|
Nitrogen Difluoride
Nitrogen difluoride, also known as difluoroamino, is a reactive radical molecule with formula . This small molecule is in equilibrium with its dimer dinitrogen tetrafluoride. : As the temperature increases the proportion of increases. The molecule is unusual in that it has an odd number of electrons, yet is stable enough to study experimentally. Properties The energy needed to break the N–N bond in is , with an entropy change of 38.6 eu. molecule dimensions and angles For comparison, the dissociation energy of the N–N bond is in , in , and in . The enthalpy of formation of (Δ''H''f) is . At room temperature is mostly associated with only 0.7% in the form of at pressure. When the temperature rises to 225 °C, it mostly dissociates with 99% in the form of . In , the N–F bond length is 1.3494 Å and the angle subtended at F–N–F is 103.33°. In the infrared spectrum the N–F bond in has a symmetrical stretching frequency of 1075 cm∠... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
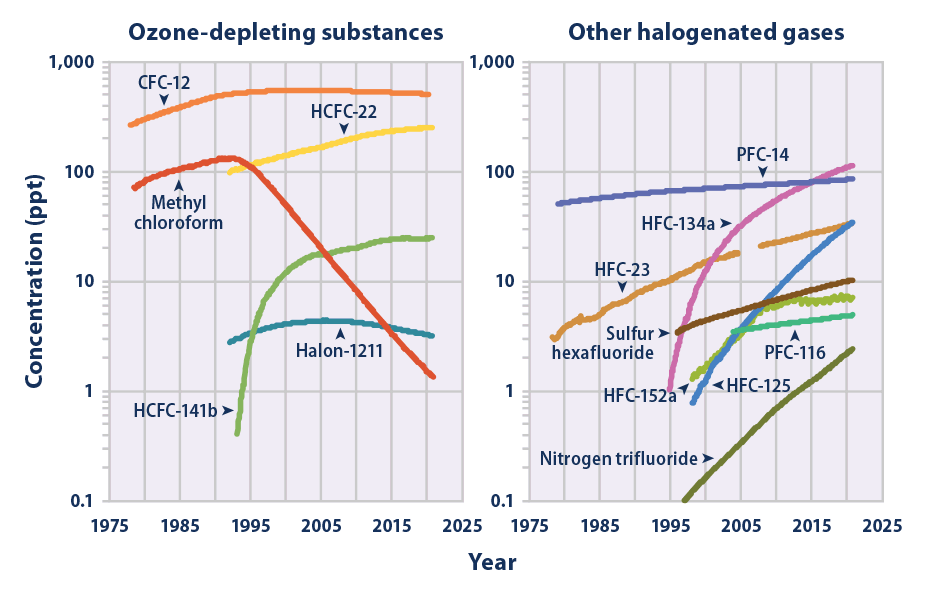
Nitrogen Trifluoride
Nitrogen trifluoride () is an inorganic, colorless, non-flammable, toxic gas with a slightly musty odor. It finds increasing use within the manufacturing of flat-panel displays, photovoltaics, LEDs and other microelectronics. Nitrogen trifluoride is also an extremely strong and long-lived greenhouse gas. Its atmospheric burden exceeded 2 parts per trillion during 2019 and has doubled every five years since the late 20th century. Synthesis and reactivity Nitrogen trifluoride did not exist in significant quantities on Earth prior to its synthesis by humans. It is a rare example of a binary fluoride that can be prepared directly from the elements only at very uncommon conditions, such as an electric discharge. After first attempting the synthesis in 1903, Otto Ruff prepared nitrogen trifluoride by the electrolysis of a molten mixture of ammonium fluoride and hydrogen fluoride. It proved to be far less reactive than the other nitrogen trihalides nitrogen trichloride, nitrogen trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF (millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range. Rather, it indicates that microwaves are "small" (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used prior to microwave te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Monofluoride
Nitrogen monofluoride (fluoroimidogen) is a metastable species that has been observed in laser studies. It is isoelectronic with O2. Like boron monofluoride, it is an instance of the rare multiply-bonded fluorine atom. It is unstable with respect to its formal dimer, dinitrogen difluoride, as well as to its elements, nitrogen and fluorine. Nitrogen monofluoride is produced when radical species (H, O, N, CH3) abstract a fluorine atom from nitrogen difluoride (NF2). Stoichiometrically, the reaction is extremely efficient, regenerating a radical for long-lasting chain propagation. However, radical impurities in the end product also catalyze that product's decomposition. Azide decomposition offers a less-efficient but more pure technique: fluorine azide (which can be formed ''in situ'' via reaction of atomic fluorine with hydrazoic acid) decomposes upon shock into NF and N2. Many NF-producing reactions give the product in an excited state with characteristic chemiluminescence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excimer
An excimer (originally short for excited dimer) is a short-lived dimeric or heterodimeric molecule formed from two species, at least one of which has a valence shell completely filled with electrons (for example, noble gases). In this case, formation of molecules is possible only if such atom is in an electronic excited state. Heteronuclear molecules and molecules that have more than two species are also called exciplex molecules (originally short for excited complex). Excimers are often diatomic and are composed of two atoms or molecules that would not bond if both were in the ground state. The lifetime of an excimer is very short, on the order of nanoseconds. Formation and decay Under the molecular orbital formalism, a typical ground-state molecule has electrons in the lowest possible energy levels. According to the Pauli principle, at most two electrons can occupy a given orbital, and if an orbital contains two electrons they must be in opposite spin states. The highest occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Monofluoride
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xenon-135 is pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain-reducing effects. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, is due to the euphoric effects upon inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is also used as an oxidiser in rocket propellants, and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines. Nitrous oxide's atmospheric concentration reached 333 parts per billion (ppb) in 2020, increasing at a rate of abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Monoxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the "Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Nitric oxide should not be confused with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a brown gas and major air pollutant, or with nitrous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye (unit)
The debye (symbol: D) (; ) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation, it is a vector whose direction is in the direction of the unit vector of the position vector of the positive charge w.r.t negative charge: :p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb-centimeters.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. :1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in older scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Dipole Moment
The electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system, that is, a measure of the system's overall polarity. The SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb-meter (Câ‹…m). The debye (D) is another unit of measurement used in atomic physics and chemistry. Theoretically, an electric dipole is defined by the first-order term of the multipole expansion; it consists of two equal and opposite charges that are infinitesimally close together, although real dipoles have separated charge.Many theorists predict elementary particles can have very tiny electric dipole moments, possibly without separated charge. Such large dipoles make no difference to everyday physics, and have not yet been observed. (See electron electric dipole moment). However, when making measurements at a distance much larger than the charge separation, the dipole gives a good approximation of the actual electric field. The dipole is represented by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u) is a non-SI unit of mass widely used in physics and chemistry. It is defined as of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and at rest. The atomic mass constant, denoted ''m''u, is defined identically, giving . This unit is commonly used in physics and chemistry to express the mass of atomic-scale objects, such as atoms, molecules, and elementary particles, both for discrete instances and multiple types of ensemble averages. For example, an atom of helium-4 has a mass of . This is an intrinsic property of the isotope and all helium-4 atoms have the same mass. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), , has an average mass of approximately . However, there are no acetylsalicylic acid molecules with this mass. The two most common masses of individual acetylsalicylic acid molecules are , having the most common isotopes, and , in which one carbon is carbon-13. The molecular mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectrum
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Tetrafluoride
Tetrafluorohydrazine or perfluorohydrazine, , is a colourless, reactive inorganic gas. It is a fluorinated analog of hydrazine. It is a highly hazardous chemical that explodes in the presence of organic materials. Tetrafluorohydrazine is manufactured from nitrogen trifluoride using an iron catalyst or iron(II) fluoride. It is used in some chemical syntheses, as a precursor or a catalyst. Tetrafluorohydrazine was considered for use as a high-energy liquid oxidizer in some never-flown rocket fuel formulas in 1959. Properties Tetrafluorohydrazine is in equilibrium with its radical monomer nitrogen difluoride. : N2F4 2 NF2• At room temperature N2F4 is mostly associated with only 0.7% in the form of NF2 at 5mm Hg pressure. When the temperature rises to 225 °C, it mostly dissociates with 99% in the form of NF2. molecule dimensions and angles The energy needed to break the N-N bond in N2F4 is 20.8 kcal/mol, with an entropy change of 38.6 eu. For comparison, the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |