|
Norway House, Manitoba
Norway House is a population centre of over 5,000 people, some north of Lake Winnipeg, on the bank of the eastern channel of Nelson River, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. The population centre shares the name ''Norway House'' with the northern community of Norway House and Norway House 17, a First Nation reserve of the Norway House Cree Nation (Kinosao Sipi Cree Nation). Thus, Norway House has both a Chief and a Mayor. The community is located by air north of Winnipeg, by air east of The Pas, and by air south of Thompson. To drive from Winnipeg, it is approximately ; from Thompson, it is about . Major economic activities include commercial fishing, trapping, logging, and government services. Seasonal unemployment varies, with peaks as high as 70%. Norway House was an important establishment of the Hudson's Bay Company for most of the 19th century, serving as a major depot, and from the 1830s, as the seat of the Council of the Northern Department of Rupert's Land. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the British government to merge. Before the Company After the French landed in Quebec in 1608, spread out and built a fur trade empire in the St. Lawrence basin. The French competed with the Dutch (from 1614) and English (1664) in New York and the English in Hudson Bay (1670). Unlike the French who travelled into the northern interior and traded with First Nations in their camps and villages, the English made bases at trading posts on Hudson Bay, inviting the indigenous people to trade. After 1731, pushed trade west beyond Lake Winnipeg. After the British conquest of New France in 1763 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business division is Hudson's Bay, commonly referred to as The Bay ( in French). After incorporation by English royal charter in 1670, the company functioned as the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America for nearly 200 years until the HBC sold the land it owned (the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land) to Canada in 1869 as part of the Deed of Surrender, authorized by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. At its peak, the company controlled the fur trade throughout much of the English- and later British-controlled North America. By the mid-19th century, the company evolved into a mercantile business selling a wide variety of products from furs to fine homeware in a small number of sales shops (as opposed to trading posts) acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starting with the Neolithic Revolution when animals were first domesticated, from around 13,000 BC onwards, predating farming of the first crops. By the time of early civilisations such as ancient Egypt, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs were being raised on farms. Major changes took place in the Columbian exchange, when Old World livestock were brought to the New World, and then in the British Agricultural Revolution of the 18th century, when livestock breeds like the Dishley Longhorn cattle and Lincoln Longwool sheep were rapidly improved by agriculturalists, such as Robert Bakewell, to yield more meat, milk, and wool. A wide range of other species, such as horse, water buffalo, llama, rabbit, and guinea pig, are used as livestock in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer Herding
Reindeer herding is when reindeer are herded by people in a limited area. Currently, reindeer are the only semi-domesticated animal which naturally belongs to the North. Reindeer herding is conducted in nine countries: Norway, Finland, Sweden, Russia, Greenland, Alaska (the United States), Mongolia, China and Canada. A small herd is also maintained in Scotland. Reindeer herding is conducted by individuals within some kind of cooperation, in forms such as families, districts, Sámi and Yakut villages and sovkhozy (collective farms). A person who conducts reindeer herding is called a reindeer herder and approximately 100,000 people are engaged in reindeer herding today around the circumpolar North. Domestication The domestication of the reindeer does not lend itself to a simple explanation. There is no doubt that when the glaciers retreated at the end of the last Ice Age, people followed reindeer to the North, using traps during the reindeer hunt. Modern archaeological data (rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspecies. A 2022 revision of the genus elevated five of the subspecies to species (see Taxonomy below). They have a circumpolar distribution and are native to the Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal forest, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest species, the Svalbard reindeer (''R. t. platyrhynchus''), to the largest subspecies, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies are in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Playgreen Lake
Playgreen Lake, or Play Green Lake, is a lake in the province of Manitoba in Canada. The lake covers an area of and it is a part of the Nelson River watershed. The lake is the ninth largest lake in the province. It is located along the Nelson River some north from the north end of Lake Winnipeg. It was first mapped by noted British surveyor, map-maker, chief fur trader and explorer Peter Fidler in 1809.Hudson's Bay Company Archives, Archives of Manitoba, Peter Fidler Track Maps, Journals of Exploration and Survey, 1809, E.3/4, folios 4 & 5. Hydrography The Nelson River flows into Playgreen Lake from Lake Winnipeg then flows from two channels into Cross Lake. The east channel and the Jack River flow from the southeast portion of the lake into Little Playgreen Lake then the Nelson east channel continues in a northerly direction passing through Pipestone Lake on its way to Cross Lake. The Echimamish River on this section leads to the Hayes River and York Factory on the Hudson Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegians
Norwegians ( no, nordmenn) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians are descended from the Norse of the Early Middle Ages who formed a unified Kingdom of Norway in the 9th century. During the Viking Age, Norwegians and other Norse peoples conquered, settled and ruled parts of the British Isles, the Faroe Islands, Iceland and Greenland. Norwegians are closely related to other North Germanic peoples and descendants of the Norsemen such as Danes, Swedes, Icelanders and the Faroe Islanders, as well as groups such as the Scots whose nation they significantly settled and left a lasting impact in. The Norwegian language is part of the larger Scandinavian dialect continuum of generally mutually intelligible languages in Scandinavia. Norwegian people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl Of Selkirk
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Indiana * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel) 1969 novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
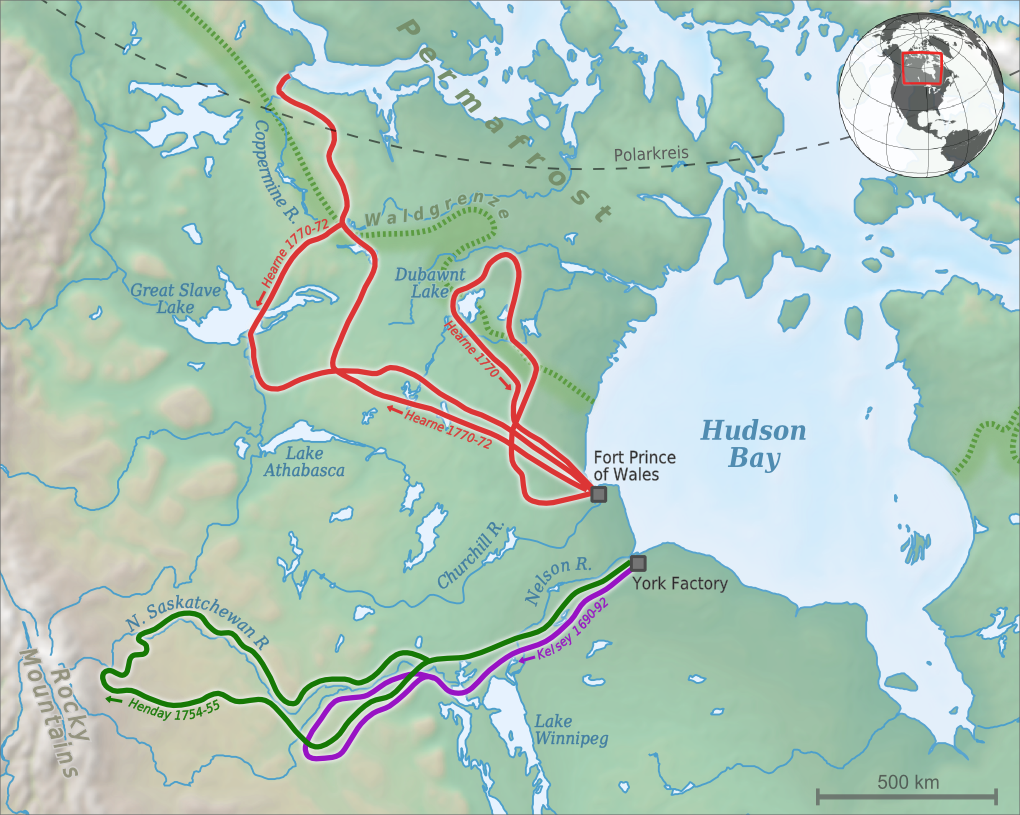
Anthony Henday
Anthony Henday ( fl. 1750–1762) was one of the first Europeans to explore the interior of what would eventually become western Canada. He ventured farther westward than any white man had before him. As an employee of the Hudson's Bay Company he travelled across the prairies in the 1750s, journeying into what is now central Alberta, possibly arriving at the present site of Red Deer. He camped along the North Saskatchewan River, perhaps on the present site of Rocky Mountain House or Edmonton, and is said to have been the first European to see the Rocky Mountains, if only from a distance. His purpose was to encourage First Nations in the upper watershed of the Saskatchewan River to come to Hudson Bay to trade, but due to the great distance involved, their inability to build canoes and paddle them, and fear of attack by Cree along the river, Blackfoot and other western prairie First Nations were reluctant to make the journey. Early life Henday was from the Isle of Wight, Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to Western Europe and parts of Asia. Its trade developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |