|
Northwestern Blot
The northwestern blot, also known as the northwestern assay, is a hybrid analytical technique of the western blot and the northern blot, and is used in molecular biology to detect interactions between RNA and proteins. A related technique, the western blot, is used to detect a protein of interest that involves transferring proteins that are separated by gel electrophoresis onto a nitrocellulose membrane. A colored precipitate clusters along the band on the membrane containing a particular target protein. A northern blot is a similar analytical technique that, instead of detecting a protein of interest, is used to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) on a similar membrane. The northwestern blot combines the two techniques, and specifically involves the identification of labeled RNA that interact with proteins that are immobilized on a similar nitrocellulose membrane. History Edwin Southern first created the Southern blot, an analytical technique used to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
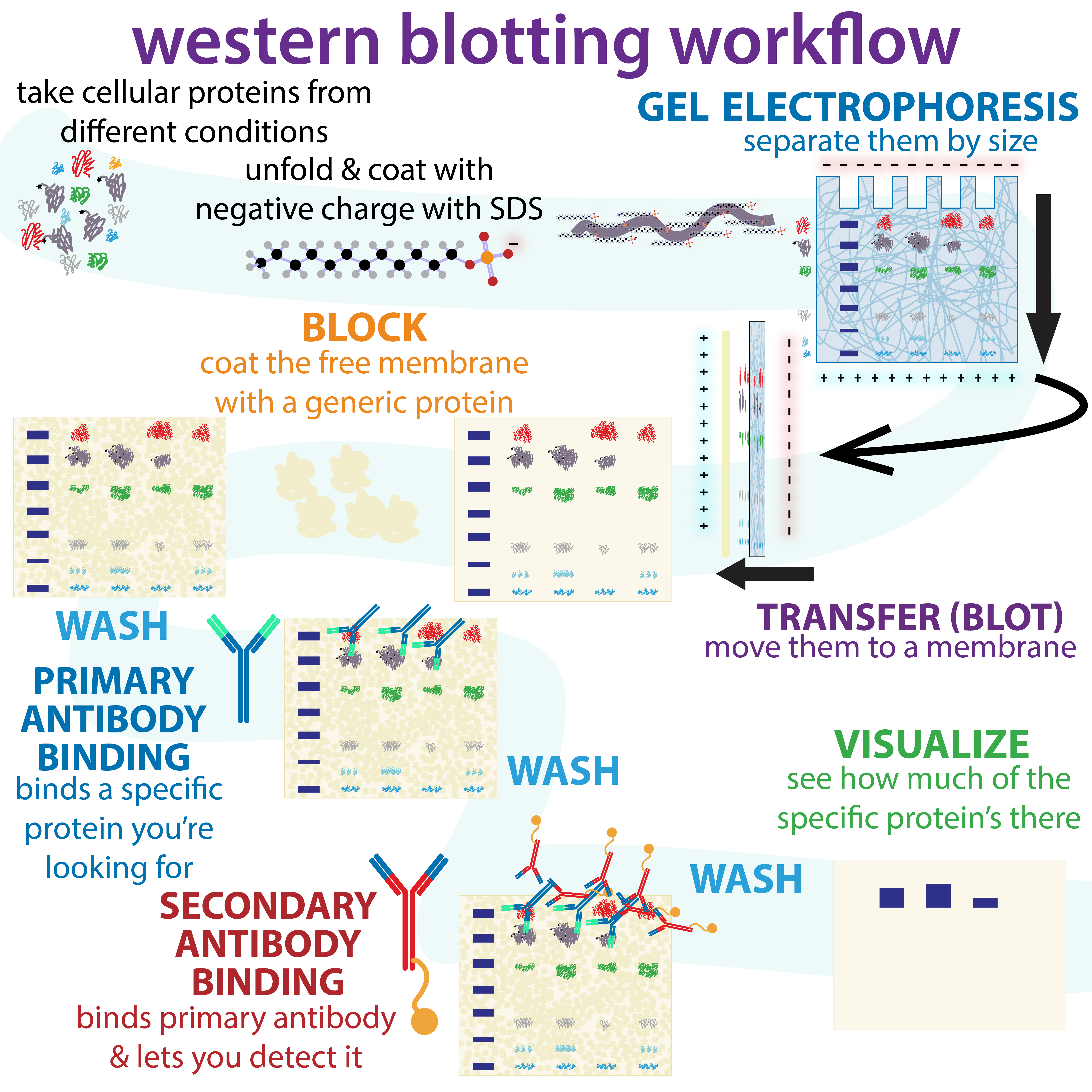
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tween 20
Polysorbate 20 (common commercial brand names include Kolliphor PS 20, Scattics, Alkest TW 20, Tween 20, and Kotilen-20) is a polysorbate-type nonionic surfactant formed by the ethoxylation of sorbitan monolaurate. Its stability and relative nontoxicity allows it to be used as a detergent and emulsifier in a number of domestic, scientific, and pharmacological applications. As the name implies the ethoxylation process leaves the molecule with 20 repeat units of polyethylene glycol; in practice these are distributed across 4 different chains, leading to a commercial product containing a range of chemical species. Food applications Polysorbate 20 is used as a wetting agent in flavored mouth drops such as Ice Drops, helping to provide a spreading feeling to other ingredients like Denatured alcohol, SD alcohol and mint flavor. The World Health Organization has suggested acceptable daily intake limits of 0–25 mg of polyoxyethylene sorbitan esters per kg body weight. Biotechnic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
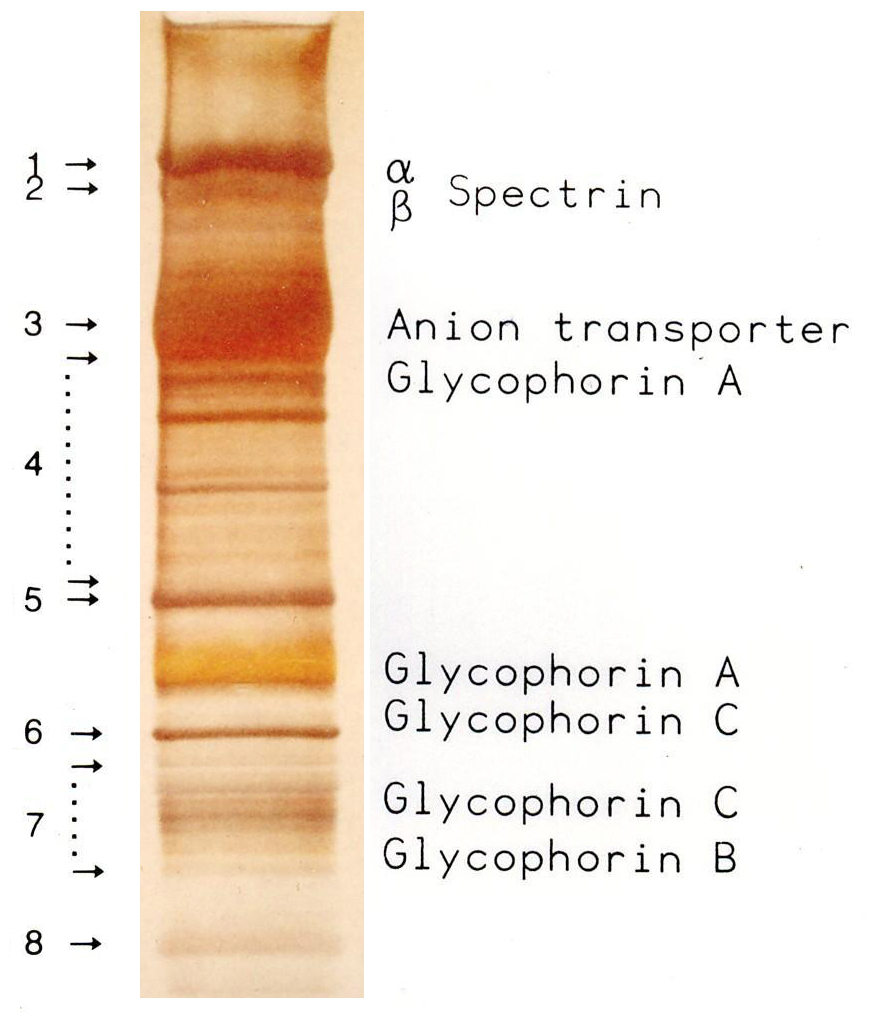
SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is a discontinuous electrophoretic system developed by Ulrich K. Laemmli which is commonly used as a method to separate proteins with molecular masses between 5 and 250 kDa. The combined use of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, also known as sodium lauryl sulfate) and polyacrylamide gel allows to eliminate the influence of structure and charge, and proteins are separated solely on the basis of differences in their molecular weight. Properties SDS-PAGE is an electrophoresis method that allows protein separation by mass. The medium (also referred to as ′matrix′) is a polyacrylamide-based discontinuous gel. The polyacrylamide-gel is typically sandwiched between two glass plates in a slab gel. Although tube gels (in glass cylinders) were used historically, they were rapidly made obsolete with the invention of the more convenient slab gels. In addition, SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) is used. About 1.4 grams of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules ( DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too small to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for the separation of nanoparticles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Blot
The eastern blot, or eastern blotting, is a biochemical technique used to analyze protein post-translational modifications including the addition of lipids, phosphates, and glycoconjugates. It is most often used to detect carbohydrate epitopes. Thus, eastern blot can be considered an extension of the biochemical technique of western blot. Multiple techniques have been described by the term "eastern blot(ting)", most use phosphoprotein blotted from sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gel on to a polyvinylidene fluoride or nitrocellulose membrane. Transferred proteins are analyzed for post-translational modifications using probes that may detect lipids, carbohydrate, phosphorylation or any other protein modification. Eastern blotting should be used to refer to methods that detect their targets through specific interaction of the post-translational modifications and the probe, distinguishing them from a standard far-western blot. In principle, easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Blot
The southwestern blot, is a lab technique that involves identifying as well as characterizing DNA-binding proteins by their ability to bind to specific oligonucleotide probes. Determination of molecular weight of proteins binding to DNA is also made possible by the technique. The name originates from a combination of ideas underlying Southern blotting and Western blotting techniques of which they detect DNA and protein respectively. Similar to other types of blotting, proteins are separated by SDS-PAGE and are subsequently transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Thereafter southwestern blotting begins to vary with regards to procedure as since the first blotting’s, many more have been proposed and discovered with goals of enhancing results. Former protocols were hampered by the need for large amounts of proteins and their susceptibility to degradation while being isolated. Southwestern blotting was first described by Brian Bowen, Jay Steinberg, U.K. Laemmli, and Harold Weintra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
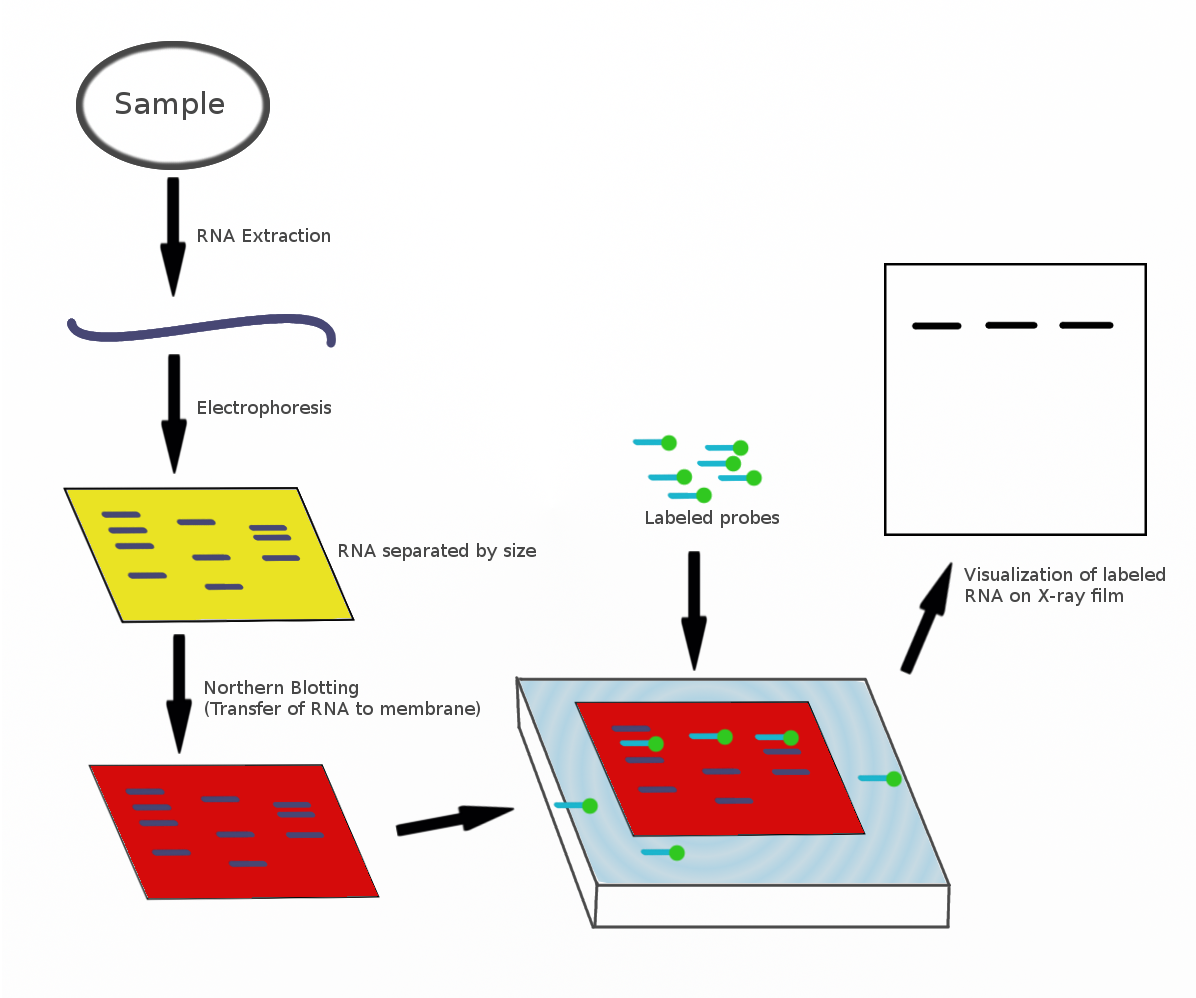
Northern Blot
