|
Lesch–Nyhan Syndrome
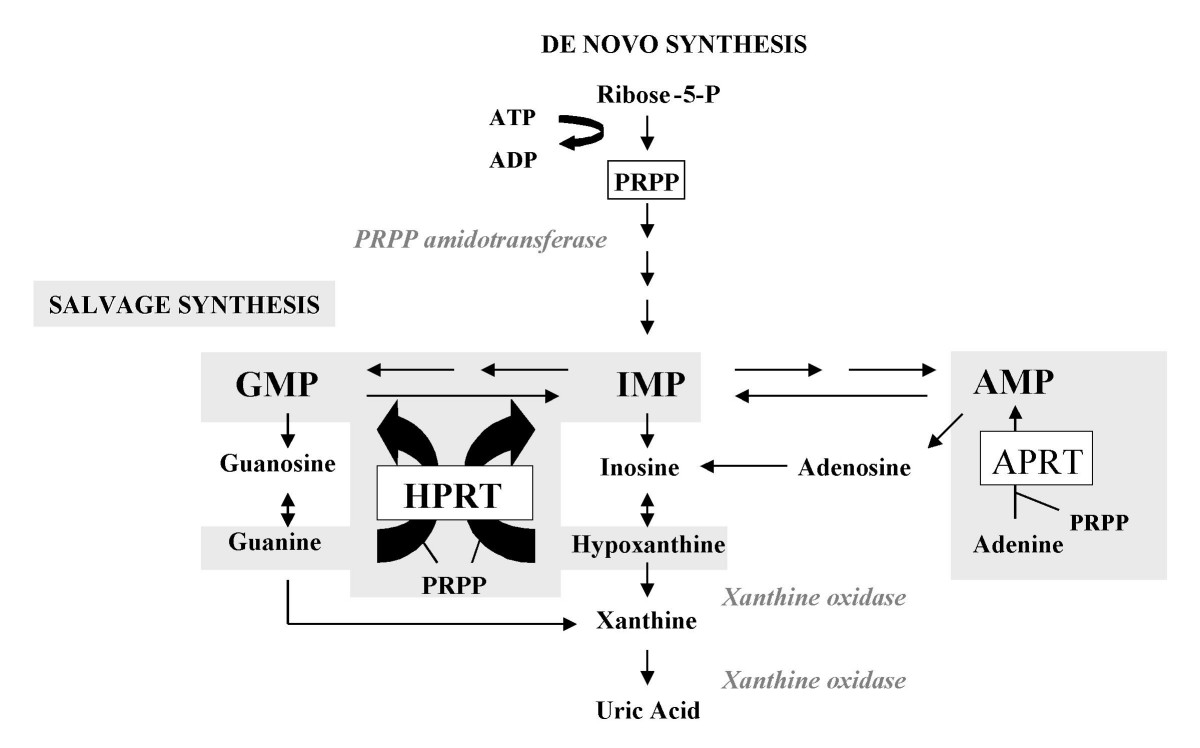
Lesch–Nyhan syndrome (LNS) is a rare inherited disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). This deficiency occurs due to mutations in the '' HPRT1'' gene located on the X chromosome. LNS affects about 1 in 380,000 live births. The disorder was first recognized and clinically characterized by American medical student Michael Lesch and his mentor, pediatrician William Nyhan, at Johns Hopkins. The HGPRT deficiency causes a build-up of uric acid in all body fluids. The combination of increased synthesis and decreased utilization of purines leads to high levels of uric acid production. This results in both high levels of uric acid in the blood and urine, associated with severe gout and kidney problems. Neurological signs include poor muscle control and moderate intellectual disability. These complications usually appear in the first year of life. Beginning in the second year of life, a particularly striking feature of LNS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatophagia
Dermatophagia (from Ancient Greek ''δέρμα'' — ''skin'' and ''φαγεία'' ''eating'') or dermatodaxia (from ''δήξις'', ''biting'') is a compulsion disorder of gnawing or biting one's own skin, most commonly at the fingers. This action can either be conscious or unconscious. Those affected with dermatophagia typically bite the skin around the nails, leading to bleeding and discoloration over time. Some people also bite on their skin on their finger knuckles which can lead to pain and bleeding just by moving their fingers. In herpetology, dermatophagia is used to correctly describe the act in which amphibians and reptiles eat the skin they shed, but this is not what occurs in humans. Those diagnosed with this disorder do not develop wounds on the bitten areas of their hands or lose any skin. Instead, they experience a thickening of the skin being repeatedly bitten. Contemporary research suggests a link between impulse-control disorders and obsessive–compulsive disord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPRT1
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) is an enzyme encoded in humans by the ''HPRT1'' gene. HGPRT is a transferase that catalyzes conversion of hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate and guanine to guanosine monophosphate. This reaction transfers the 5-phosphoribosyl group from 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) to the purine. HGPRT plays a central role in the generation of purine nucleotides through the purine salvage pathway. Function HGPRT catalyzes the following reactions: HGPRTase functions primarily to salvage purines from degraded DNA to reintroduce into purine synthetic pathways. In this role, it catalyzes the reaction between guanine and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form GMP, or between hypoxanthine and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form inosine monophosphate. Substrates and inhibitors Comparative homology modelling of this enzyme in ''L. donovani'' suggest that among all of the computationally screened compounds, pent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etiology (medicine)
Cause, also known as etiology () and aetiology, is the reason or origination of something. The word '' etiology'' is derived from the Greek , ''aitiologia'', "giving a reason for" (, ''aitia'', "cause"; and , '' -logia''). Description In medicine, etiology refers to the cause or causes of diseases or pathologies. Where no etiology can be ascertained, the disorder is said to be idiopathic. Traditional accounts of the causes of disease may point to the "evil eye". The Ancient Roman scholar Marcus Terentius Varro put forward early ideas about microorganisms in a 1st-century BC book titled ''On Agriculture''. Medieval thinking on the etiology of disease showed the influence of Galen and of Hippocrates. Medieval European doctors generally held the view that disease was related to the air and adopted a Miasma theory of disease, miasmatic approach to disease etiology. Etiological discovery in medicine has a history in Robert Koch's demonstration that species of the pathogenic b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntington's Disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is a neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental abilities. A general lack of coordination and an unsteady gait often follow. It is also a basal ganglia disease causing a hyperkinetic movement disorder known as chorea. As the disease advances, uncoordinated, involuntary body movements of chorea become more apparent. Physical abilities gradually worsen until coordinated movement becomes difficult and the person is unable to talk. Mental abilities generally decline into dementia. The specific symptoms vary somewhat between people. Symptoms usually begin between 30 and 50 years of age but can start at any age. The disease may develop earlier in each successive generation. About eight percent of cases start before the age of 20 years, and are known as ''juvenile HD'', which typically present with the slow movement symptoms of Parkinso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-injury
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury and self-mutilation have been used for any self-harming behavior regardless of suicidal intent. It is not the same as masochism, as no sexual or nonsexual pleasure is obtained. The most common form of self-harm is using a sharp object to cut the skin. Other forms include scratching, hitting, or burning body parts. While earlier usage included interfering with wound healing, excessive skin-picking, hair-pulling, and the ingestion of toxins, current usage distinguishes these behaviors from self-harm. Likewise, tissue damage from drug abuse or eating disorders is not considered self-harm because it is ordinarily an unintended side-effect but context may be needed as intent for such acts varies. Although self-harm is by definition non-suicidal, it may still b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensity in less than 12 hours. The joint at the base of the big toe is affected in about half of cases. It may also result in tophi, kidney stones, or kidney damage. Gout is due to persistently elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. This occurs from a combination of diet, other health problems, and genetic factors. At high levels, uric acid crystallizes and the crystals deposit in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues, resulting in an attack of gout. Gout occurs more commonly in those who: regularly drink beer or sugar-sweetened beverages; eat foods that are high in purines such as liver, shellfish, or anchovies; or are overweight. Diagnosis of gout may be confirmed by the presence of crystals in the joint fluid or in a deposit o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperuricosuria
Hyperuricosuria is a medical term referring to the presence of excessive amounts of uric acid in the urine. For men this is at a rate greater than 800 mg/day, and for women, 750 mg/day. Notable direct causes of hyperuricosuria are dissolution of uric acid crystals in the kidneys or urinary bladder, and hyperuricemia. Notable indirect causes include uricosuric drugs, rapid breakdown of bodily tissues containing large quantities of DNA and RNA, and a diet high in purine. Medications that may contribute to the cure or amelioration of hyperuricosuria include allopurinol which acts by inhibiting xanthine oxidase and reducing uric acid production. Hyperuricosuria ''may'' be a medical sign of: *Gout (very common) *Kidney stones of uric acid ( uric acid nephrolithiasis) * Acute uric acid nephropathy *Acute kidney failure *Tumor lysis syndrome *Fanconi syndrome * Dent's disease (very rare) Classification Acute hyperuricosuria is a common complication of tumor lysis syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
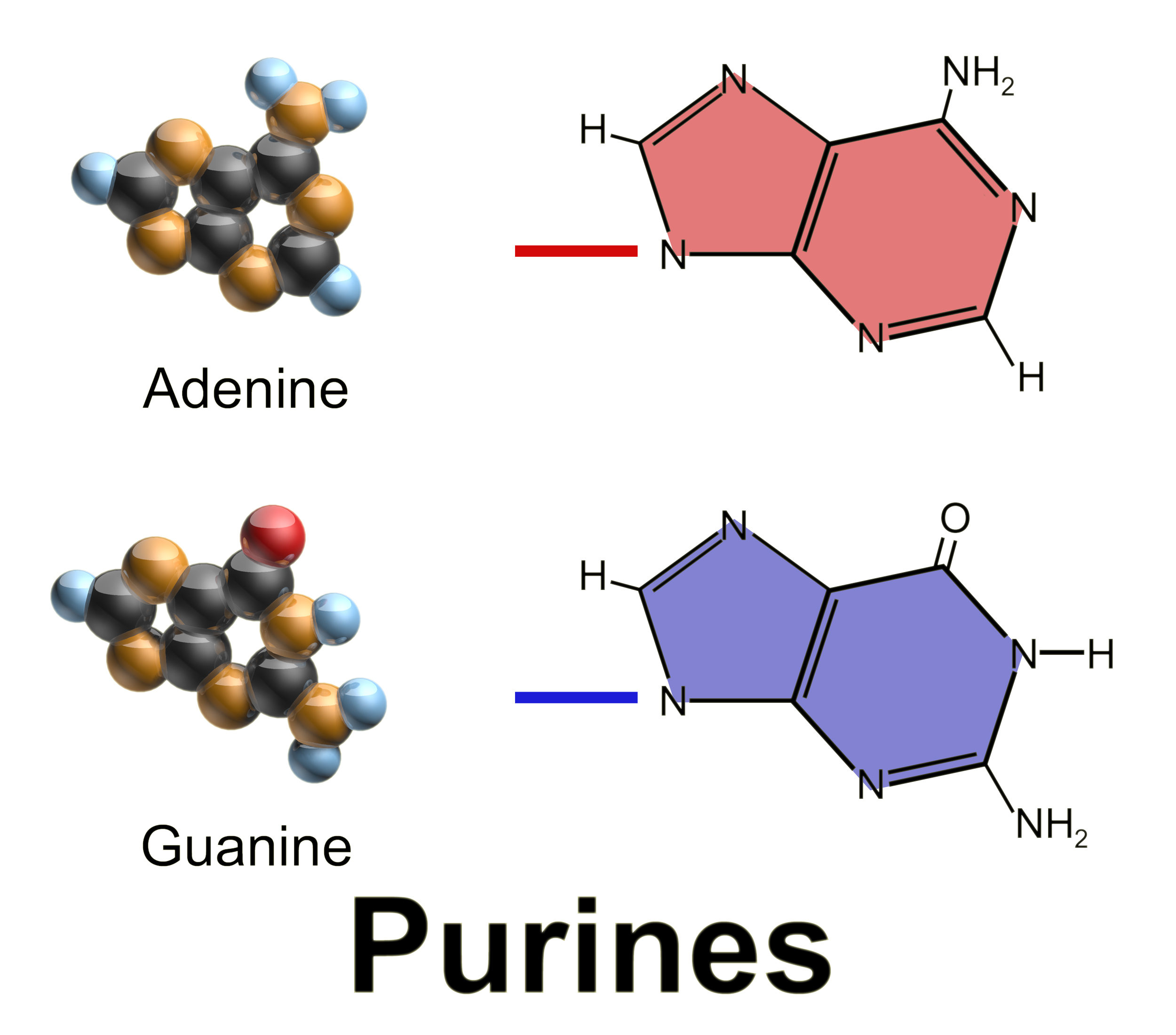
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and black eye peas) and spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, anchovies, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and gravy. A moderate amount of purine is also contained in red meat, beef, pork, poultry, fish and seafood, asparagus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism (also often described as keto–enol tautomerism). Although the lactim form is expected to possess some degree of aromaticity, uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ole Daniel Enersen
Ole Daniel Enersen (born March 14, 1943, in Oslo, Norway) is a Norwegian climber, photographer, journalist, writer, and medical historian. In 1965 he made the first ascent of the Trollveggen mountain in Romsdalen, Norway, along with Leif Normann Petterson, Odd Eliassen and Jon Teigland. In 2000 he published a novel in the fantasy genre, titled ''Dragen som elsket meg'' ("The dragon that loved me"). He publishes and maintains Who Named It?, a large online dictionary of medical eponyms. See also *Who Named It? ''Whonamedit?'' is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliograp ... References 1943 births Norwegian medical historians Living people Norwegian mountain climbers Norwegian male writers Writers from Oslo {{Climbing-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins School Of Medicine
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (JHUSOM) is the medical school of Johns Hopkins University, a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1893, the School of Medicine shares a campus with the Johns Hopkins Hospital and Johns Hopkins Children's Center, established in 1889. It has consistently ranked among the top medical schools in the United States in terms of the number/amount of research grants/funding awarded by the National Institutes of Health, among other measures. History The founding physicians (the "Four Doctors") of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine included pathologist William Henry Welch (1850–1934), the first dean of the school and a mentor to generations of research scientists; a Canadian, internist Sir William Osler (1849–1919), regarded as the ''Father of Modern Medicine'', having been perhaps the most influential physician of the late 19th and early 20th centuries as author of ''The Principles and Practice of Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Nyhan
William Leo Nyhan (born March 13, 1926) is an American physician best known as the co-discoverer of Lesch–Nyhan syndrome. Nyhan currently serves as professor of pediatrics at UC San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California. He has held positions at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and the University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine and has served on a number of advisory committees, pediatric advisory boards, and research foundation boards. Nyhan's areas of research span a variety of amino acid metabolism disorders, among them 4-hydroxybutyric aciduria, 3-methylglutaconyl-Co A hydratase deficiency, multiple carboxylase deficiency, methylmalonic acidemia, and propionic acidemia. He has studied the neuropathology of propionic acidemia, including the manifestation of basal ganglia infarction and its neurologic, non-metabolic presentation. Currently, he conducts research into the causes of progressive neurologic disability caused by methylmalonic acidemia f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)