|
Normanist Theory
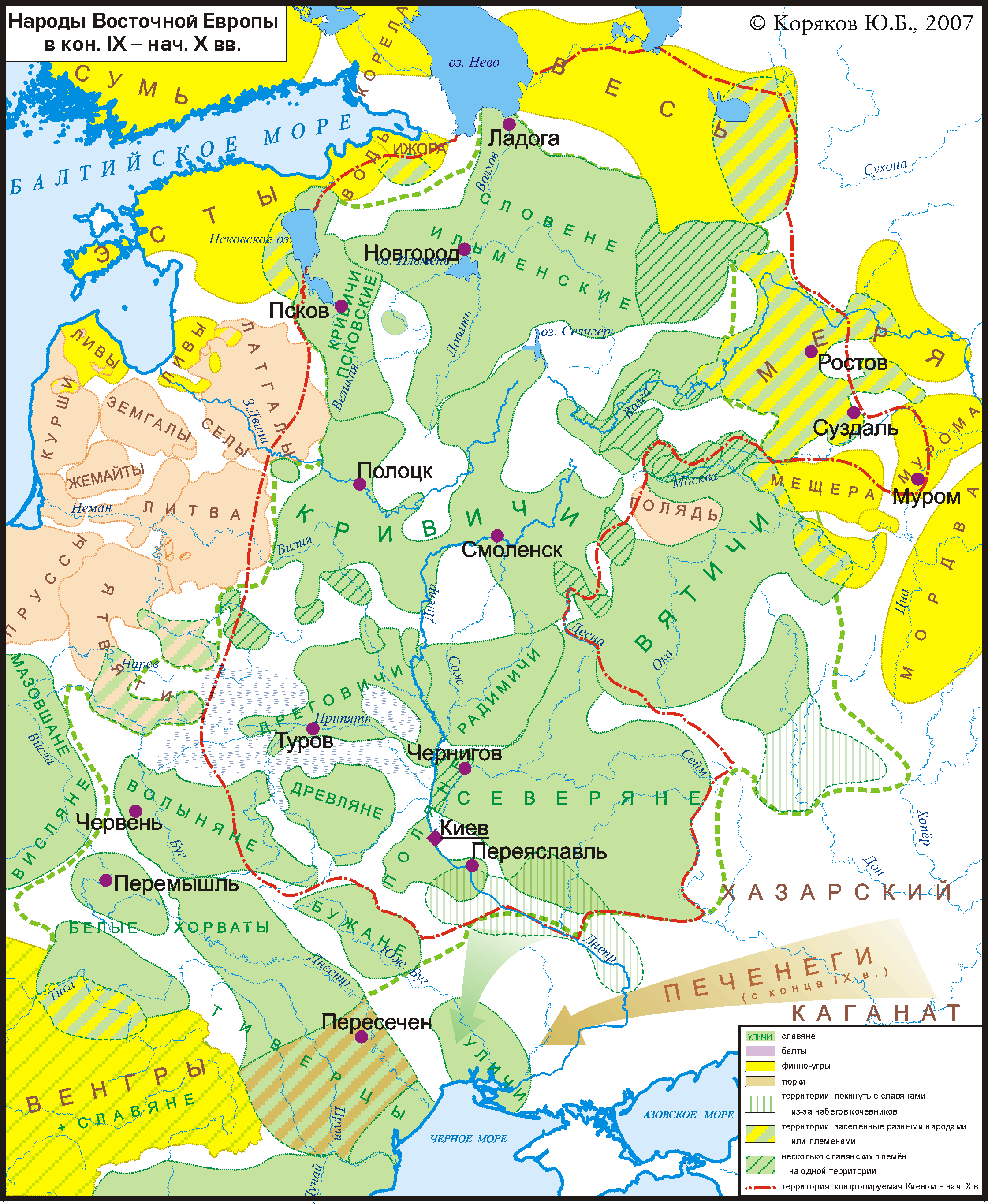
Anti-Normanism is a movement of historical revisionism in opposition to the mainstream narrative of the Viking Age in Eastern Europe, and concerns the origin of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and their historic predecessor, Kievan Rus'. At the centre of the disagreement is the Rus' people, a people generally considered to be of Scandinavian origin and who arrived in Eastern Europe in the 8th and 9th centuries, but who during the 10th and 11th centuries merged with Fenno-Ugrics, Balts and East Slavs, and together with them formed Kievan Rus' with Old East Slavic as a common language, and with the name Rus' as a common marker of identity. The origin of Kievan Rus' is infamously contentious, and relates to its perceived importance for the legitimation of nation-building, imperialism, and independence movements within the Slavic-speaking world, and for legitimating different political relationships between eastern and western European countries. The Norsemen that ventured into the waterw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stepan Krasheninnikov
Stepan Petrovich Krasheninnikov (russian: Степа́н Петро́вич Крашени́нников; – ) was a Russian explorer of Siberia, naturalist and geographer who gave the first full description of Kamchatka in the early 18th century. He was elected to the Russian Academy of Sciences in 1745. The Krasheninnikov Volcano on Kamchatka is named in his honour. Early life Krasheninnikov was educated in the Slavic Greek Latin Academy of Moscow (1724–32), where Lomonosov was his class-mate. As part of Vitus Bering’s extensive preparations for the Second Kamchatka Expedition, 12 students from the academy were selected as potential student interns or assistants for the professors – Krasheninnikov being one of them. Thus, he furthered his education in St Petersburg before embarking upon the Second Kamchatka Expedition (1731–42). The Second Kamchatka Expedition Krasheninnikov was to study plants, animals and minerals, but in addition he developed a strong interes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov (; russian: Михаил (Михайло) Васильевич Ломоносов, p=mʲɪxɐˈil vɐˈsʲilʲjɪvʲɪtɕ , a=Ru-Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov.ogg; – ) was a Russian Empire, Russian polymath, scientist and writer, who made important contributions to literature, education, and science. Among his discoveries were the atmosphere of Venus and the law of conservation of mass in chemical reactions. His spheres of science were natural science, chemistry, physics, mineralogy, history, art, philology, optical devices and others. The founder of modern geology,Vernadsky, V. (1911) Pamyati M.V. Lomonosova. Zaprosy zhizni, 5: 257-262 (in Russian) [In memory of M.V. Lomonosov] Lomonosov was also a poet and influenced the formation of the modern Russian language, Russian literary language. Early life and family Lomonosov was born in the village of Kholmogorsky District, Mishaninskaya (later renamed Lomonosovo, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Lomonosovo in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Of Russia
Elizabeth Petrovna (russian: Елизаве́та (Елисаве́та) Петро́вна) (), also known as Yelisaveta or Elizaveta, reigned as Empress of Russia from 1741 until her death in 1762. She remains one of the most popular Russian monarchs because of her decision not to execute a single person during her reign, her numerous construction projects, and her strong opposition to Prussian policies. The second-eldest daughter of Tsar Peter the Great (), Elizabeth lived through the confused successions of her father's descendants following her half-brother Alexei's death in 1718. The throne first passed to her mother Catherine I of Russia (), then to her nephew Peter II, who died in 1730 and was succeeded by Elizabeth's first cousin Anna. After the brief rule of Anna's infant great-nephew, Ivan VI, Elizabeth seized the throne with the military's support and declared her own nephew, the future Peter III, her heir. During her reign Elizabeth continued the policies of he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirill Razumovski
Count Kirill Grigoryevich Razumovski, anglicized as Cyril Grigoryevich Razumovski (russian: Кирилл Григорьевич Разумовский, uk, Кирило Григорович Розумовський ''Kyrylo Hryhorovych Rozumovsky''; 18 March 1728 – 1 January 1803) was a Russian Imperial statesman of Ukrainian Cossack descent, who served as the last Hetman of Zaporozhian Host on both sides of the Dnieper (from 1750 until 1764) and then as a Field marshal in the Russian Imperial Army. Razumovsky was the President of the St. Petersburg Imperial Academy of Sciences from 1746 until 1798. Biography Razumovsky was born to a family of low rank Cossack Hryhoriy Rozum in Lemeshi Russian Empire, Kiev Regiment on 18 March 1728.Putro, O. Kyrylo Rozumovsky (РОЗУМОВСЬКИЙ КИРИЛО ГРИГОРОВИЧ)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. The village Lemeshi where Razumovsky was born to this day stands in Chernihiv Raion, Chernihiv Oblast, Ukraine. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rurikid Dynasty
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was a noble lineage founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who established himself in Novgorod around the year AD 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' (after the conquest of Kiev by Oleg of Novgorod in 882) before it Kievan Rus'#Final disintegration, finally disintegrated in the mid-13th century, as well as the successor Rus' principalities and Rus' prince republics of Novgorod Republic, Novgorod, Pskov Republic, Pskov, Vladimir-Suzdal, Ryazan Principality, Ryazan, Principality of Smolensk, Smolensk, Galicia-Volhynia (after 1199), Principality of Chernigov, Chernigov, and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (from 1263). Following the disintegration of Kievan Rus', the most powerful state to eventually arise was the Grand Duchy of Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ''Primary Chronicle'', as well as also, after the author it has traditionally been ascribed to, '' Nestor's Chronicle'', is an Old East Slavic chronicle (letopis) of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110, originally compiled in Kiev around 1113. The work’s name originates from the opening sentence of the text, which reads: “These are the narratives of bygone years regarding the origin of the land of Rus’ ( Old East Slavic: Рѹсь), the first princes of Kyiv, and from what source the land of Rus’ had its beginning.” The work has long been considered to be a fundamental source in the interpretation of the history of the East Slavs. The ''Chronicle's'' content is known today from several surviving editions and codices that have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottlieb-Siegfried Bayer
Theophilus (Gottlieb) Siegfried Bayer (1694–1738), was a German classical scholar with specialization in Sinology. He was a Sinologist and professor of Greek and Roman Antiquities at St Petersburg Academy of Sciences between 1726 and 1737. Personal details Bayer was a native of Königsberg, East Prussia. His father Johann Friedrich was from the German Protestant minority in Hungary, but had moved to East Prussia where he worked as a painter. The youthful T. S. Bayer was an excellent student at the University of Königsberg, studying Latin, Greek and Hebrew. He was a Rector of the Königsberg Cathedral from 1721 to 1726, and also worked as a librarian at the Königsberg Public Library. Bayer collection He had a library of more than 200 manuscripts, Chinese and other Oriental books, including: * Telugu and Tamil Palm-leaf manuscripts * Oriental history and philology-related notes * Correspondence with Jesuits in Peking. After his death in Saint Petersburg his widow handed over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the Academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the Academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the Academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The Academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhardt Friedrich Müller
Gerhardt is a masculine name of Germanic origin. It can refer to the following: As a first name * Ants Eskola (1908–1989), Soviet-Estonian actor and singer born Gerhardt Esperk * Gerhardt Laves (1906–1993), American linguist * Gerhardt Neef (1946–2010), German footballer As a surname *Alban Gerhardt (born 1969), German cellist *Anna Gerhardt (born 1998), German association football player *Carl Jakob Adolf Christian Gerhardt (1833–1902), German internist *Charles Gerhardt (conductor) (1927–1999), American conductor *Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (1816–1856), French chemist *Charles H. Gerhardt (1895–1976), American general *Dieter Gerhardt (born 1935), commodore in the South African Navy and Soviet spy *Elena Gerhardt (1883–1961), German singer *Hans-Jürgen Gerhardt (born 1954), East German bobsledder *Ida Gerhardt (1905–1997), Dutch poet *Joe Gerhardt (1855–1922), Major League Baseball player *Joseph Gerhardt (1817–1881), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Norse people) were a North Germanic ethnolinguistic group of the Early Middle Ages, during which they spoke the Old Norse language. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages and is the predecessor of the modern Germanic languages of Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a large-scale expansion in all directions, giving rise to the Viking Age. In English-language scholarship since the 19th century, Norse seafaring traders, settlers and warriors have commonly been referred to as Vikings. Historians of Anglo-Saxon England distinguish between Norse Vikings (Norsemen) from Norway who mainly invaded and occupied the islands north and north-west of Britain, Ireland and western Britain, and Danish Vikings, who principally invaded and occupied eastern Britain. Modern descendants of Norsemen are the Danes, Icelanders, Faroe Islanders, Norwegians, and Swedes, who are now generally referred to as "Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)