The northern blot, or RNA blot,Gilbert, S. F. (2000) Developmental Biology, 6th Ed. Sunderland MA, Sinauer Associates. is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.Kevil, C. G., Walsh, L., Laroux, F. S., Kalogeris, T., Grisham, M. B., Alexander, J. S. (1997) An Improved, Rapid Northern Protocol. Biochem. and Biophys. Research Comm. 238:277–279. With northern blotting it is possible to observe cellular control over structure and function by determining the particular gene expression rates during differentiation and morphogenesis, as well as in abnormal or diseased conditions. Northern blotting involves the use of electrophoresis to separate RNA samples by size, and detection with a hybridization probe complementary to part of or the entire target sequence. Strictly speaking, the term 'northern blot' refers specifically to the capillary transfer of RNA from the electrophoresis gel to the blotting m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoradiography
An autoradiograph is an image on an X-ray film or nuclear emulsion produced by the pattern of decay emissions (e.g., beta particles or gamma rays) from a distribution of a radioactive substance. Alternatively, the autoradiograph is also available as a digital image (digital autoradiography), due to the recent development of scintillation gas detectors or rare earth phosphorimaging systems. The film or emulsion is apposed to the labeled tissue section to obtain the autoradiograph (also called an autoradiogram). The ''auto-'' prefix indicates that the radioactive substance is within the sample, as distinguished from the case of historadiography or microradiography, in which the sample is marked using an external source. Some autoradiographs can be examined microscopically for localization of silver grains (such as on the interiors or exteriors of cells or organelles) in which the process is termed micro-autoradiography. For example, micro-autoradiography was used to examine whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |