|
North Northern Scots
North Northern Scots refers to the dialects of Scots spoken in Caithness, the Black Isle and Easter Ross. Caithness The dialect of Caithness is generally spoken in the lowlying land to the east of a line drawn from Clyth Ness to some 4 miles west of Thurso. To the west of that Scottish Gaelic used to be spoken. The Caithness varieties have been influenced by both Gaelic and Norn. The dialect spoken in the neighbourhood of John o' Groats resembles that of Orkney to some extent. Phonology The phonology of the Caithness varieties generally follows the pattern of the Mid Northern Scots varieties but: *Initial j or g, which is realised in most other Scots dialects, may be realised . *The k in the cluster kn may be pronounced in for example, ''knife'' and ''knowe'' (knoll). *th, usually or in other Scots dialect, may be realised in a few words, for example ''muith'' (sultry) and ''thresh''. The initial ''th'' dropped in all pronominals, for example ''the'', ''they'' (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Language
Scots ( endonym: ''Scots''; gd, Albais, ) is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland (where the local dialect is known as Ulster Scots). Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, Northern Isles and northern Ulster, it is sometimes called Lowland Scots or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides and Galloway after the 16th century. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1300). Scots is recognised as an indigenous language of Scotland, a regional or minority language of Europe, as well as a vulnerable language by UNESCO. In the 2011 United Kingdom census, 2011 Scottish Census, over 1.5 million people in Scotland reported being able to speak Scots. As there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
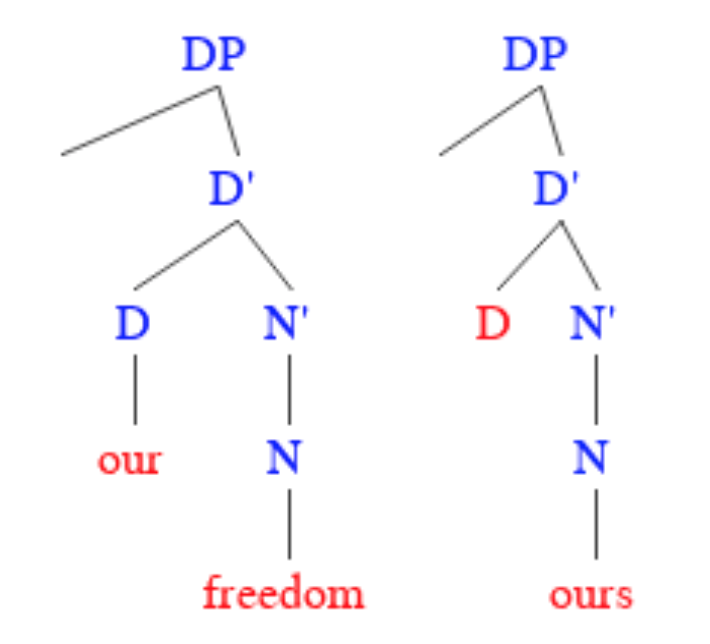
Pronominal
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Subtypes include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The name of the adjective that belongs with a "pronoun" is called a "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Dialects
Scots usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: * Scots language, a language of the West Germanic language family native to Scotland * Scots people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland * Scoti, a Latin name for the Gaels * SCOTS, abbreviation for Royal Regiment of Scotland * Scottish Corpus of Texts and Speech (SCOTS), a linguistic resource See also * Southern Culture on the Skids (SCOTS), an American rock band * Scot's Lo-Cost, a grocery store owned by Weis Markets * Scotch (other) * Scots Church (other) * Scots College (other) * Scott's (other) * Scottish (other) * Scotts (other) * Pound Scots, historical currency * Scots pine ''Pinus sylvestris'', the Scots pine (UK), Scotch pine (US) or Baltic pine, is a species of tree in the pine family Pinaceae that is native to Eurasia. It can readily be identified by its combination of fairly short, blue-green leaves and orang ..., a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
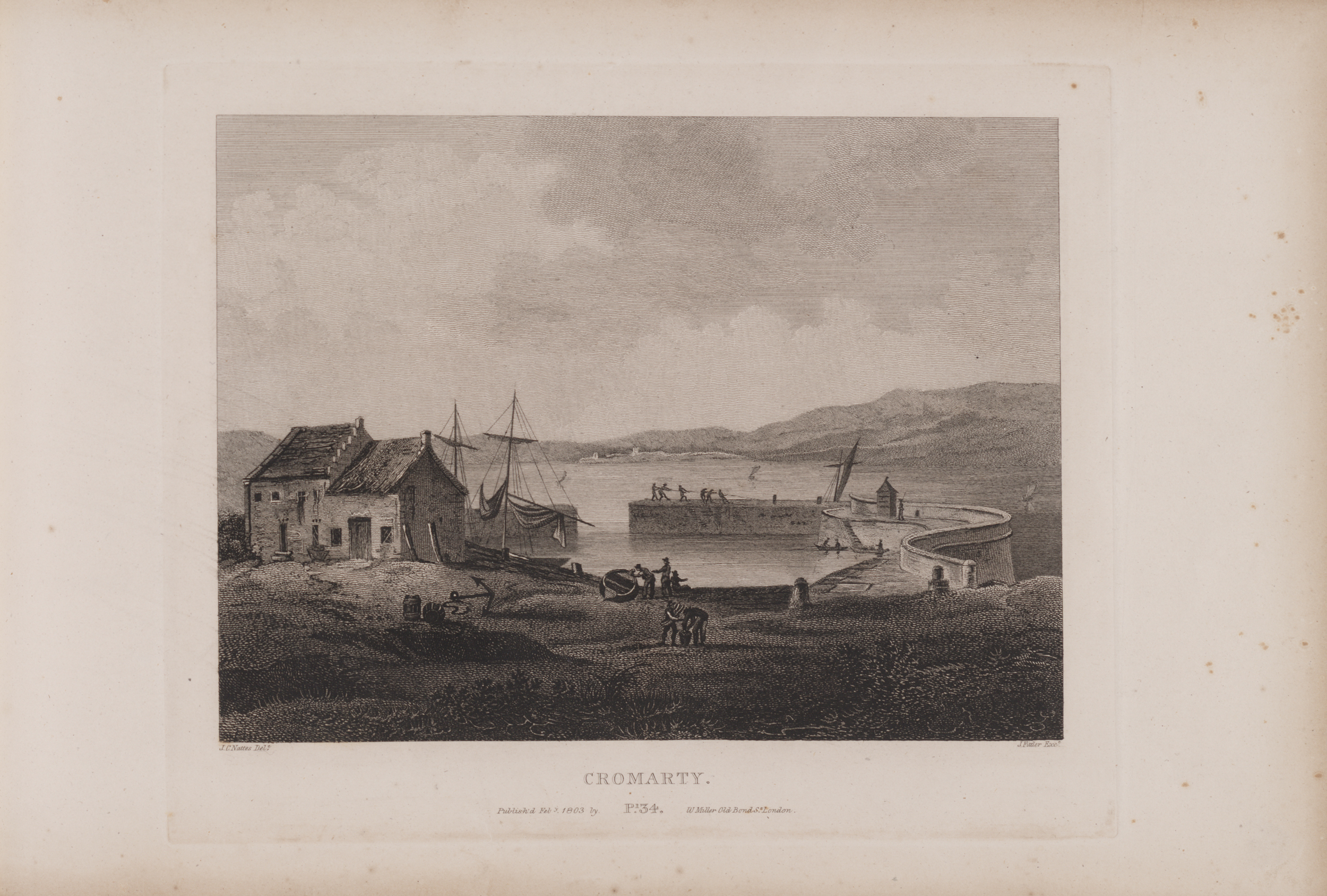
Cromarty
Cromarty (; gd, Cromba, ) is a town, civil parish and former royal burgh in Ross and Cromarty, in the Highland area of Scotland. Situated at the tip of the Black Isle on the southern shore of the mouth of Cromarty Firth, it is seaward from Invergordon on the opposite coast. In the 2001 census, it had a population of 719. History The name ''Cromarty'' variously derives from the Gaelic ''crom'' (crooked), and from ''bati'' (bay), or from ''àrd'' (height), meaning either the "crooked bay", or the "bend between the heights" (referring to the high rocks, or Sutors, which guard the entrance to the Firth), and gave the title to the Earldom of Cromartie. In 1264, its name was ''Crumbathyn''. Cromarty is a sea port, and its economy was closely linked to the sea for most of its history. Fishing was the major industry, with salmon stations around the surrounding coast, and boats going out to catch herring. Other trade was also by boat: Cromarty's connections to surrounding towns were l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-dropping
''H''-dropping or aitch-dropping is the deletion of the voiceless glottal fricative or "''H''-sound", . The phenomenon is common in many dialects of English, and is also found in certain other languages, either as a purely historical development or as a contemporary difference between dialects. Although common in most regions of England and in some other English-speaking countries, and linguistically speaking a neutral evolution in languages, H-dropping is often stigmatized as a sign of careless or uneducated speech. The reverse phenomenon, ''H''-insertion or ''H''-adding, is found in certain situations, sometimes as an allophone or hypercorrection by H-dropping speakers, and sometimes as a spelling pronunciation or out of perceived etymological correctness. A particular example of this is the spread of 'haitch' for 'aitch'. In English Historical /h/-loss In Old English phonology, the sounds , , and (described respectively as glottal, velar and palatal voiceless fricatives) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromarty Dialect
The Cromarty dialect of North Northern Scots was spoken in Cromarty, Scotland. The dialect originated from people who moved north from the Firth of Forth in the 15th and 16th centuries. The last native speaker of the dialect, Bobby Hogg, died in 2012 at age 92. BBC News, 2 October 2012. The dialect had a heavy influence from both and Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic an ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland English
Highland English ( sco, Hieland Inglis) is the variety of Scottish English spoken by many in the Scottish Highlands and the Hebrides. It is more strongly influenced by Gaelic than are other forms of Scottish English. Phonology *The '' svarabhakti'' ("helping vowel") that is used in some consonant combinations in Gaelic and Scots is sometimes used in the Hebrides, so that "film" may be pronounced "fillum".Shuken, Cynthia "Highland and Island English", in Trudgill, Peter (1984). ''Language in the British Isles''. Cambridge University Press. p. 152. References Sources * Sabban, Annette (1982), ''Sprachkontakt: zur Variabilität des Englischen im gälischsprachigen Gebiet Schottlands ; eine empirische Studie'', Heidelberg: Groos. * Watson, Murray (2003) ''Being English in Scotland''. Edinburgh University Press. See also * Lowland Scots ;Other English dialects influenced by Celtic languages * Anglo-Cornish * Anglo-Manx * Bungi creole * Hiberno-English * Welsh English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avoch
Avoch harbour Avoch ( ; from the gd, Abhach – meaning mouth of the stream) is a harbour-village located on the south-east coast of the Black Isle, on the Moray Firth. History Origins Ormond Castle or ''Avoch Castle'' was a stronghold built on the site and served as a royal castle to William the Lion; passed on to the Morays of Petty then Archibald the Grim, Lord of Galloway, upon his marriage to Joanna de Moravia in 1362. Descendants of Archibald, were to take the title of Earl of Ormonde from the castle. Legend has it that the village was founded by survivors of the Spanish Armada in 1588. Estate owners Avoch was in the control of David Chalmers, Lord Ormond from 1560/61 but he forfeited his castle and control of Avoch in 1568 when he was exiled due to his part in assisting the escape of Mary Queen of Scots. The castle and village then passed to Andrew Munro of Milntown. In the late 16th century the Munro of Pittonachy family held the estate of Pittonachy in the parish un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moray Firth
The Moray Firth (; Scottish Gaelic: ''An Cuan Moireach'', ''Linne Mhoireibh'' or ''Caolas Mhoireibh'') is a roughly triangular inlet (or firth) of the North Sea, north and east of Inverness, which is in the Highland council area of north of Scotland. It is the largest firth in Scotland, stretching from Duncansby Head (near John o' Groats) in the north, in the Highland council area, and Fraserburgh in the east, in the Aberdeenshire council area, to Inverness and the Beauly Firth in the west. Therefore, three council areas have Moray Firth coastline: Highland to the west and north of the Moray Firth and Highland, Moray and Aberdeenshire to the south. The firth has more than 800 kilometres (about 500 miles) of coastline, much of which is cliff. Etymology The firth is named after the 10th-century Province of Moray, whose name in turn is believed to derive from the sea of the firth itself. The local names ''Murar'' or ''Morar'' are suggested to derive from , the Gaelic for sea, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Dialect (Scotland)
Doric, the popular name for Mid Northern Scots or Northeast Scots, refers to the Scots language as spoken in the northeast of Scotland. There is an extensive body of literature, mostly poetry, ballads, and songs, written in Doric. In some literary works, Doric is used as the language of conversation while the rest of the work is in Lallans Scots or British English. A number of 20th and 21st century poets have written poetry in the Doric dialect. Nomenclature The term "Doric" was formerly used to refer to all dialects of Lowland Scots, but during the twentieth century it became increasingly associated with Mid Northern Scots. The name possibly originated as a jocular reference to the Doric dialect of the Ancient Greek language. Greek Dorians lived in Laconia, including Sparta, and other more rural areas, and were alleged by the ancient Greeks to have spoken laconically and in a language thought harsher in tone and more phonetically conservative than the Attic spoken in Athens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, one that functions as a noun. In English, it has the properties of both verb and noun, such as being modifiable by an adverb and being able to take a direct object. The term "''-ing'' form" is often used in English to refer to the gerund specifically. Traditional grammar makes a distinction within ''-ing'' forms between present participles and gerunds, a distinction that is not observed in such modern grammars as ''A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language'' and ''The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language''. Traditional use The Latin gerund, in a restricted set of syntactic contexts, denotes the sense of the verb in isolation after certain prepositions, and in certain uses of the genitive, dative, and ablative cases. It is very rarely combined with dependent sentence elements such as object. To express such concepts, the construction w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Present Participle
In linguistics, a participle () (from Latin ' a "sharing, partaking") is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adjective, as in a ''laughing face''". “Participle” is a traditional grammatical term from Greek and Latin that is widely used for corresponding verb forms in European languages and analogous forms in Sanskrit and Arabic grammar. Cross-linguistically, participles may have a range of functions apart from adjectival modification. In European and Indian languages, the past participle is used to form the passive voice. In English, participles are also associated with periphrastic verb forms (continuous and perfect) and are widely used in adverbial clauses. In non-Indo-European languages, ‘participle’ has been applied to forms that are alternatively regarded as converbs (see Sireniki Eskimo below), gerunds, ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |