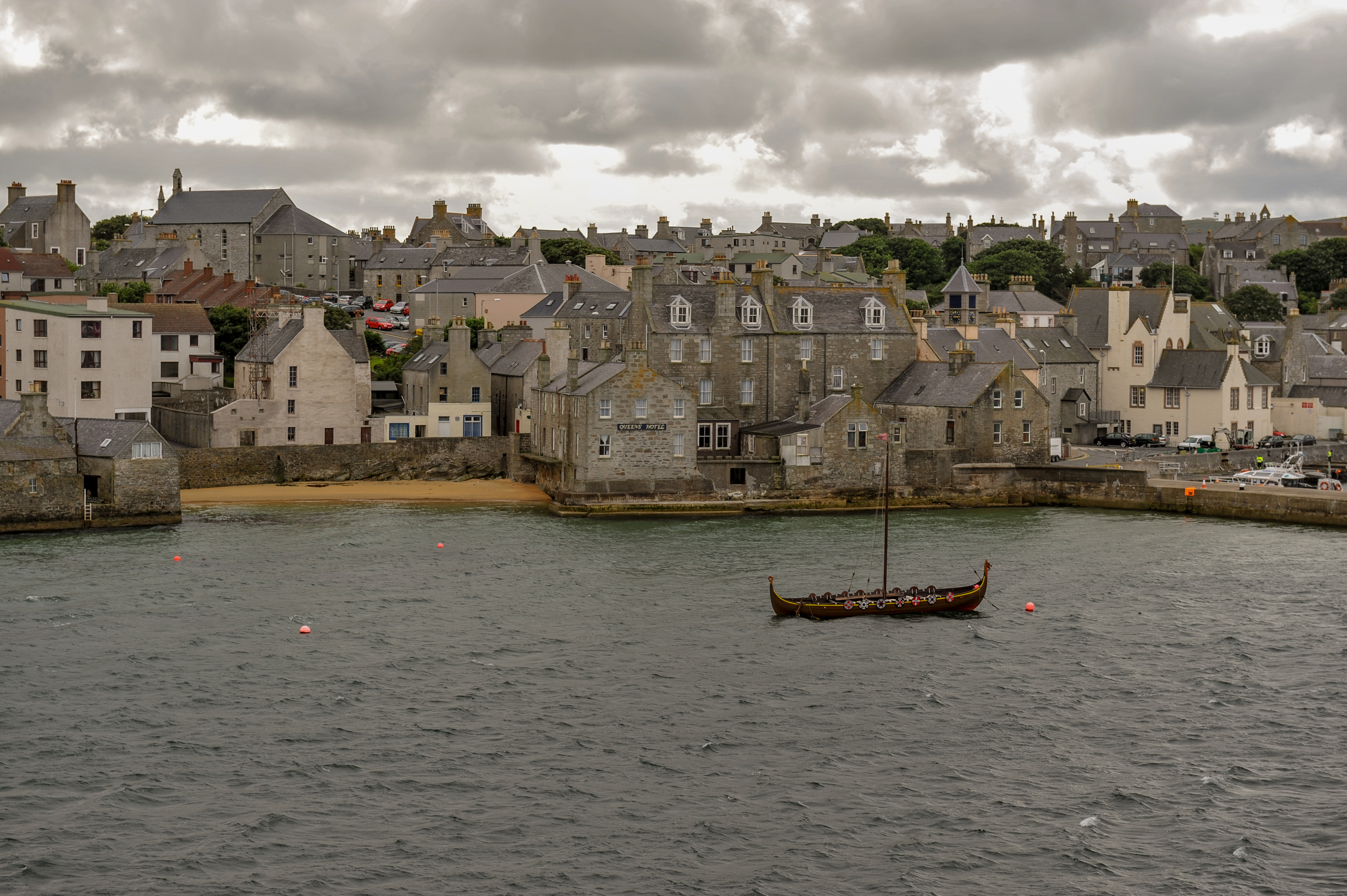|
Norman Lamont (1942)
Norman Stewart Hughson Lamont, Baron Lamont of Lerwick, (born 8 May 1942) is a British politician and former Conservative MP for Kingston-upon-Thames. He served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1990 until 1993. He was created a life peer in 1998. Lamont was a supporter of the Eurosceptic organisation Leave Means Leave. Early life Lamont was born in Lerwick, in the Shetland Islands, where his father was the islands' surgeon. He was educated at Loretto School, Musselburgh, Scotland, and read economics at Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge, where he was Chairman of the Cambridge University Conservative Association and President of the Cambridge Union Society in 1964. Corporate career Before entering Parliament he worked for N M Rothschild & Sons, the investment bank, and became director of Rothschild Asset Management. Lamont currently, in addition to his role as a working peer, is a director of and a consultant to various companies in the financial sector. He is a director of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' ( abbreviation: ''Rt Hon.'' or variations) is an honorific style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire and the Commonwealth of Nations. The term is predominantly used today as a style associated with the holding of certain senior public offices in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and to a lesser extent, Australia. ''Right'' in this context is an adverb meaning 'very' or 'fully'. Grammatically, ''The Right Honourable'' is an adjectival phrase which gives information about a person. As such, it is not considered correct to apply it in direct address, nor to use it on its own as a title in place of a name; but rather it is used in the third person along with a name or noun to be modified. ''Right'' may be abbreviated to ''Rt'', and ''Honourable'' to ''Hon.'', or both. ''The'' is sometimes dropped in written abbreviated form, but is always pronounced. Countries with common or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alex Eadie
Alexander Eadie (23 June 192026 January 2012), known as Alex Eadie, was a Scottish Labour politician. Early life Born in Buckhaven, Fife, he was the son of a coal miner, who was later killed in a pit accident. Educated at Buckhaven Senior Secondary School, he left school aged 14 to work part-time at Lochhead Colliery, while he trained as a mining engineer. Eadie stood for the Scottish presidency of the National Union of Mineworkers in 1961 against Alex Moffat, brother of the outgoing president Abe Moffat. Media commentators gave him little chance as a Fabian Society member in a union executive dominated by communists, but he came within 3,000 votes of victory. He was subsequently in 1965 elected to the Scottish NUM executive, representative for the county of Clackmannanshire. Political career Eadie joined the Scottish Labour Party in 1943, and was elected Scottish president of the Young Co-Operators in 1945. He later served as a member of the SLP Executive. He was a coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Peer
In the United Kingdom, life peers are appointed members of the peerage whose titles cannot be inherited, in contrast to hereditary peers. In modern times, life peerages, always created at the rank of baron, are created under the Life Peerages Act 1958 and entitle the holders to seats in the House of Lords, presuming they meet qualifications such as age and citizenship. The legitimate children of a life peer are entitled to style themselves with the prefix "The Honourable", although they cannot inherit the peerage itself. Before 1887 The Crown, as '' fount of honour'', creates peerages of two types, being hereditary or for life. In the early days of the peerage, the Sovereign had the right to summon individuals to one Parliament without being bound to summon them again. Over time, it was established that once summoned, a peer would have to be summoned for the remainder of their life, and later, that the peer's heirs and successors would also be summoned, thereby firmly entren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge
Fitzwilliam College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college traces its origins back to 1869 and the foundation of the Non-Collegiate Students Board, a venture intended to offer academically excellent students of all backgrounds a chance to study at the university. The institution was originally based at Fitzwilliam Hall (later renamed Fitzwilliam House), opposite the Fitzwilliam Museum in south-west Cambridge. Having moved to its present site in the north of the city, Fitzwilliam attained collegiate status in 1966. Female undergraduates were first admitted in 1978, around the time most colleges were first admitting women. Fitzwilliam is now home to around 475 undergraduates, 500 graduate students and 90 fellows. By overall student numbers, it is the seventh-largest college in Cambridge as of 2018/19. Notable alumni of Fitzwilliam College include six Nobel Laureates, a large number of prominent academics, public officials, businesspeople, clergy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loretto School
Loretto School, founded in 1827, is an independent boarding and day school for boys and girls aged 0 to 18. The campus occupies in Musselburgh, East Lothian, Scotland. History The school was founded by the Reverend Thomas Langhorne in 1827. Langhorne came from Crosby Ravensworth in Westmorland. He named the school for Loretto House, his then home, which was itself named for a medieval chapel dedicated to Our Lady of Loreto which had formerly stood on the site of the school. The school was later taken over by his son, also Thomas Langhorne. The last link with the Langhorne family was Thomas' son John, who was a master at Loretto from 1890 to 1897, and later headmaster at John Watson's Institution. Loretto was later under the headmastership of Dr. Hely Hutchinson Almond from 1862 to 1903. In the 1950s the school increased the accommodation in science laboratories, established arts as a part of the curriculum and introduced the chapel service as part of the daily school life. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Party (UK)
The Conservative Party, officially the Conservative and Unionist Party and also known colloquially as the Tories, is one of the Two-party system, two main political parties in the United Kingdom, along with the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party. It is the current Government of the United Kingdom, governing party, having won the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 general election. It has been the primary governing party in Britain since 2010. The party is on the Centre-right politics, centre-right of the political spectrum, and encompasses various ideological #Party factions, factions including One-nation conservatism, one-nation conservatives, Thatcherism, Thatcherites, and traditionalist conservatism, traditionalist conservatives. The party currently has 356 Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament, 264 members of the House of Lords, 9 members of the London Assembly, 31 members of the Scottish Parliament, 16 members of the Senedd, Welsh Parliament, 2 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom. The islands lie about to the northeast of Orkney, from mainland Scotland and west of Norway. They form part of the border between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. Their total area is ,Shetland Islands Council (2012) p. 4 and the population totalled 22,920 in 2019. The islands comprise the Shetland (Scottish Parliament constituency), Shetland constituency of the Scottish Parliament. The local authority, the Shetland Islands Council, is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. The islands' administrative centre and only burgh is Lerwick, which has been the capital of Shetland since 1708, before which time the capital was Scalloway. The archipelago has an oceanic climate, complex geology, rugged coastline, and many low, rolling hills. The lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lerwick
Lerwick (; non, Leirvik; nrn, Larvik) is the main town and port of the Shetland archipelago, Scotland. Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick had a population of about 7,000 residents in 2010. Centred off the north coast of the Scottish mainland and on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland, Lerwick lies north-by-northeast of Aberdeen; west of the similarly sheltered port of Bergen in Norway; and south east of Tórshavn in the Faroe Islands. One of the UK's coastal weather stations is situated there, with the local climate having small seasonal variation due to the maritime influence. Being located further north than Saint Petersburg and the three mainland Nordic capitals, Lerwick's nights in the middle of summer only get dark twilight and winters have below six hours of complete daylight. History Lerwick is a name with roots in Old Norse and its local descendant, Norn, which was spoken in Shetland until the mid-19th century. The name "Lerwick" means ''bay of clay''. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Commissions (United Kingdom)
The boundary commissions in the United Kingdom are non-departmental public bodies responsible for determining the boundaries of constituencies for elections to the House of Commons. There are four boundary commissions: * Boundary Commission for England * Boundary Commission for Scotland * Boundary Commission for Wales * Boundary Commission for Northern Ireland Each commission comprises four members, three of whom take part in meetings. The Speaker of the House of Commons is ''ex officio'' chairman of each of the boundary commissions. However, the Speaker does not play any part in proceedings, and a Justice is appointed to each boundary commission as Deputy Chairman Commissioner. Considerations and process The boundary commissions, which are required to report every eight years, must apply a set series of rules when devising constituencies. These rules are set out in the Parliamentary Constituencies Act 1986, as amended by the Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Boyd-Carpenter, Baron Boyd-Carpenter
John Archibald Boyd-Carpenter, Baron Boyd-Carpenter, PC, DL (2 June 1908 – 11 July 1998) was a British Conservative politician. Early life He was the only son of Conservative politician Sir Archibald Boyd-Carpenter MP and his wife Annie Dugdale. He was educated at Stowe School, Buckinghamshire, and at Balliol College, Oxford, where he was President of the Oxford Union in 1930. He graduated with a BA in History, and a Diploma in Economics in 1931. He was Harmsworth Law Scholar at the Middle Temple in 1933 and called to Bar the next year, and practised in the London and South-East Circuit. War service Boyd-Carpenter joined the Scots Guards in 1940 and held various staff appointments, including with the Allied Military Government in Italy, retiring with the rank of Major. Political career Boyd-Carpenter contested the Limehouse district for the London County Council in 1934. He was elected as Conservative Member of Parliament for Kingston-upon-Thames in 1945, holding the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston-upon-Thames (UK Parliament Constituency)
Kingston or Kingston-upon-Thames was a parliamentary constituency which covered the emerging southwest, outer London suburb of Kingston upon Thames (until 1965 in Surrey) and which existed between 1885 and 1997 and returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the UK Parliament. The Conservative candidate won each election during its 112-year existence. History The seated was created for the 1885 general election as a county division called Kingston equivalent to the northwest corner of the former two-seat Mid Surrey division. It became a borough constituency for the present purposes of election expenses and type of returning officer at the 1918 general election, when it was formally renamed Kingston-upon-Thames. It was abolished for the 1997 general election. Its territory was then divided between the new constituencies of Kingston and Surbiton and Richmond Park. The constituency's most high-profile MP was the Conservative Norman Lamont, who was Chancel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of Parliament (United Kingdom)
In the United Kingdom, a member of Parliament (MP) is an individual elected to serve in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Electoral system All 650 members of the UK House of Commons are elected using the first-past-the-post voting system in single member constituencies across the whole of the United Kingdom, where each constituency has its own single representative. Elections All MP positions become simultaneously vacant for elections held on a five-year cycle, or when a snap election is called. The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 set out that ordinary general elections are held on the first Thursday in May, every five years. The Act was repealed in 2022. With approval from Parliament, both the 2017 and 2019 general elections were held earlier than the schedule set by the Act. If a vacancy arises at another time, due to death or resignation, then a constituency vacancy may be filled by a by-election. Under the Representation of the People Act 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)