|
Sacbe
Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatán Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, Yucatán A sacbe, plural sacbeob (Yucatec Maya: singular ''sakbej'', plural ''sakbejo'ob''), or "white way", is a raised paved road built by the Maya civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Most connect temples, plazas, and groups of structures within ceremonial centers or cities, but some longer roads between cities are also known. The term "sacbe" is Yucatec Maya for "white road"; white perhaps because there is evidence that they were originally coated with limestone stucco or plaster, which was over a stone and rubble fill.Roys and Shook 1966, 43 Etymology The word "Beh" operates as the root term for "Sacbe" it is a Mayan term for "road, pathway, or trail." Beh is spelled alternately as Be, bej, bey, be, bih, as well as "beel" in the possessive. It has many distinctions from English concepts of roads, pathways, or trails. Beh's metaphoric meanings are just as important if not more important tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacbe Dzibilchaltun
Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatán Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, Yucatán A sacbe, plural sacbeob (Yucatec Maya: singular ''sakbej'', plural ''sakbejo'ob''), or "white way", is a raised paved road built by the Maya civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Most connect temples, plazas, and groups of structures within ceremonial centers or cities, but some longer roads between cities are also known. The term "sacbe" is Yucatec Maya for "white road"; white perhaps because there is evidence that they were originally coated with limestone stucco or plaster, which was over a stone and rubble fill.Roys and Shook 1966, 43 Etymology The word "Beh" operates as the root term for "Sacbe" it is a Mayan term for "road, pathway, or trail." Beh is spelled alternately as Be, bej, bey, be, bih, as well as "beel" in the possessive. It has many distinctions from English concepts of roads, pathways, or trails. Beh's metaphoric meanings are just as important if not more important tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coba
Coba ( es, Cobá) is an ancient Maya city on the Yucatán Peninsula, located in the Mexican state of Quintana Roo. The site is the nexus of the largest network of stone causeways of the ancient Maya world, and it contains many engraved and sculpted stelae that document ceremonial life and important events of the Late Classic Period (AD 600–900) of Mesoamerican civilization. The adjacent modern village bearing the same name, reported a population of 1,278 inhabitants in the 2010 Mexican federal census. The ruins of Coba lie 47 km (approx. 29 mi) northwest of Tulum, in the State of Quintana Roo, Mexico. The geographical coordinates of Coba Group (main entrance for tourist area of the archaeological site) are North 19° 29.6’ and West 87° 43.7’. The archaeological zone is reached by a two-kilometer branch from the asphalt road connecting Tulum with Nuevo Xcán (a community of Lázaro Cárdenas, another municipality of Quintana Roo) on the Valladolid to Cancún hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
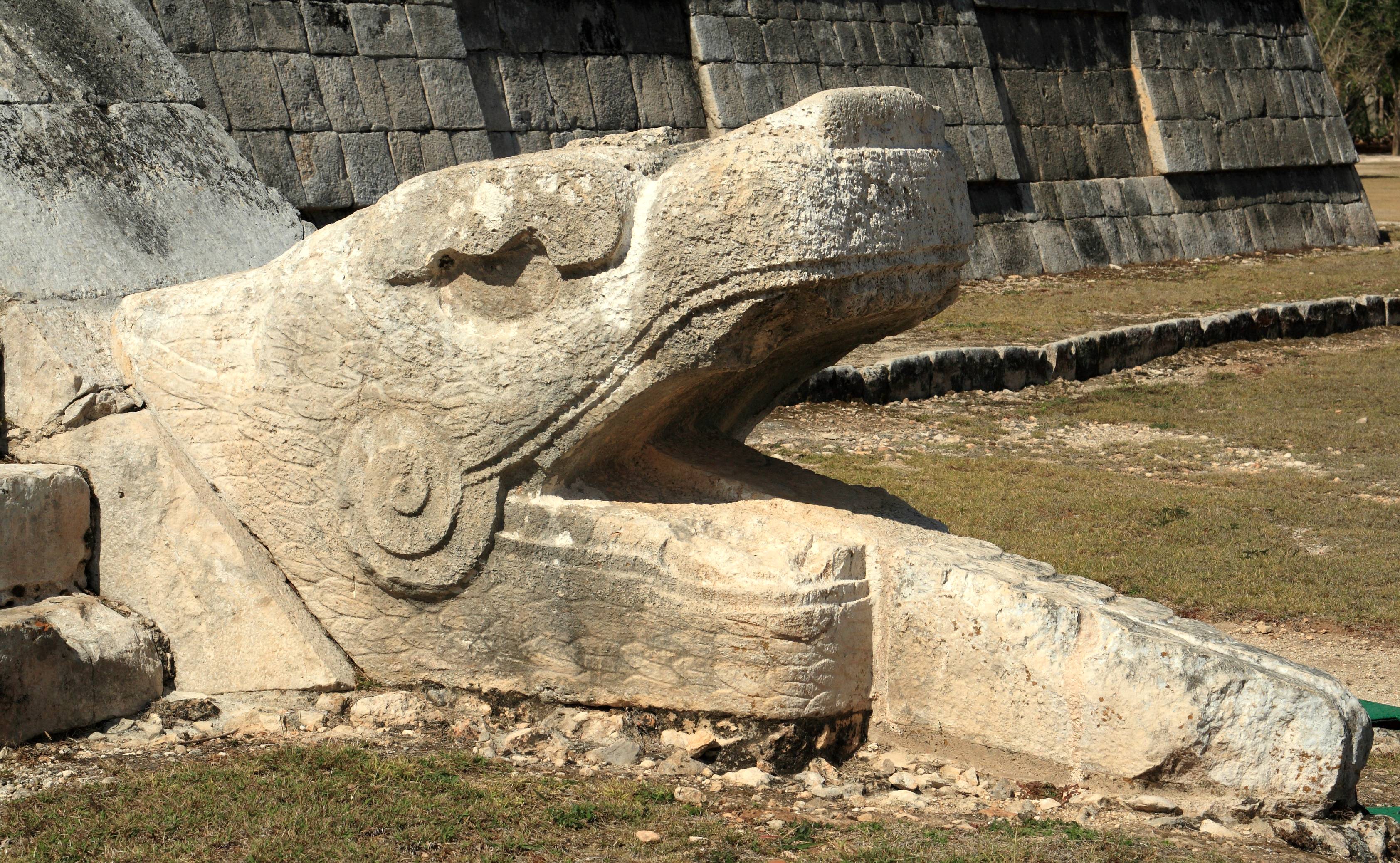
Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza , es, Chichén Itzá , often with the emphasis reversed in English to ; from yua, Chiʼchʼèen Ìitshaʼ () "at the mouth of the well of the Itza people" was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal Classic period. The archeological site is located in Tinúm Municipality, Yucatán State, Mexico. Chichen Itza was a major focal point in the Northern Maya Lowlands from the Late Classic (c. AD 600–900) through the Terminal Classic (c. AD 800–900) and into the early portion of the Postclassic period (c. AD 900–1200). The site exhibits a multitude of architectural styles, reminiscent of styles seen in central Mexico and of the Puuc and Chenes styles of the Northern Maya lowlands. The presence of central Mexican styles was once thought to have been representative of direct migration or even conquest from central Mexico, but most contemporary interpretations view the presence of these non-Maya styles more as the result of cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Mirador
El Mirador (which translates as "the lookout", "the viewpoint", or "the belvedere") is a large pre-Columbian Middle and Late Preclassic (1000 BC - 250 AD) Mayan settlement, located in the north of the modern department of El Petén, Guatemala. It is part of the Mirador-Calakmul Karst Basin of northern Guatemala. ansen, R., Morales-Aguilar, C., Thompson, J., Ensley, R., Hernández, E., Schreiner, T., . . . Martínez, G. (2022). LiDAR analyses in the contiguous Mirador-Calakmul Karst Basin, Guatemala: An introduction to new perspectives on regional early Maya socioeconomic and political organization. Ancient Mesoamerica, 1-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the same area as their ancestors. The Archaic period, before 2000 BC, saw the first developments in agricul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izamal
Izamal () is a small city in the Mexican state of Yucatán, east of state capital Mérida, in southern Mexico. Izamal was continuously occupied throughout most of Mesoamerican chronology; in 2000, the city's estimated population was 15,000 people. Izamal is known in Yucatán as the Yellow City (most of its buildings are painted yellow) and the City of Hills (that actually are the remains of ancient temple pyramids). Pre-Columbian Izamal Izamal is an important archaeological site of the Pre-Columbian Maya civilization. It is probably the biggest city of the Northern Yucatec Plains, covering a minimal urban extension of . Its monumental buildings exceed 1,000,000 cubic meters of constructive volume and at least two raised causeways, known by their Mayan term ''sacbeob'', connect it with other important centers, Ruins of Ake, located to the west and Kantunil, 18 kilometers to the south, evidencing the religious, political and economic power of this political unit over a terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Cenote
The Sacred Cenote ( es, cenote sagrado, , "sacred well"; alternatively known as the "Well of Sacrifice") is a water-filled sinkhole in limestone at the pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site of Chichen Itza, in the northern Yucatán Peninsula. It is located to the north of Chichen Itza's civic precinct, to which it is connected by a ''sacbe'', a raised pathway. According to both Maya and Spanish post-Conquest sources, pre-Columbian Maya deposited valuables and human bodies into the cenote as a form of sacrifice to the rain god Chaac. Edward Herbert Thompson dredged the Cenote Sagrado from 1904 to 1910, and recovered artifacts of gold, jade, pottery, and incense, as well as human remains. Beginning in the 1950s several Mexican-driven projects were conducted in the cenote, including a 1961 project that used an airlift dredge. Description and history The northwestern Yucatán Peninsula is a limestone plain, with no rivers or streams, lakes or ponds. The region is pockmarked with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
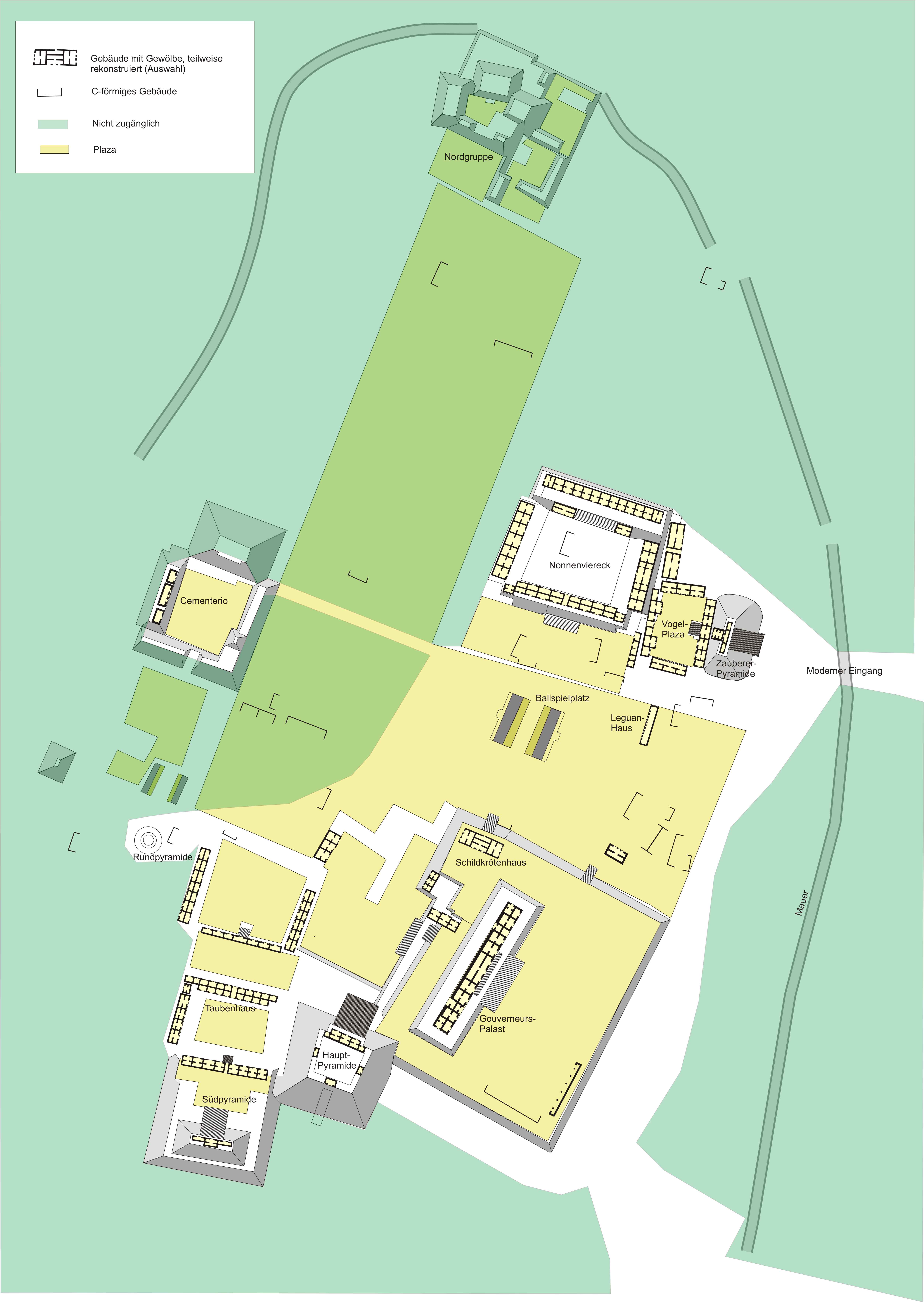
Uxmal
Uxmal (Yucatec Maya: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichen Itza and Calakmul in Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in Belize, and Tikal in Guatemala. It is located in the Puuc region of the eastern Yucatán Peninsula, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in recognition of its significance. Uxmal is located 62 km south of Mérida, capital of Yucatán state in Mexico. Its buildings are noted for their size and decoration. Ancient roads called ''sacbes'' connect the buildings, and also were built to other cities in the area such as Chichén Itzá in modern-day Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in modern-day Belize, and Tikal in modern-day Guatemala. Its buildings are typical of the Puuc style, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrio
''Barrio'' () is a Spanish language, Spanish word that means "Quarter (urban subdivision), quarter" or "neighborhood". In the modern Spanish language, it is generally defined as each area of a city, usually delimited by functional (e.g. residential, commercial, industrial, etc.), social, architectural or morphological features. In Spain, several Latin America, Latin American countries and the Philippines, the term may also be used to officially denote a division of a municipality. ''Barrio'' is an arabism (Classical Arabic ''barrī'': "wild" via Andalusian Arabic ''bárri'': "exterior"). Usage In Argentina and Uruguay, a ''barrio'' is a division of a municipality officially delineated by the local authority at a later time, and it sometimes keeps a distinct character from other areas (as in the Barrios and Communes of Buenos Aires, barrios of Buenos Aires even if they have been superseded by larger administrative divisions). The word does not have a special socioeconomic connotat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenote
A cenote ( or ; ) is a natural pit, or sinkhole, resulting from the collapse of limestone bedrock that exposes groundwater. The regional term is specifically associated with the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where cenotes were commonly used for water supplies by the ancient Maya, and occasionally for sacrificial offerings. The term derives from a word used by the lowland Yucatec Maya——to refer to any location with accessible groundwater. Similar rock-sided sinkholes like cenotes are common geological forms in low-altitude regions, particularly on islands, coastlines, and platforms with young post-Paleozoic limestone with little soil development. The term ''cenote'' has also been used to describe similar karst features in other countries such as Cuba and Australia. Definition and description Cenotes are surface connections to subterranean water bodies. While the best-known cenotes are large open-water pools measuring tens of meters in diameter, such as those at Chichen It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pack Animal
A pack animal, also known as a sumpter animal or beast of burden, is an individual or type of working animal used by humans as means of transporting materials by attaching them so their weight bears on the animal's back, in contrast to draft animals which pull loads but do not carry them. Traditional pack animals are diverse including camels, goats, yaks, reindeer, water buffaloes, and llamas as well as the more familiar pack animals like dogs, horses, donkeys, and mules. Nomenclature The term ''pack animal'' is traditionally used in contrast to ''draft animal'', which is a working animal that typically pulls a load behind itself (such as a plow, a cart, a sled or a heavy log) rather than carrying cargo directly on its back. For instance, sled dogs pull loads but do not normally carry them, while working elephants have been used for centuries to haul logs out of forests. The term ''pack animal'' can also refer to animals which naturally live and hunt in packs in the wild, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, Oceania, Africa, and Asia, colonizing and opening trade routes. They brought much of the Americas under the dominion of Spain and Portugal. After arrival in the West Indies in 1492, the Spanish, usually led by hidalgos from the west and south of Spain, began building an American empire in the Caribbean using islands such as Hispaniola, Cuba, and Puerto Rico as bases. From 1519 to 1521, Hernán Cortés waged a campaign against the Aztec Empire, ruled by Moctezuma II. From the territories of the Aztec Empire, conquistadors expanded Spanish rule to northern Central America and parts of what is now the southern and western United States, and from Mexico sailing the Pacific Ocean to the Philippines. Other conquistadors took over the Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)


