|
Nikodem Popławski
Nikodem Janusz Popławski (born March 1, 1975) is a Polish theoretical physicist, most widely noted for the hypothesis that every black hole could be a doorway to another universe and that the universe was formed within a black hole which itself exists in a larger universe. This hypothesis was listed by ''National Geographic'' and '' Science'' magazines among their top ten discoveries of 2010. Black holes as doorways Popławski's approach is based on the Einstein–Cartan theory of gravity which extends general relativity to matter with intrinsic angular momentum (spin). Spin in curved spacetime requires that the affine connection cannot be constrained to zero and its antisymmetric part, the torsion tensor, must be a variable in Hamilton's principle of stationary action which gives the field equations. Torsion gives the correct generalization of the conservation law for the total (orbital plus intrinsic) angular momentum to the presence of the gravitational field, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toruń
)'' , image_skyline = , image_caption = , image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg , image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg , nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town , pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship#Poland#Europe , pushpin_relief=1 , pushpin_label_position = top , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Voivodeship , subdivision_name1 = , leader_title = City mayor , leader_name = Michał Zaleski , established_title = Established , established_date = 8th century , established_title3 = City rights , established_date3 = 1233 , area_total_km2 = 115.75 , population_as_of = 31 December 2021 , population_total = 196,935 (16th) Data for territorial unit 0463000. , population_density_km2 = 1716 , population_metro = 297646 , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , coordinates = , elevation_m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gravitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area.: : \tau = , where: : = the shear stress; : = the force applied; : = the cross-sectional area of material with area parallel to the applied force vector. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as: \tau_w:=\mu\left(\frac\right)_ Where \mu is the dynamic viscosity, u the flow velocity and y the distance from the wall. It is used, for example, in the description of arterial blood flow in which case which ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
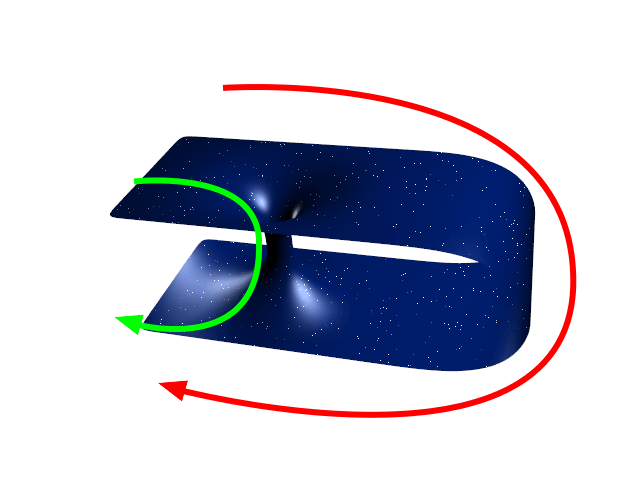
Wormhole
A wormhole (Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special Solutions of the Einstein field equations, solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are consistent with the General relativity, general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen. Many scientists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a Four-dimensional space, fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. Theoretically, a wormhole might connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years, or short distances such as a few meters, or different points in time, or even multiverse, different universes. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event Horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s. In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact objects that even light cannot escape. At that time, the Newtonian theory of gravitation and the so-called corpuscular theory of light were dominant. In these theories, if the escape velocity of the gravitational influence of a massive object exceeds the speed of light, then light originating inside or from it can escape temporarily but will return. In 1958, David Finkelstein used general relativity to introduce a stricter definition of a local black hole event horizon as a boundary beyond which events of any kind cannot affect an outside observer, leading to information and firewall paradoxes, encouraging the re-examination of the concept of local event horizons and the notion of black holes. Several theories were subsequently developed, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Singularity
A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity or simply singularity is a condition in which gravitational field, gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular spacetime and cannot be determined by "where" or "when". Gravitational singularities exist at a junction between general relativity and quantum mechanics; therefore, the properties of the singularity cannot be described without an established theory of quantum gravity. Trying to find a complete and precise definition of singularities in the theory of general relativity, the current best theory of gravity, remains a difficult problem. A singularity in general relativity can be defined by the Curvature invariant (general relativity), scalar invariant Curvature of Riemannian manifolds, curvature becoming Infinity, infinite or, better, by a Geodesics in general relativity, geodesic being Geodesic manifold#Non-examples, incom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is a particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Generally, it has a half-odd-integer spin: spin , spin , etc. In addition, these particles obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Fermions include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions. In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referred to as the spin-statistics relation is, in fact, a spin statistics-quantum numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Dirac Equation
:''See Ricci calculus and Van der Waerden notation for the notation.'' In quantum field theory, the nonlinear Dirac equation is a model of self-interacting Dirac fermions. This model is widely considered in quantum physics as a toy model of self-interacting electrons. The nonlinear Dirac equation appears in the Einstein–Cartan–Sciama–Kibble theory of gravity, which extends general relativity to matter with intrinsic angular momentum ( spin). This theory removes a constraint of the symmetry of the affine connection and treats its antisymmetric part, the torsion tensor, as a variable in varying the action. In the resulting field equations, the torsion tensor is a homogeneous, linear function of the spin tensor. The minimal coupling between torsion and Dirac spinors thus generates an axial-axial, spin–spin interaction in fermionic matter, which becomes significant only at extremely high densities. Consequently, the Dirac equation becomes nonlinear (cubic) in the spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton's Principle
In physics, Hamilton's principle is William Rowan Hamilton's formulation of the principle of stationary action. It states that the dynamics of a physical system are determined by a variational problem for a functional based on a single function, the Lagrangian, which may contain all physical information concerning the system and the forces acting on it. The variational problem is equivalent to and allows for the derivation of the '' differential'' equations of motion of the physical system. Although formulated originally for classical mechanics, Hamilton's principle also applies to classical fields such as the electromagnetic and gravitational fields, and plays an important role in quantum mechanics, quantum field theory and criticality theories. Mathematical formulation Hamilton's principle states that the true evolution of a system described by generalized coordinates between two specified states and at two specified times and is a stationary point (a point where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion Tensor
In differential geometry, the notion of torsion is a manner of characterizing a twist or screw of a moving frame around a curve. The torsion of a curve, as it appears in the Frenet–Serret formulas, for instance, quantifies the twist of a curve about its tangent vector as the curve evolves (or rather the rotation of the Frenet–Serret frame about the tangent vector). In the geometry of surfaces, the ''geodesic torsion'' describes how a surface twists about a curve on the surface. The companion notion of curvature measures how moving frames "roll" along a curve "without twisting". More generally, on a differentiable manifold equipped with an affine connection (that is, a connection in the tangent bundle), torsion and curvature form the two fundamental invariants of the connection. In this context, torsion gives an intrinsic characterization of how tangent spaces twist about a curve when they are parallel transported; whereas curvature describes how the tangent spaces roll al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Connection
In differential geometry, an affine connection is a geometric object on a smooth manifold which ''connects'' nearby tangent spaces, so it permits tangent vector fields to be differentiated as if they were functions on the manifold with values in a fixed vector space. Connections are among the simplest methods of defining differentiation of the sections of vector bundles. The notion of an affine connection has its roots in 19th-century geometry and tensor calculus, but was not fully developed until the early 1920s, by Élie Cartan (as part of his general theory of connections) and Hermann Weyl (who used the notion as a part of his foundations for general relativity). The terminology is due to Cartan and has its origins in the identification of tangent spaces in Euclidean space by translation: the idea is that a choice of affine connection makes a manifold look infinitesimally like Euclidean space not just smoothly, but as an affine space. On any manifold of positive dimension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |