|
Nobuyo Maeda
Nobuyo N. Maeda is a Japanese geneticist and medical researcher, who works on complex human diseases including atherosclerosis, diabetes and high blood pressure, and is particularly known for creating the first mouse model for atherosclerosis. Maeda has worked in the United States since 1978; as of 2017, she is the Robert H. Wagner Distinguished Professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Early life and education Maeda was born in Sendai, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan in the early 1950s, the second of three sisters. Her father was a chemical engineering professor. She attended Tohoku University in Sendai, where she received a BSc in chemistry (1972) and an MSc in bio-organic chemistry (1974), followed by a PhD in the same subject in 1977; her thesis was entitled "Isolation and characterization of neurotoxins from the venoms of sea snakes, and the use of amino acid sequences in taxonomy". Career and awards Maeda first briefly worked in the laboratory of Nobuo Tamiy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneticist
A geneticist is a biologist or physician who studies genetics, the science of genes, heredity, and variation of organisms. A geneticist can be employed as a scientist or a lecturer. Geneticists may perform general research on genetic processes or develop genetic technologies to aid in the pharmaceutical or and agriculture industries. Some geneticists perform experiments in model organisms such as ''Drosophila'', ''C. elegans'', zebrafish, rodents or humans and analyze data to interpret the inheritance of biological traits. A basic science geneticist is a scientist who usually has earned a PhD in genetics and undertakes research and/or lectures in the field. A medical geneticist is a physician who has been trained in medical genetics as a specialization and evaluates, diagnoses, and manages patients with hereditary conditions or congenital malformations; and provides genetic risk calculations and mutation analysis. Education Geneticists participate in courses from many are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Evolution
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes. Major topics in molecular evolution concern the rates and impacts of single nucleotide changes, neutral evolution vs. natural selection, origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of speciation, evolution of development, and ways that evolutionary forces influence genomic and phenotypic changes. History The history of molecular evolution starts in the early 20th century with comparative biochemistry, and the use of "fingerprinting" methods such as immune assays, gel electrophoresis and paper chromatography in the 1950s to explore homologous proteins. The field of molecular evolution came into its own in the 1960s and 1970s, following the rise of molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Nobel Foundation
The Nobel Foundation ( sv, Nobelstiftelsen) is a private institution founded on 29 June 1900 to manage the finances and administration of the Nobel Prizes. The foundation is based on the last will of Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite. It also holds Nobel Symposia on important breakthroughs in science and topics of cultural or social significance. History , born on 21 October 1833 in Stockholm Sweden, was a chemist, engineer, innovator, armaments manufacturer and the inventor of dynamite. He owned Bofors, a major armaments manufacturer, which he had redirected from its original business as an iron and steel mill. Nobel held 355 different patents, dynamite being the most famous. Nobel amassed a sizeable personal fortune during his lifetime, thanks mostly to this invention. In 1896 Nobel died of a stroke in his villa in San Remo, Italy where he had lived his final years.AFP"Alfred Nobel's last will and testament", '' The Local''(5 October 2009): accessed 14 January 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesch–Nyhan Syndrome
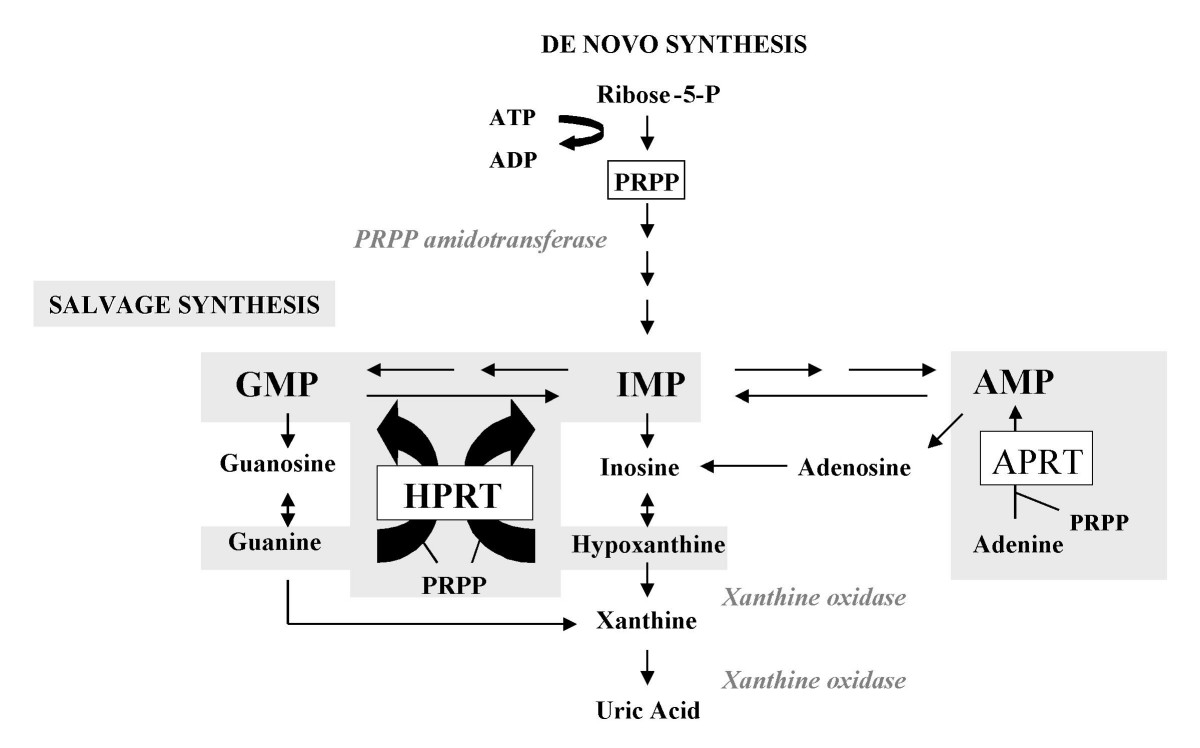
Lesch–Nyhan syndrome (LNS) is a rare inherited disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). This deficiency occurs due to mutations in the ''HPRT1'' gene located on the X chromosome. LNS affects about 1 in 380,000 live births. The disorder was first recognized and clinically characterized by American medical student Michael Lesch and his mentor, pediatrician William Nyhan, at Johns Hopkins. The HGPRT deficiency causes a build-up of uric acid in all body fluids. The combination of increased synthesis and decreased utilization of purines leads to high levels of uric acid production. This results in both high levels of uric acid in the blood and urine, associated with severe gout and kidney problems. Neurological signs include poor muscle control and moderate intellectual disability. These complications usually appear in the first year of life. Beginning in the second year of life, a particularly striking feature of LNS is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxanthine-guanine Phosphoribosyltransferase
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) is an enzyme encoded in humans by the ''HPRT1'' gene. HGPRT is a transferase that catalyzes conversion of hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate and guanine to guanosine monophosphate. This reaction transfers the 5-phosphoribosyl group from 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) to the purine. HGPRT plays a central role in the generation of purine nucleotides through the purine salvage pathway. Function HGPRT catalyzes the following reactions: HGPRTase functions primarily to salvage purines from degraded DNA to reintroduce into purine synthetic pathways. In this role, it catalyzes the reaction between guanine and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form GMP, or between hypoxanthine and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form inosine monophosphate. Substrates and inhibitors Comparative homology modelling of this enzyme in '' L. donovani'' suggest that among all of the computationally screened compounds, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mario Capecchi
Mario Ramberg Capecchi (born 6 October 1937) is an Italian-born molecular geneticist and a co-awardee of the 2007 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discovering a method to create mice in which a specific gene is turned off, known as knockout mice. He shared the prize with Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies. He is currently Distinguished Professor of Human Genetics and Biology at the University of Utah School of Medicine. Life Mario Capecchi was born in Verona, Italy, as the only child of Luciano Capecchi and Lucy Ramberg, an Italian-born daughter of American-born Impressionist painter Lucy Dodd Ramberg and German archaeologist Walter Ramberg. His parents weren't married, and due to the chaos in Europe caused by World War II, the story of his early life is remarkable, but the details are unclear. In 1941 he and his mother were living near Bolzano, about 160 miles north of his father in Reggio Emilia when his mother was arrested and deported for pamphleteering and belonging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses. Horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Targeting
Gene targeting (also, replacement strategy based on homologous recombination) is a genetic technique that uses homologous recombination to modify an endogenous gene. The method can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene and modify individual base pairs (introduce point mutations). The process of gene targeting provides a way to alter specific genes in order to better identify their biological roles. Gene targeting can be permanent or conditional. Conditions can be a specific time during development / life of the organism or limitation to a specific tissue, for example. Gene targeting requires the creation of a specific vector for each gene of interest. However, it can be used for any gene, regardless of transcriptional activity or gene size. Methods In general, DNA containing part of the gene to be targeted, a reporter gene, and a (dominant) selectable marker is assembled in bacteria. Gene targeting methods are established for several model organisms and may vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, And Vascular Biology
''Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology'' (''ATVB'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published on behalf of the American Heart Association by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, an imprint of Wolters Kluwer. It covers basic and clinical research related to vascular biology, pathophysiology and complications of atherosclerosis, and thrombotic mechanisms in blood vessels. The journal was established in 1981 as ''Arteriosclerosis'' (), which was published bimonthly. From 1991 to 1994 it was published monthly under the title ''Arteriosclerosis and Thrombosis: A Journal of Vascular Biology'' (). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 8.311, ranking it 8th in the category "Hematology" and 5th in the category "Peripheral Vascular Disease". Alan Daugherty has been the editor-in-chief since 2012. Open access option ''ATVB'' offers an open access option for full-length, original contributions. The corresponding author may select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haptoglobin
Haptoglobin (abbreviated as Hp) is the protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HP'' gene. In blood plasma, haptoglobin binds with high affinity to ''free'' hemoglobin released from erythrocytes, and thereby inhibits its deleterious oxidative activity. Compared to Hp, hemopexin binds to ''free'' heme. The haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex will then be removed by the reticuloendothelial system (mostly the spleen). In clinical settings, the haptoglobin assay is used to screen for and monitor intravascular hemolytic anemia. In intravascular hemolysis, free hemoglobin will be released into circulation and hence haptoglobin will bind the hemoglobin. This causes a decline in haptoglobin levels. Function Hemoglobin that has been released into the blood plasma by damaged red blood cells has harmful effects. The ''HP'' gene encodes a preproprotein that is processed to yield both alpha and beta chains, which subsequently combines as a tetramer to produce haptoglobin. Haptoglobin function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Family
A gene family is a set of several similar genes, formed by duplication of a single original gene, and generally with similar biochemical functions. One such family are the genes for human hemoglobin subunits; the ten genes are in two clusters on different chromosomes, called the α-globin and β-globin loci. These two gene clusters are thought to have arisen as a result of a precursor gene being duplicated approximately 500 million years ago. Genes are categorized into families based on shared nucleotide or protein sequences. Phylogenetic techniques can be used as a more rigorous test. The positions of exons within the coding sequence can be used to infer common ancestry. Knowing the sequence of the protein encoded by a gene can allow researchers to apply methods that find similarities among protein sequences that provide more information than similarities or differences among DNA sequences. If the genes of a gene family encode proteins, the term '' protein family'' is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange (a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |