|
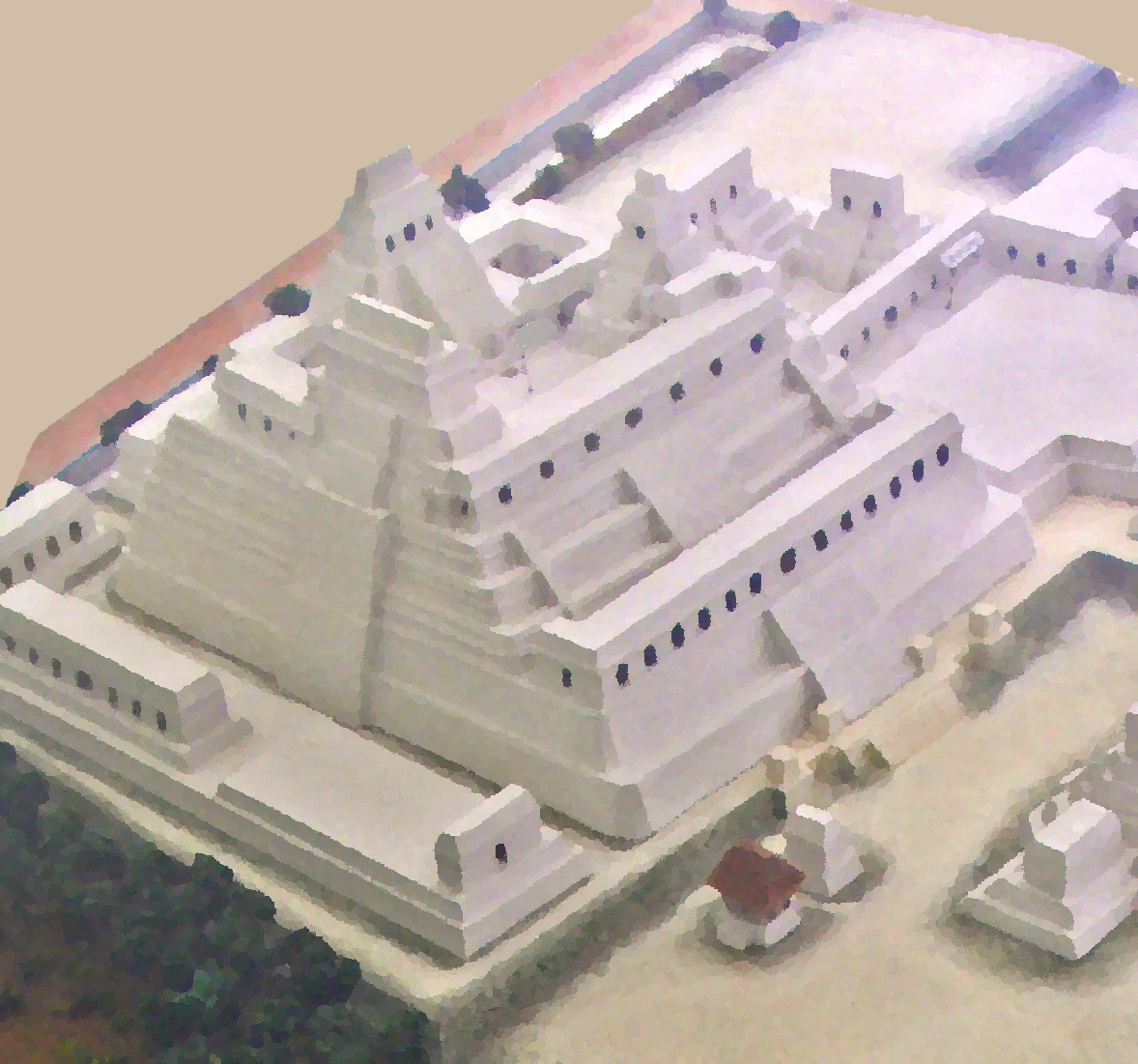
North Acropolis, Tikal
The North Acropolis of the ancient Maya city of Tikal in Guatemala is an architectural complex that served as a royal necropolis and was a centre for funerary activity for over 1300 years. The acropolis is located near the centre of the city and is one of the most studied of Maya architectural complexes. Excavations were carried out from 1957 to 1969 by the University of Pennsylvania, directed by Edwin M. Shook and William Coe.Martin and Grube 2000, p. 43. The first traces of human activity at the site date to approximately 800 BCE, with the first structures being built about 350 BCE. Around 250 CE the complex underwent a major redevelopment with the construction of a massive basal platform that supported a cluster of temples; this was followed around 450 CE by the addition of a row of four pyramids on a terrace to the south of the main platform. A number of royal tombs have been excavated that have been identified with named kings, including the tombs of Yax Nuun Ayiin I (rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nord Akropolis Tikal
Nord, a word meaning "north" in several European languages, may refer to: Acronyms * National Organization for Rare Disorders, an American nonprofit organization * New Orleans Recreation Department, New Orleans, Louisiana, US Film and television * ''Nord'' (1991 film), a film directed by Xavier Beauvois * ''Nord'' (2009 film), or ''North'', a Norwegian film directed by Rune Denstad Langlo Music * ''Nord'' (Siddharta album), 2001 * ''Nord'' (Year of No Light album), 2006 * ''Nord'', an album by Luna Amară, 2018 * Nord, the brand name for musical instruments produced by Clavia. * ''A. G. NORD'', the fifth disc from the album 7G, by A. G. Cook. * ''Nord'' (Gåte album), 2021 People * Christiane Nord (born 1943), German translation scholar * Daniel Nord, Swedish civil servant * Elizabeth Nord (1902–1986), American labor organizer * , Norwegian software expert * John Nord (born 1959), American professional wrestler * (1912–2003), German anti-Nazi activist * Kathleen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Script
Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs, is historically the native writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered. The earliest inscriptions found which are identifiably Maya date to the 3rd century BCE in San Bartolo, Guatemala. Maya writing was in continuous use throughout Mesoamerica until the Spanish conquest of the Maya in the 16th and 17th centuries. Maya writing used logograms complemented with a set of syllabic glyphs, somewhat similar in function to modern Japanese writing. Maya writing was called "hieroglyphics" or hieroglyphs by early European explorers of the 18th and 19th centuries who found its general appearance reminiscent of Egyptian hieroglyphs, although the two systems are unrelated. Though modern Mayan languages are almost entirely written using the Latin alphabet rather than Maya script, there have been recent developments encouraging a revival of the Maya gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jade Use In Mesoamerica
The use of jade in Mesoamerica for symbolic and ideological ritual was highly influenced by its rarity and value among pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Olmec, the Maya, and the various groups in the Valley of Mexico. Although jade artifacts have been created and prized by many Mesoamerican peoples, the Motagua River valley in Guatemala was previously thought to be the sole source of jadeite in the region. This extreme durability makes fine grained or fibrous jadeite and nephrite highly useful for Mesoamerican technology. It was often worked or carved as ornamental stones, a medium upon which glyphs were inscribed, or shaped into figurines, weapons, and other objects. Many jade artifacts crafted by later Mesoamerican civilizations appear cut from simple jade axes, implying that the earliest jadeite trade was based in utilitarian function. Jade and Jadeite In general terms, jade refers to two distinct minerals: nephrite, a calcium and magnesium rich amphibole mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
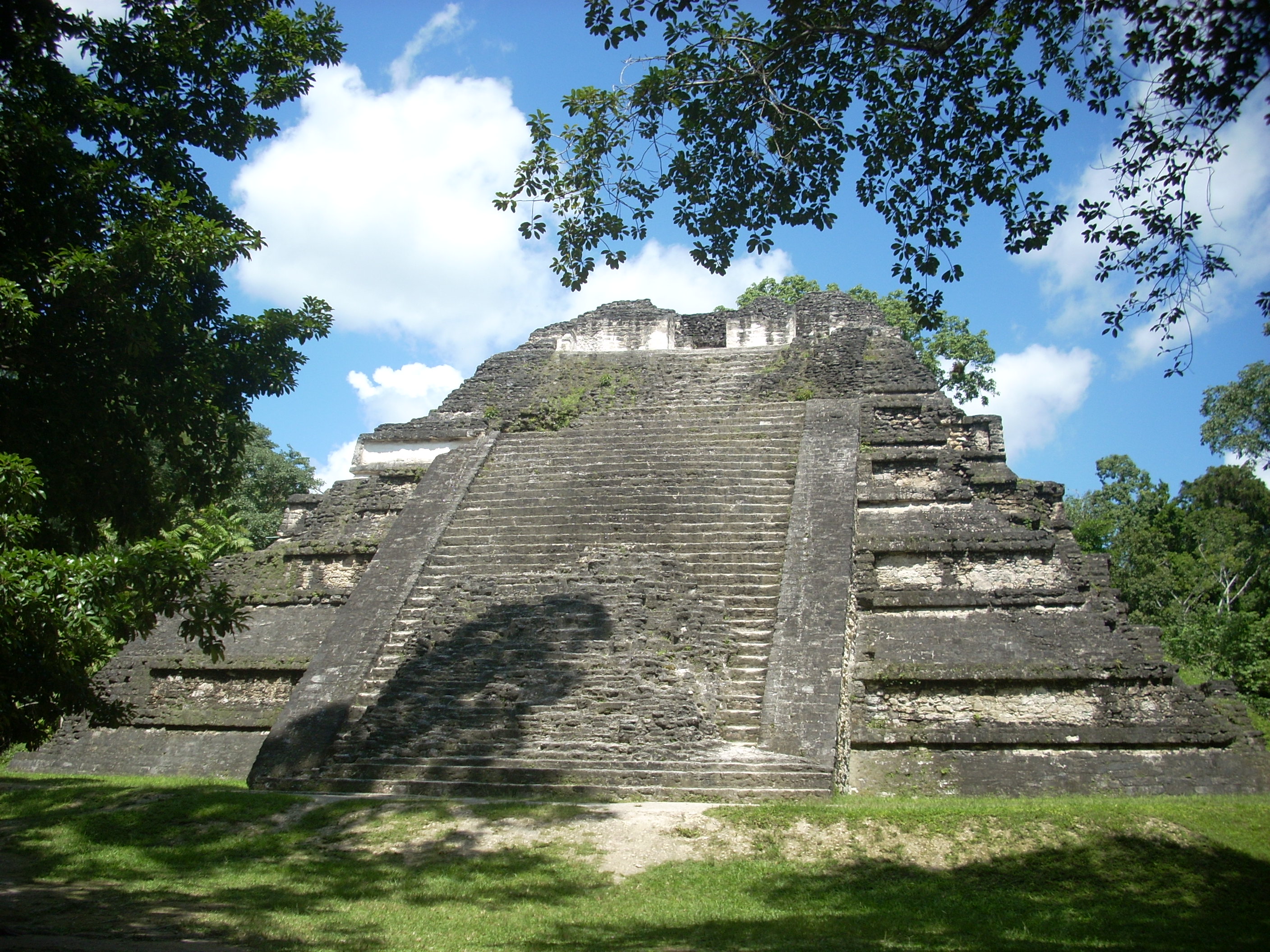
Tikal Temple I
Tikal Temple I is the designation given to one of the major structures at Tikal, one of the largest cities and archaeological sites of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in Mesoamerica. It is located in the Petén Basin region of northern Guatemala. It also is known as the Temple of the Great Jaguar because of a lintel that represents a king sitting upon a jaguar throne.Muñoz Cosme & Quintana Samayoa 1996, p.302. An alternative name is the Temple of Ah Cacao, after the ruler buried in the temple.''Ah Cacao'' being an earlier nickname for the Tikal ruler Jasaw Chan K'awiil I, whose tomb the temple contains. Temple I is a typically Petén-styled limestone stepped pyramid structure that is dated to approximately 732 AD. Situated at the heart of a World Heritage Site, the temple is surmounted by a characteristic roof comb, a distinctive Maya architectural feature. Building Temple I on the eastern side of the Great Plaza was a significant deviation from the established tradition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbel Arch
A corbel arch (or corbeled / corbelled arch) is an arch-like construction method that uses the architectural technique of corbeling to span a space or void in a structure, such as an entranceway in a wall or as the span of a bridge. A corbel vault uses this technique to support the superstructure of a building's roof. A corbel arch is constructed by offsetting successive horizontal courses of stone (or brick) beginning at the springline of the walls (the point at which the walls break off from verticality to form an arc toward the apex at the archway's center) so that they project towards the archway's center from each supporting side, until the courses meet at the apex of the archway (often, the last gap is bridged with a flat stone). For a corbeled vault covering, the technique is extended in three dimensions along the lengths of two opposing walls. Although an improvement in load-bearing efficiency over the post and lintel design, corbeled arches are not entirely self-support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triadic Pyramid
Triadic pyramids were an innovation of the Preclassic Maya civilization consisting of a dominant structure flanked by two smaller inward-facing buildings, all mounted upon a single basal platform. The largest known triadic pyramid was built at El Mirador in the Petén Basin of Guatemala; it covers an area six times as large as that covered by Tikal Temple IV, which is the largest pyramid at that city. The three superstructures all have stairways leading up from the central plaza on top of the basal platform. Triadic pyramid structures are found at early cities in the Maya lowlands. Overview Triadic pyramid complexes were most frequently oriented towards the west although other orientations were common, particularly at those cities that possessed more than one triadic pyramid; the second most frequent orientation appears to be north-south. There are only a few Middle Preclassic examples of the triadic pyramid complex, although their exact chronology might not be secure. No se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundo Perdido, Tikal
The Mundo Perdido (Spanish for "Lost World") is the largest ceremonial complex dating from the Preclassic period at the ancient Maya city of Tikal, in the Petén Department of northern Guatemala.Martin and Grube 2000, p.28. The complex was organised as a large E-Group astronomical complex consisting of a pyramid aligned with a platform to the east that supported three temples. The Mundo Perdido complex was rebuilt many times over the course of its history. By AD 250–300 its architectural style was influenced by the great metropolis of Teotihuacan in the Valley of Mexico, including the use of the ''talud-tablero'' form. During the Early Classic period (c. 250–600) the Mundo Perdido became one of the twin foci of the city, the other being the North Acropolis.Martin and Grube 2000, p.29. From AD 250 to 378 it may have served as the royal necropolis. The Mundo Perdido complex was given its name by the archaeologists of the University of Pennsylvania. The large plaza centred up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacbe
Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatán Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, Yucatán A sacbe, plural sacbeob ( Yucatec Maya: singular ''sakbej'', plural ''sakbejo'ob''), or "white way", is a raised paved road built by the Maya civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Most connect temples, plazas, and groups of structures within ceremonial centers or cities, but some longer roads between cities are also known. The term "sacbe" is Yucatec Maya for "white road"; white perhaps because there is evidence that they were originally coated with limestone stucco or plaster, which was over a stone and rubble fill.Roys and Shook 1966, 43 Etymology The word "Beh" operates as the root term for "Sacbe" it is a Mayan term for "road, pathway, or trail." Beh is spelled alternately as Be, bej, bey, be, bih, as well as "beel" in the possessive. It has many distinctions from English concepts of roads, pathways, or trails. Beh's metaphoric meanings are just as important if not more important t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preclassic Maya
The Preclassic period in Maya history stretches from the beginning of permanent village life c. 1000 BC until the advent of the Classic Period c. 250 AD, and is subdivided into Early (prior to 1000 BC), Middle (1000–400 BC), and Late (400 BC – 250 AD). Major archaeological sites of this period include Nakbe, Uaxactun, Seibal, San Bartolo, Cival, and El Mirador. Maya society underwent a series of profound transformations between c. 100 AD and 250 AD, which resulted in the cessation of monumental building at many Preclassic cities and the inferred collapse of their political and economic systems, often characterized as the "Preclassic Collapse." History Early Preclassic (2000 BC–1000 BC) The roots of Maya civilization remain obscure, although broad parameters are increasingly well known. Paleo-environmental data indicate the presence of agriculturalists in the Maya lowlands by c. 3000 BC, although permanent agricultural settlements seem to have developed only gradually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian (first human habitation until 3500 BCE); the Archaic (before 2600 BCE), the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE – 250 CE), the Classic (250–900 CE), and the Postclassic (); as well as the post European contact Colonial Period (1521–1821), and Postcolonial, or the period after independence from Spain (1821–present). The periodisation of Mesoamerica by researchers is based on archaeological, ethnohistorical, and modern cultural anthropology research dating to the early twentieth century. Archaeologists, ethnohistorians, historians, and cultural anthropologists continue to work to develop cultural histories of the region. Overview Paleo-Indian period 10,000–3500 BCE The Paleo-Indian (less frequently, ''Lithic'') period or era is that which spans from the first signs of human presence in the region, to the establishment of agricult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)