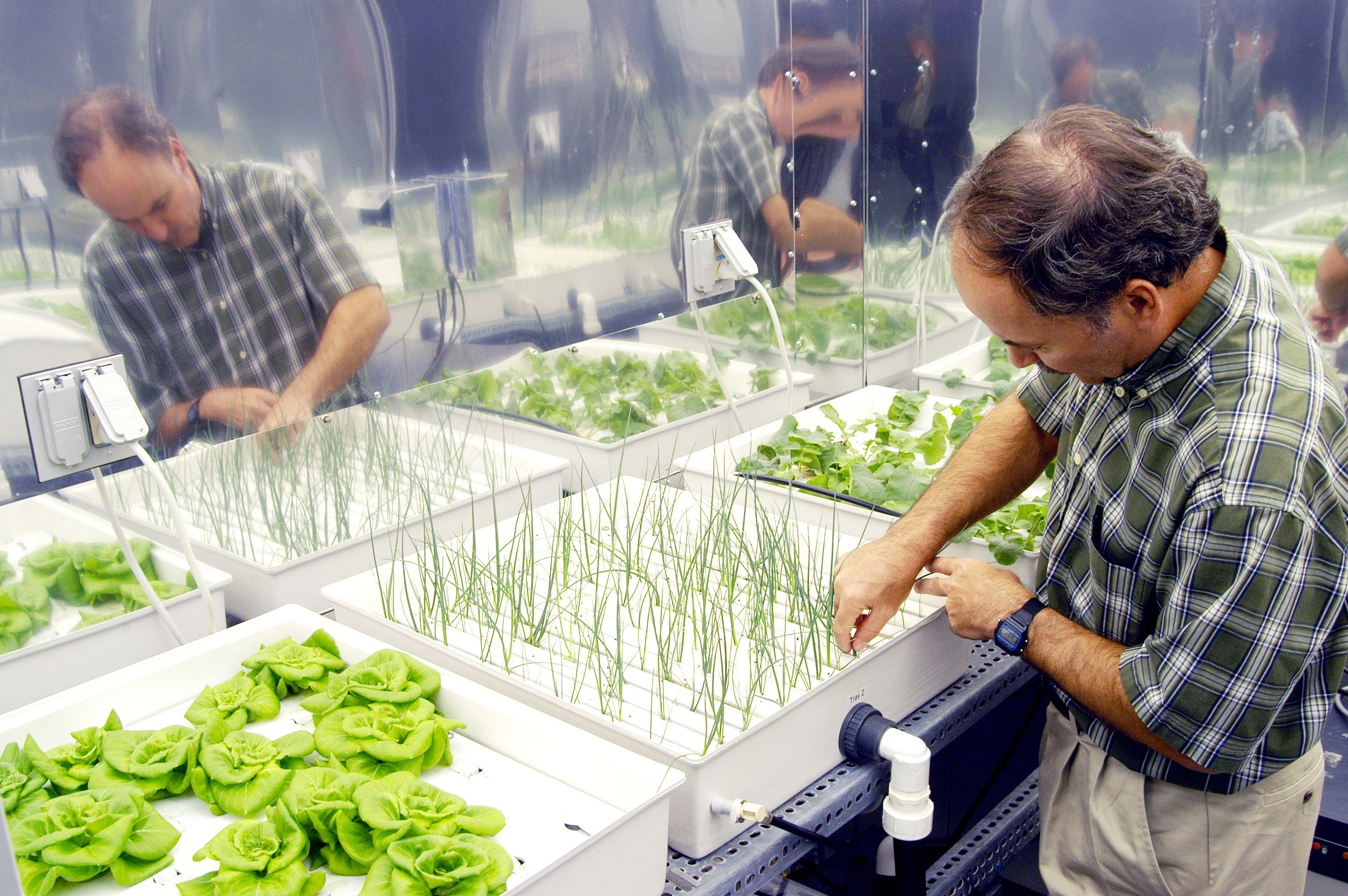
Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water-based mineral nutrient solutions in aqueous solvents. Terrestrial or aquatic plants may grow with their roots exposed to the nutritious liquid or in addition, the roots may be mechanically supported by an inert medium such as perlite, gravel, or other substrates. Despite inert media, roots can cause changes of the rhizosphere pH and root exudates can affect rhizosphere biology and physiological balance of the nutrient solution by secondary metabolites. Transgenic plants grown hydroponically allow the release of pharmaceutical proteins as part of the root exudate into the hydroponic medium. The nutrients used in hydroponic systems can come from many different organic or inorganic sources, including fish excrement, duck manure, purchased chemical fertilizers, or artificial nutrient solutions. Plants are commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These structures range in size from small sheds to industrial-sized buildings. A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frame. The interior of a greenhouse exposed to sunlight becomes significantly warmer than the external temperature, protecting its contents in cold weather. Many commercial glass greenhouses or hothouses are high tech production facilities for vegetables, flowers or fruits. The glass greenhouses are filled with equipment including screening installations, heating, cooling, and lighting, and may be controlled by a computer to optimize conditions for plant growth. Different techniques are then used to manage growing conditions, including air temperature, relative humidity and vapour-pressure deficit, in ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year for use primarily in the production of fertilizers. At higher temperatures it is a reddish-brown gas. It can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Nitrogen dioxide is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. It is included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above , becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below , and converts to the colorless dinitrogen tetroxide () below . The bond length between the nitrogen atom and the oxygen atom is 119.7 pm. This bond length is consistent with a bond order between one and two. Unlike ozone, O3, the ground electronic state of nitrogen dioxide is a doublet state, since nitrogen has one unpaired electron, which decreases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Earth Metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Structurally, they (together with helium) have in common an outer s-orbital which is full; that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2. All the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the decay chain of uranium and thorium and not as a primordial element. There have been experiments, all unsuccessful, to try to synthesize element 120, the next potential member of the group. Characteristics Chemical As with other groups, the members of this family show patterns in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Properties Calcium hydroxide is poorly soluble in water, with a retrograde solubility increasing from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. With a solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following dissolution reaction: : Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2 OH− At ambient temperature, calcium hydroxide (portlandite) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.Karl-Heinz Zapp "Ammonium Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Global production was estimated at 21.6 million tonnes in 2017. Its other major use is as a component of explosive mixtures used in mining, quarrying, and civil construction. It is the major constituent of ANFO, a popular industrial explosive which accounts for 80% of explosives used in North America; similar formulations have been used in improvised explosive devices. Many countries are phasing out its use in consumer applications due to concerns over its potential for misuse. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrophosphate Process
The nitrophosphate process (also known as the Odda process) is a method for the industrial production of nitrogen fertilizers invented by Erling Johnson in the municipality of Odda, Norway around 1927. The process involves acidifying phosphate rock with dilute nitric acid to produce a mixture of phosphoric acid and calcium nitrate. :Ca5(PO4)3OH + 10 HNO3 → 3 H3PO4 + 5 Ca(NO3)2 + H2O The mixture is cooled to below 0 °C, where the calcium nitrate crystallizes and can be separated from the phosphoric acid. :2 H3PO4 + 3 Ca(NO3)2 + 12 H2O → 2 H3PO4 + 3 Ca(NO3)2·4H2O The resulting calcium nitrate produces nitrogen fertilizer. The filtrate is composed mainly of phosphoric acid with some nitric acid and traces of calcium nitrate, and this is neutralized with ammonia to produce a compound fertilizer. :Ca(NO3)2 + 4 H3PO4 + 8 NH3 → CaHPO4 + 2 NH4NO3 + 3(NH4)2HPO4 If potassium chloride or potassium sulfate is added, the result will be NPK fertilizer. The process was an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porsgrunn
is a city and municipality in Telemark in the county of Vestfold og Telemark in Norway. It is part of the traditional region of Grenland. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Porsgrunn. The municipality of Porsgrunn was established on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt). The town of Brevik and the rural district of Eidanger were merged into the municipality of Porsgrunn on 1 January 1964. The conurbation of Porsgrunn and Skien is considered by Statistics Norway to be the seventh-largest city in Norway. General information Name The place is first mentioned in 1576 (''"Porsgrund"'') by the writer Peder Claussøn Friis in his work ''Concerning the Kingdom of Norway'' (see the article: Norwegian literature). He writes: "Two and a half miles from the sea, the Skien river flows into the fjord, and that place is called Porsgrund." The name was probably given during medieval times to the then swampy area by the nuns of Gimsøy Abbey, who went here to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkeland–Eyde Process
The Birkeland–Eyde process was one of the competing industrial processes in the beginning of nitrogen-based fertilizer production. It is a multi-step nitrogen fixation reaction that uses electrical arcs to react atmospheric nitrogen (N2) with oxygen (O2), ultimately producing nitric acid (HNO3) with water. The resultant nitric acid was then used as a source of nitrate (NO3−) in the reaction HNO3 + H2O -> H3O+ + NO3- which may take place in the presence of water or another proton acceptor. It was developed by Norwegian industrialist and scientist Kristian Birkeland along with his business partner Sam Eyde in 1903, based on a method used by Henry Cavendish in 1784. A factory based on the process was built in Rjukan and Notodden in Norway, combined with the building of large hydroelectric power facilities. The Birkeland–Eyde process is relatively inefficient in terms of energy consumption. Therefore, in the 1910s and 1920s, it was gradually replaced in Norway by a combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |