|
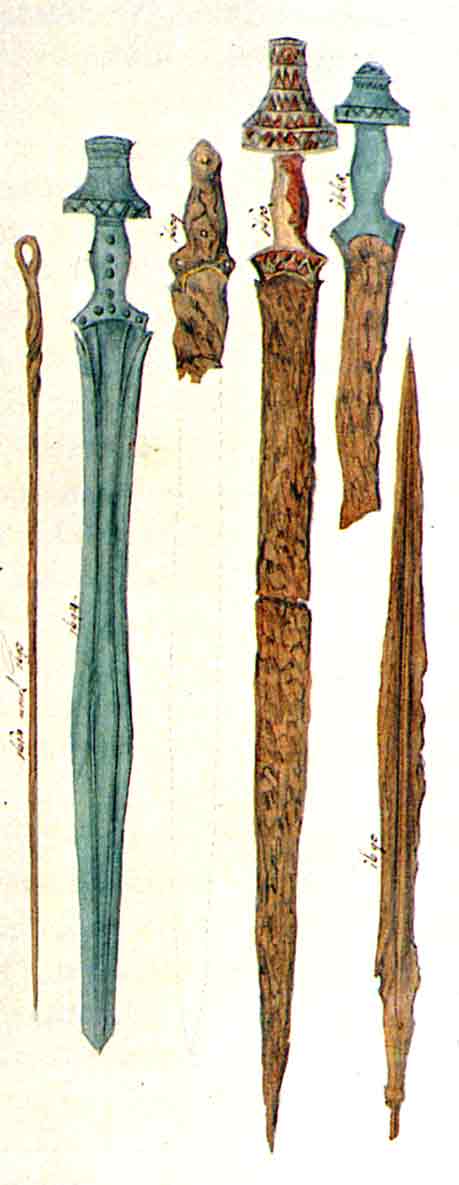
Noric Steel
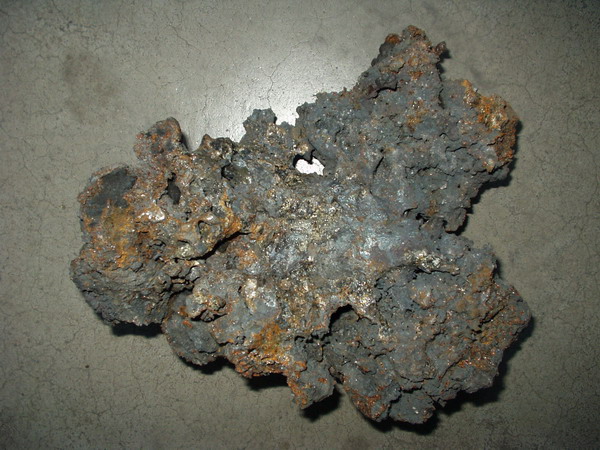
Noric steel was a steel from Noricum, a Celtic kingdom located in modern Austria and Slovenia. The proverbial hardness of Noric steel is expressed by Ovid: ''"...durior ..ferro quod noricus excoquit ignis..."'' which roughly translates to "...harder than iron which Noric fire tempers Anaxarete.html" ;"title="as Anaxarete">as Anaxarete towards the advances of Iphis]..." and it was widely used for the weapons of the Roman military after Noricum joined the Empire in 16 BC. The iron ore was quarried at two mountains in modern Austria still called ''Erzberg'' "ore mountain" today, one at Hüttenberg, Carinthia and the other at Eisenerz, Styria, separated by . The latter is the site of the modern Erzberg mine. Buchwald identifies a sword of found in Krenovica, Moravia as an early example of Noric steel due to a chemical composition consistent with Erzberg ore. A more recent sword, dating to and found in Zemplin, eastern Slovakia, is of extraordinary length for the period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zemplín (region)
Zemplín is the name of an informal traditional region located in eastern Slovakia. It includes the Slovak part of the former Zemplén county, often including the Slovak part of the Ung county (Slovak: ''Užská župa''/''Užský komitát''). Geography Zemplín region stretches from the Carpathian Mountains in the north to the lowest point in Slovakia at AMSL. The region is situated in the easternmost part of Slovakia (except for the region between Vihorlatské vrchy and the Latorica river, if the former territory of Ung county isn't included). Rivers in the region include: Bodrog, Laborec, Latorica, Uzh, Ondava and a small part of the Tisza river. Zemplín is no longer an administrative region, but is divided between two of the 21 official tourism regions, Lower Zemplín and Upper Zemplín. Administratively, the region is divided between Košice Region, which includes Trebišov and the western part of Michalovce District (if Ung county is included, eastern part of Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Danish Academy Of Sciences And Letters
{{Infobox organization , name = The Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters , full_name = , native_name = Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab , native_name_lang = , logo = Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters seal.svg , logo_size = 150 , logo_alt = , logo_caption = , image = Carlsbergfondet.JPG , image_size = , alt = , caption = The building on H.C. Andersens Boulevard. , map = , map_size = , map_alt = , map_caption = , map2 = , map2_size = , map2_alt = , map2_caption = , abbreviation = , nickname = , pronounce = , pronounce ref = , pronounce comment = , pronounce 2 = , named_after = , motto = , predecessor = , merged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
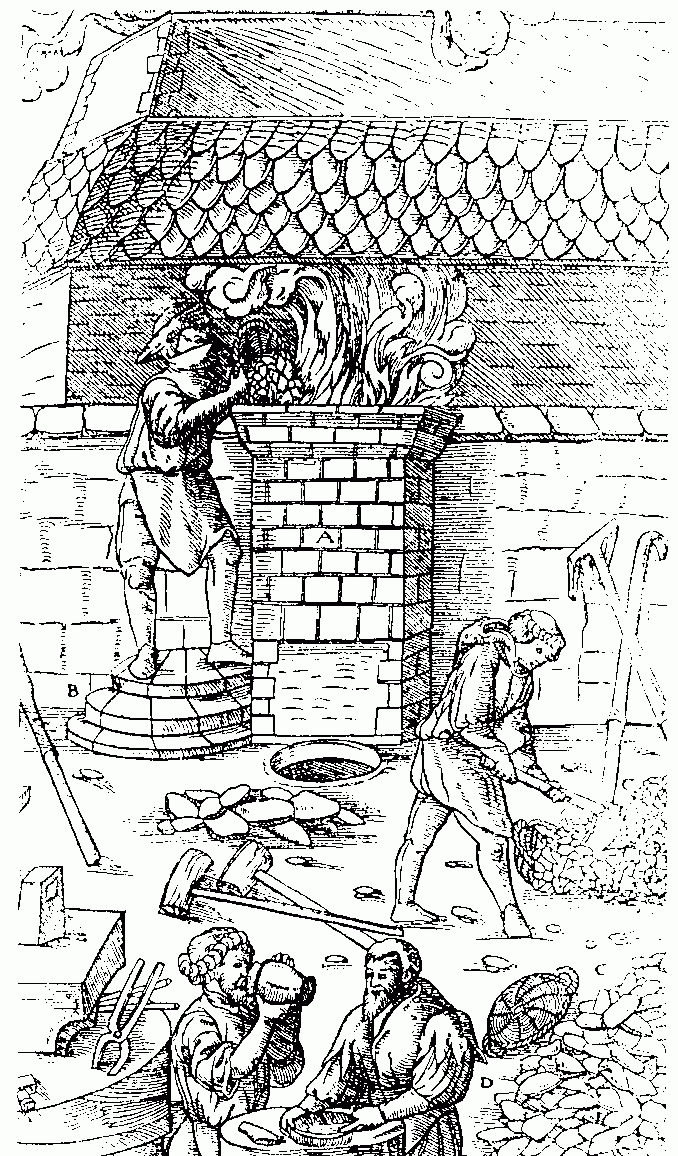
Crucible Steel
Crucible steel is steel made by melting pig iron (cast iron), iron, and sometimes steel, often along with sand, glass, ashes, and other fluxes, in a crucible. In ancient times steel and iron were impossible to melt using charcoal or coal fires, which could not produce temperatures high enough. However, pig iron, having a higher carbon content and thus a lower melting point, could be melted, and by soaking wrought iron or steel in the liquid pig-iron for a long time, the carbon content of the pig iron could be reduced as it slowly diffused into the iron, turning both into steel. Crucible steel of this type was produced in South and Central Asia during the medieval era. This generally produced a very hard steel, but also a composite steel that was inhomogeneous, consisting of a very high-carbon steel (formerly the pig-iron) and a lower-carbon steel (formerly the wrought iron). This often resulted in an intricate pattern when the steel was forged, filed or polished, with possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamahagane Steel
''Tamahagane'' (玉鋼) is a type of steel made in the Japanese tradition. The word ''tama'' means "precious". The word ''hagane'' means "steel". Tamahagane is used to make Japanese swords, knives, and other kinds of tools. The carbon content of the majority of analyzed Japanese swords historically lies between 0.5–0.7 mass%; however, the range extends up to 1.5%. Production Tamahagane is made of an iron sand (''satetsu'') found in Shimane, Japan. There are two main types of iron sands: ''akame satetsu'' (赤目砂鉄) and ''masa satetsu'' (真砂砂鉄). Akame is lower quality, masa is better quality. The 'murage' decides the amount of the mixing parts. Depending on the desired result, the murage mixes one or more types of sands. The iron sand is put in a tatara, a clay tub furnace. The clay tub measures about tall, long and {{convert, 4, ft, m wide. The tub is dried and heated to about 1,000 ° C (1800 ° F). Then, it is mixed with charcoal to add carbon to the ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulat Steel
Bulat is a type of steel alloy known in Russia from medieval times; it was regularly mentioned in Russian legends as the material of choice for cold steel. The name ''булат'' is a Russian transliteration of the Persian word ''fulad'', meaning steel. This type of steel was used by the armies of nomadic peoples. Bulat steel was the main type of steel used for swords in the armies of Genghis Khan. Bulat Steel is generally agreed to be a Russian name for wootz steel, the production method of which has been lost for centuries, and the bulat steel used today makes use of a more recently developed technique. History The secret of bulat manufacturing was lost by the beginning of the 19th century. It is known that the process involved dipping the finished weapon into a vat containing a special liquid of which spiny restharrow extract was a part (the plant's name in Russian, ''stalnik'', reflects its historical role), then holding the sword aloft while galloping on a horse, allowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wootz Steel
Wootz steel, also known as Seric steel, is a crucible steel characterized by a pattern of bands and high carbon content. These bands are formed by sheets of microscopic carbides within a tempered martensite or pearlite matrix in higher carbon steel, or by ferrite and pearlite banding in lower carbon steels. It was a pioneering steel alloy developed in India in the mid-1st millennium BC and exported globally. History Wootz steel originated in the mid-1st millennium BC in South India, in present-day Tiruchirappalli, Kodumanal, Erode, Tamil Nadu. There are several ancient Tamil, North Indian, Greek, Chinese and Roman literary references to high carbon Tamil steel. In later times, wootz steel was also made in Golconda in Telangana, Karnataka and Sri Lanka. The steel was exported as cakes of steely iron that came to be known as "Wootz". The method was to heat black magnetite ore in the presence of carbon in a sealed clay crucible inside a charcoal furnace to completely remov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus Steel
Damascus steel was the forged steel of the blades of swords smithed in the Near East from ingots of Wootz steel either imported from Southern India or made in production centres in Sri Lanka, or Khorasan, Iran. These swords are characterized by distinctive patterns of banding and mottling reminiscent of flowing water, sometimes in a "ladder" or "rose" pattern. Such blades were reputed to be tough, resistant to shattering, and capable of being honed to a sharp, resilient edge. Wootz (Indian), Pulad (Persian), Fuladh (Arabic), Bulat (Russian) and Bintie (Chinese) are all names for historical ultra-high carbon crucible steel typified by carbide segregation. "Wootz" is an erroneous transliteration of "utsa" or "fountain" in Sanskrit, however since 1794 it has been the primary word used to refer to historical hypereutectoid crucible steel. History Origins The origin of the name "Damascus Steel" is contentious: the Islamic scholars al-Kindi (full name Abu Ya'qub ibn Ishaq al-Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toledo Steel
Toledo steel, historically known for being unusually hard, is from Toledo, Spain, which has been a traditional sword-making, metal-working center since about the Roman period, and came to the attention of Rome when used by Hannibal in the Punic Wars. It soon became a standard source of weaponry for Roman legions. Toledo steel was famed for its high quality alloy. History The name "Toledo steel" comes from the city where these special steel products were most-notably crafted: Toledo, Spain. Toledo steel forging techniques were developed from ancient Spanish customs and used to forge many different types of weapons over the course of many centuries. In simple terms, the Toledo steel technique consisted of a steel blade that enveloped a wrought iron strip, thus preventing the steel from bending or cracking. As such, the strong and durable Toledo steel weapons were said to have had a "soul of iron". In ancient Iberia, blacksmiths in Toledo applied their unique method of forging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ferrous Metallurgy
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ores began, but by the end of the 2nd millennium BC iron was being produced from iron ores in the region from Greece to India,Riederer, Josef; Wartke, Ralf-B.: "Iron", Cancik, Hubert; Schneider, Helmuth (eds.): Brill's New Pauly, Brill 2009Early Antiquity By I.M. Drakonoff. 1991. University of Chicago Press. . p. 372 and Sub-Saharan Africa. The use of wrought iron (worked iron) was known by the 1st millennium BC, and its spread defined the Iron Age. During the medieval period, smiths in Europe found a way of producing wrought iron from cast iron (in this context known as pig iron) using finery forges. All these processes required charcoal as fuel. By the 4th century BC southern India had started exporting Wootz steel (with a carbon c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and the Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Austria, England, Southern Germany, the Czech Republic, parts of Northern Italy and Central Italy, Slovenia and Hungary, as well as adjacent parts of the Netherlands, Slovakia, Serbia, Croatia, Transylvania (western Romania), and Transcarpathia (western Ukraine). The Celtiberians of western Iberia shared many aspects of the culture, though not generally the artistic style. To the north extended the contemporary P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age Sword
Swords made of iron (as opposed to bronze) appear from the Early Iron Age (c. 12th century BC), but do not become widespread before the 8th century BC. Early Iron Age swords were significantly different from later steel swords. They were work-hardened, rather than quench-hardened, which made them about the same or only slightly better in terms of strength and hardness to earlier bronze swords. This meant that they could still be bent out of shape during use. The easier production, however, and the greater availability of the raw material allowed for much larger scale production. Eventually smiths learned of processes to refine smelted iron and make steel. By quenching (making the steel hard and brittle) and tempering (removing the brittleness), swords could be made that would suffer much less damage, and would spring back into shape if bent. It took a long time, however, before this was done consistently, and even until the end of the early medieval period, many swords were stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |