|
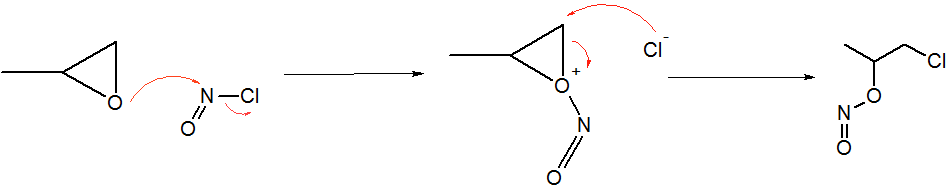
Nitrosyl Cyanide
Nitrosyl cyanide, a blue-green gas, is the compound with the molecular formula ONCN. The compound has been invoked as a product of the oxidation of cyanamide catalyzed by the enzyme glucose oxidase. Structure, synthesis, reactivity The structure of nitrosyl cyanide is planar. It is strongly bent at the internal nitrogen, analogous to the structure of nitrosyl chloride. The C-N-O angle is 113°. The NCN angle is 170°. The compound can be created by the reaction of nitrosyl chloride and silver cyanide at low temperatures. It is not typically isolated, but trapped by Diels-Alder reactions, e.g. with butadiene. Cycloadditions occur across the N=O bond. It forms a reversible adduct with 9,10-dimethylantracene. Related compound * Nitryl cyanide (O2NCN), a colorless gas (b.p. 7 °C).{{cite journal , doi=10.1002/anie.201404209, title=Nitryl Cyanide, NCNO2, year=2014, last1=Rahm, first1=Martin, last2=Bélanger-Chabot, first2=Guillaume, last3=Haiges, first3=Ralf, last4=Christe, first4= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanamide
Cyanamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula carbon, Cnitrogen, N2hydrogen, H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a nitrile group attached to an amino group. Derivatives of this compound are also referred to as cyanamides, the most common being calcium cyanamide (CaCN2). Tautomers and self-condensations Containing both a nucleophilic and electrophilic site within the same molecule, cyanamide undergoes various reactions with itself. Cyanamide exists as two tautomers, one with the connectivity N≡C–NH2 and the other with the formula HN=C=NH ("carbodiimide" tautomer). The N≡C–NH2 form dominates, but in a few reactions (e.g. silylation) the diimide form appears to be important. Cyanamide dimerizes to give 2-Cyanoguanidine, 2-cyanoguanidine (dicyandiamide). This dimerization is disfavored by acids and is inhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Oxidase
The glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx or GOD) also known as notatin (EC number 1.1.3.4) is an oxidoreductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present. Glucose oxidase is widely used for the determination of free glucose in body fluids (medical testing), in vegetal raw material, and in the food industry. It also has many applications in biotechnologies, typically enzyme assays for biochemistry including biosensors in nanotechnologies. It was first isolated by Detlev Müller in 1928 from ''Aspergillus niger''. Function Several species of fungi and insects synthesize glucose oxidase, which produces hydrogen peroxide, which kills bacteria. Notatin, extracted from antibacterial cultures of ''Penicillium notatum'', was originally named Penicillin A, but was renamed to avoid confusion with penicillin. Notati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosyl Chloride
Nitrosyl chloride is the chemical compound with the formula NOCl. It is a yellow gas that is commonly encountered as a component of aqua regia, a mixture of 3 parts concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of concentrated nitric acid. It is a strong electrophile and oxidizing agent. It is sometimes called Tilden's reagent, after William A. Tilden, who was the first to produce it as a pure compound. Structure and synthesis The molecule is bent. A double bond exists between N and O (distance = 1.16 Å) and a single bond between N and Cl (distance = 1.96 Å). The O=N–Cl angle is 113°. Production Nitrosyl chloride can be produced in many ways. * Combining nitrosylsulfuric acid and HCl affords the compound. This method is used industrially. :HCl + NOHSO4 → H2SO4 + NOCl * A more convenient laboratory method involves the (reversible) dehydration of nitrous acid by HCl : HNO2 + HCl → H2O + NOCl * By the direct combination of chlorine and nitric o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula (CH2=CH)2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene. Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission from motor vehicles. The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance. History In 1863, the French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitryl Cyanide
Nitryl cyanide is an energetic chemical compound with the formula NCNO2. Nitryl cyanide is a possible precursor to 2,4,6-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine. Synthesis Nitryl cyanide was first synthesized in 2014. The reaction of nitronium tetrafluoroborate with ''tert''-butyldimethylsilyl cyanide at −30 °C produces nitryl cyanide, with ''tert''-Butyldimethylsilyl fluoride and boron trifluoride as byproducts. : The conversion Conversion or convert may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman'' * "Conversion" (''Stargate Atlantis''), an episode of the television series * "The Conversion" ... of this method is only 50%, and using an excess of ''tert''-butyldimethylsilyl causes the yield to drop even further. References {{Explosive-stub Nitro compounds Cyanides Explosives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide () group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as ''C''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; ), ''S''-nitroso compounds ( nitrosothiols; ), ''N''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, ), and ''O''-nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites; ). Synthesis Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds or by the oxidation of hydroxylamines. Ortho-nitrosophenols may be produced by the Baudisch reaction. In the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement aromatic 4-nitrosoanilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamines. Properties Nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer–dimer equilibrium. The dimers, which are often pale yellow, are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deep-green monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. They exist as ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers. Due to the stability o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen(III) Compounds
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many industrially im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |