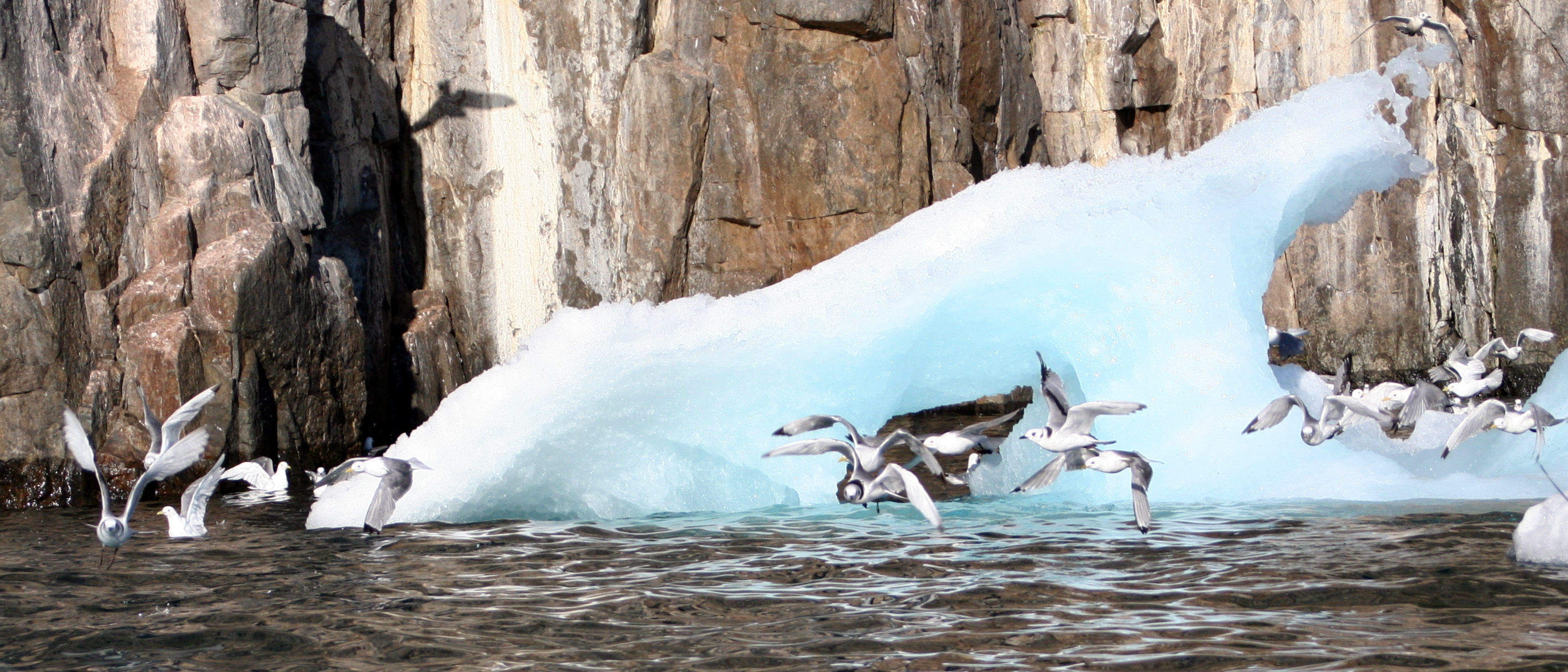|
Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area
Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area is a National Wildlife Area on Coburg Island within the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Baffin Bay's Lady Ann Strait between Ellesmere Island, to the north, and Devon Island to the south. The NWA includes Coburg Island and its surrounding marine area. Established in 1995, it is in area. Of this, a total of make up a marine area with marine and intertidal components. The NWA is one of the most important seabird nesting areas in the Canadian Arctic for black guillemot, black-legged kittiwake, northern fulmar, and thick-billed murre. It is also an important area for polar bears, walruses, ringed, and bearded seals. Narwhal and beluga whales migrate through the area. The Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area is home to many seabird species and marine animals, providing essential nutrients to nearby Indigenous communities. The wildlife area is managed by Inuit from Grise Fiord, a nearby community, along with other gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coburg Island
Coburg Island ( iu, script=latn, Nirjutiqavvik, italic=no) is an uninhabited island in Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the members of Queen Elizabeth Islands located in Baffin Bay's Lady Ann Strait. It is separated from Ellesmere Island by Glacier Strait; Devon Island is to the south. Elsewhere in Nunavut, there is also a tinSaxe-Coburg Island lying in Davis Strait, south of Leopold Island, itself east of Baffin Island's Cape Mercy (Cumberland Peninsula). Geography The island is characterized by cliffs, rocky shores, and tundra. Fauna Bowhead whale, narwhal, polar bear, seal, walrus, and white whale frequent the area. Conservation Coburg Island has several designated conservation classifications including International Biological Program site and Key Migratory Bird Terrestrial Habitat site. Along with the surrounding marine area, the island is a part of the Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area. Cambridge Point, off of the southeastern Marina Peninsula, is a Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringed Seal
The ringed seal (''Pusa hispida'') is an earless seal inhabiting the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. The ringed seal is a relatively small seal, rarely greater than 1.5 m in length, with a distinctive patterning of dark spots surrounded by light gray rings, hence its common name. It is the most abundant and wide-ranging ice seal in the Northern Hemisphere, ranging throughout the Arctic Ocean, into the Bering Sea and Okhotsk Sea as far south as the northern coast of Japan in the Pacific and throughout the North Atlantic coasts of Greenland and Scandinavia as far south as Newfoundland, and including two freshwater subspecies in northern Europe. Ringed seals are one of the primary prey of polar bears and killer whales, and have long been a component of the diet of indigenous people of the Arctic. Ringed seals are the smallest and most abundant member of the seal family that live in the Arctic and Sub-Arctic regions. The average life span of a ringed seal is 40 years, with a diet b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davis Highlands Tundra
The Davis Highlands tundra ecoregion (WWF ID: NA1109) covers the Baffin Mountains on the northeast coast of Baffin Island and Bylot Island, facing Baffin Bay in Nunavut, northern Canada. The terrain is extremely rugged, heavily glaciated, with many deep fjords, and very cold. About half of the territory is moss and lichen tundra, the other half bare rock and ice. The region is wetter than the much drier regions to the southwest of the Baffin Islands. Location and description The Baffin Islands are the southeastern half of the Arctic Cordillera, a chain of island mountains that run along the northeast of the Canada's Arctic Archipelago. They are separated from Greenland by Baffin Bay. The Baffin Island section is 900 km long; the Bylot Island mountains to the north of Baffin Island add another 100 km. The ecoregion averages only 100 km wide. The mean elevation is and the maximum is at Mount Odin. Much of the ground bare is bedrock and glaciers; open soil i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the Shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the United States. Geographical extent The Canadian Shield is a physiographic division comprising four smaller physiographic provinces: the Laurentian Upland, Kazan Region, Davis and James. The shield extends into the United States as the Adirondack Mountains (connected by the Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean. The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and North America, and the borders follow topographic features: the Bering Strait on the Pacific side and the Greenland Scotland Ridge on the Atlantic side. It is mostly covered by sea ice throughout the year and almost completely in winter. The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jones Sound
Jones Sound is a waterway in Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It lies between Devon Island and the southern end of Ellesmere Island. At its northwestern end it is linked by several channels to Norwegian Bay; at its eastern end it opens via Glacier Strait into Baffin Bay. The hamlet of Grise Fiord was established on the south shore Ellesmere Island in 1953, partly to assert Canadian sovereignty in the high Arctic. The first known European to sight the sound was the English explorer William Baffin William Baffin ( – 23 January 1622) was an English navigator, explorer and cartographer. He is primarily known for his attempt to find a Northwest Passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific, during the course of which he was the first Euro ... in 1616 who named it after one of his patrons. The next European to pass it was John Ross in 1818. References Sounds of Qikiqtaaluk Region Bodies of water of Baffin Bay Rifts and grabens {{QikiqtaalukNU-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
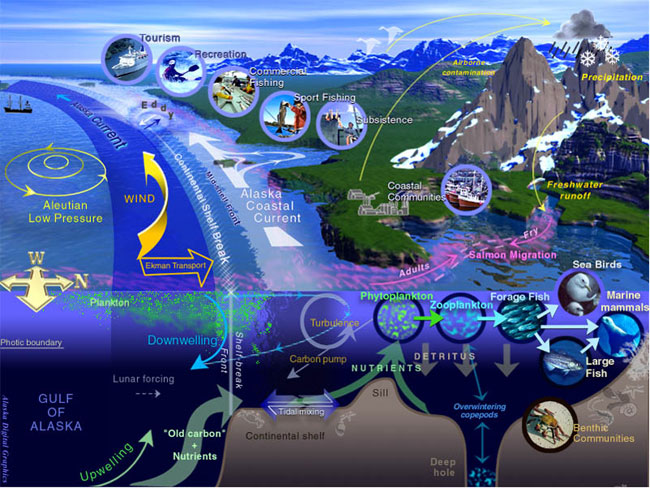
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grise Fiord
Grise Fiord (; iu, ᐊᐅᔪᐃᑦᑐᖅ, translit=Aujuittuq, lit=place that never thaws, italics=no) is an Inuit hamlet on the southern tip of Ellesmere Island, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of three populated places on the island; despite its low population (144 residents as of the 2021 Canadian census), it is the largest community (and only public community) on Ellesmere Island. The hamlet at Grise Fiord, created by the Canadian Government in 1953 through a relocation of Inuit families from Inukjuak, Quebec, is the northernmost public community in Canada. It is also one of the coldest inhabited places in the world, with an average yearly temperature of . History Creation This community (and that of Resolute) was created by the Canadian government in 1953, partly to assert sovereignty in the High Arctic during the Cold War. Eight Inuit families from Inukjuak, Quebec (on the Ungava Peninsula), were relocated after being promised homes and game to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Alaska. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut. Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories, particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. With the exception of NunatuKavut, these areas are known, primarily by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Aboriginal Canadians wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original peoples. The term ''Indigenous'' was first, in its modern context, used by Europeans, who used it to differentiate the Indigenous peoples of the Americas from the European settlers of the Americas and from the Sub-Saharan Africans who were brought to the Americas as enslaved people. The term may have first been used in this context by Sir Thomas Browne in 1646, who stated "and although in many parts thereof there be at present swarms of ''Negroes'' serving under the ''Spaniard'', yet were they all transported from ''Africa'', since the discovery of ''Columbus''; and are not indigenous or proper natives of ''America''." Peoples are usually described as "Indigenous" when they maintain traditions or other aspects of an early culture that is assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow in the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations. The first seabirds evolved in the Cretaceous period, and modern seabird families emerged in the Paleogene. In general, seabirds live longer, breed later and have fewer young than other birds do, but they invest a great deal of time in their young. Most species nest in colonies, which can vary in size from a few dozen birds to millions. Many species are famous for undertaking long annual migrations, crossing the equator or circumnavigating the Earth in some cases. They feed both at the ocean's surface and below it, and even feed on each other. Seabirds can be highly pelagic, coastal, or in some cases spend a part of the year away from the sea entirely. Seabirds and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |