|
Nonlinear System Identification
System identification is a method of identifying or measuring the mathematical model of a system from measurements of the system inputs and outputs. The applications of system identification include any system where the inputs and outputs can be measured and include industrial processes, control systems, economic data, biology and the life sciences, medicine, social systems and many more. A nonlinear system is defined as any system that is not linear, that is any system that does not satisfy the superposition principle. This negative definition tends to obscure that there are very many different types of nonlinear systems. Historically, system identification for nonlinear systemsNelles O. "Nonlinear System Identification: From Classical Approaches to Neural Networks". Springer Verlag, 2001Billings S.A. "Nonlinear System Identification: NARMAX Methods in the Time, Frequency, and Spatio-Temporal Domains". Wiley, 2013 has developed by focusing on specific classes of system and can be br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Identification
The field of system identification uses statistical methods to build mathematical models of dynamical systems from measured data. System identification also includes the optimal design#System identification and stochastic approximation, optimal design of experiments for efficiently generating informative data for regression analysis, fitting such models as well as model reduction. A common approach is to start from measurements of the behavior of the system and the external influences (inputs to the system) and try to determine a mathematical relation between them without going into many details of what is actually happening inside the system; this approach is called Black box (systems), black box system identification. Overview A dynamic mathematical model in this context is a mathematical description of the dynamic behavior of a system or process in either the time or frequency domain. Examples include: * physical system, physical processes such as the movement of a falling bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Networks
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appear to vary in a random manner. Examples include the growth of a bacterial population, an electrical current fluctuating due to thermal noise, or the movement of a gas molecule. Stochastic processes have applications in many disciplines such as biology, chemistry, ecology Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ..., neuroscience, physics, image processing, signal processing, stochastic control, control theory, information theory, computer scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a linear dimensionality reduction technique with applications in exploratory data analysis, visualization and data preprocessing. The data is linearly transformed onto a new coordinate system such that the directions (principal components) capturing the largest variation in the data can be easily identified. The principal components of a collection of points in a real coordinate space are a sequence of p unit vectors, where the i-th vector is the direction of a line that best fits the data while being orthogonal to the first i-1 vectors. Here, a best-fitting line is defined as one that minimizes the average squared perpendicular distance from the points to the line. These directions (i.e., principal components) constitute an orthonormal basis in which different individual dimensions of the data are linearly uncorrelated. Many studies use the first two principal components in order to plot the data in two dimensions and to visually identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature Selection
In machine learning, feature selection is the process of selecting a subset of relevant Feature (machine learning), features (variables, predictors) for use in model construction. Feature selection techniques are used for several reasons: * simplification of models to make them easier to interpret, * shorter training times, * to avoid the curse of dimensionality, * improve the compatibility of the data with a certain learning model class, * to encode inherent Symmetric space, symmetries present in the input space. The central premise when using feature selection is that data sometimes contains features that are ''redundant'' or ''irrelevant'', and can thus be removed without incurring much loss of information. Redundancy and irrelevance are two distinct notions, since one relevant feature may be redundant in the presence of another relevant feature with which it is strongly correlated. Feature extraction creates new features from functions of the original features, whereas feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subharmonics
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of Musical note, notes that results from inversion (music), inverting the intervals of the harmonic series (music), overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the physical production of music on instruments, undertones must be produced in unusual ways. While the overtone series is based upon arithmetic multiplication of frequencies, resulting in a harmonic series (mathematics), harmonic series, the undertone series is based on arithmetic division. Nattiez shows the undertone series on E, as Hugo Riemann, Riemann (''Handbuch der Harmonielehre'', 10th ed., 1929, p. 4) and Vincent d'Indy, D'Indy (''Cours de composition musicale'', vol. I, 1912, p. 100) had done. Terminology The Hybrid word, hybrid term ''subharmonic'' is used in music in a few different ways. In its pure sense, the term ''subharmonic'' refers strictly to any member of the subharmonic series (, , , , etc.). When the subharmonic series is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
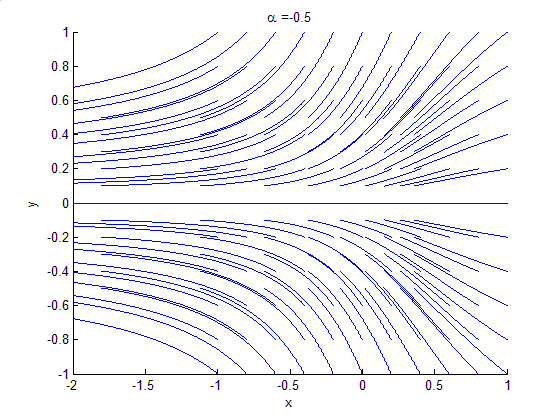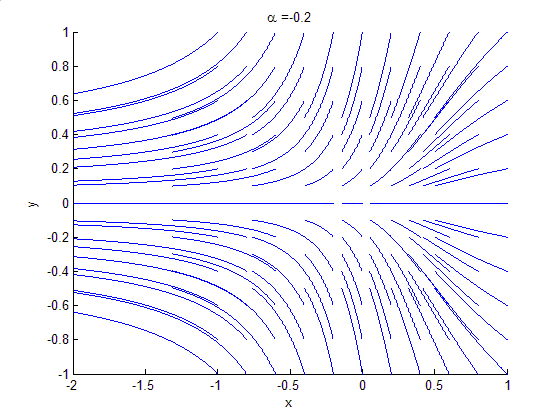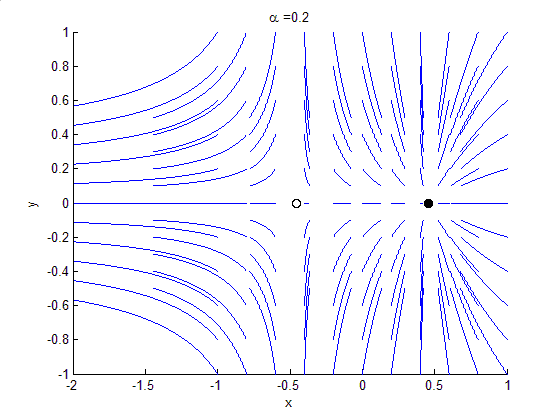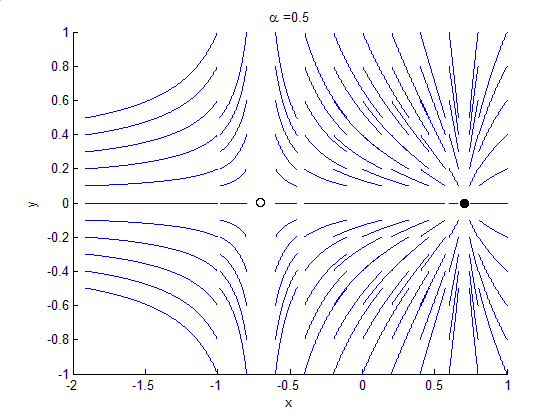
Bifurcation Theory
Bifurcation theory is the Mathematics, mathematical study of changes in the qualitative or topological structure of a given family of curves, such as the integral curves of a family of vector fields, and the solutions of a family of differential equations. Most commonly applied to the mathematics, mathematical study of dynamical systems, a bifurcation occurs when a small smooth change made to the parameter values (the bifurcation parameters) of a system causes a sudden 'qualitative' or topological change in its behavior. Bifurcations occur in both continuous systems (described by Ordinary differential equation, ordinary, Delay differential equation, delay or Partial differential equation, partial differential equations) and discrete systems (described by maps). The name "bifurcation" was first introduced by Henri Poincaré in 1885 in the first paper in mathematics showing such a behavior. Bifurcation types It is useful to divide bifurcations into two principal classes: * Local bif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of Scientific method, scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and Deterministic system, deterministic Scientific law, laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause or prevent a tornado in Texas. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelets
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the number and direction of its pulses. Wavelets are imbued with specific properties that make them useful for signal processing. For example, a wavelet could be created to have a frequency of middle C and a short duration of roughly one tenth of a second. If this wavelet were to be convolution, convolved with a signal created from the recording of a melody, then the resulting signal would be useful for determining when the middle C note appeared in the song. Mathematically, a wavelet correlates with a signal if a portion of the signal is similar. Correlation is at the core of many practical wavelet applications. As a mathematical tool, wavelets can be used to extract information from many kinds of data, including audio signals and imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arises when the brain receives and perceives a sound. Acoustic noise is any sound in the acoustic domain, either deliberate (e.g., music or speech) or unintended. In contrast, noise in electronics may not be audible to the human ear and may require instruments for detection. In audio engineering, noise can refer to the unwanted residual electronic noise signal that gives rise to acoustic noise heard as a hiss. This signal noise is commonly measured using A-weighting or ITU-R 468 weighting. In experimental sciences, noise can refer to any random fluctuations of data that hinders perception of a signal. Measurement Sound is measured based on the amplitude and frequency of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weierstrass
Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass (; ; 31 October 1815 – 19 February 1897) was a German mathematician often cited as the " father of modern analysis". Despite leaving university without a degree, he studied mathematics and trained as a school teacher, eventually teaching mathematics, physics, botany and gymnastics. He later received an honorary doctorate and became professor of mathematics in Berlin. Among many other contributions, Weierstrass formalized the definition of the continuity of a function and complex analysis, proved the intermediate value theorem and the Bolzano–Weierstrass theorem, and used the latter to study the properties of continuous functions on closed bounded intervals. Biography Weierstrass was born into a Roman Catholic family in Ostenfelde, a village near Ennigerloh, in the Province of Westphalia. Karl Weierstrass was the son of Wilhelm Weierstrass and Theodora Vonderforst, the former of whom was a government official and both of whom were Cathol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximation
An approximation is anything that is intentionally similar but not exactly equal to something else. Etymology and usage The word ''approximation'' is derived from Latin ''approximatus'', from ''proximus'' meaning ''very near'' and the prefix ''ad-'' (''ad-'' before ''p'' becomes ap- by assimilation) meaning ''to''. Words like ''approximate'', ''approximately'' and ''approximation'' are used especially in technical or scientific contexts. In everyday English, words such as ''roughly'' or ''around'' are used with a similar meaning. It is often found abbreviated as ''approx.'' The term can be applied to various properties (e.g., value, quantity, image, description) that are nearly, but not exactly correct; similar, but not exactly the same (e.g., the approximate time was 10 o'clock). Although approximation is most often applied to numbers, it is also frequently applied to such things as mathematical functions, shapes, and physical laws. In science, approximation can refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |