|
Nikkur
''Nikkur'' ( he, ניקור) is the process of making an animal kosher by removing ''chelev'' (forbidden fats) and the ''gid hanasheh'' (sciatic nerve). The basis for this practice is , "You shall not eat of any fatty suet, whether from cattle, sheep, or goats." The English word ''wikt:porge, porge'', or ''porging'' is from Judeo-Spanish ''porgar'' (from Spanish "to purge"); the Yiddish is ''treibern''. The process is done by a ''menakker''. Etymology From the Biblical root wikt:נקר, נקר ''NQR'' meaning to "put out, bore, dig, gnaw" etc. Regional practices It is much easier to perform ''nikkur'' on the front part of the animal. It is also easier to perform on non-domestic animals such as deer as the ''chelev'' does not need to be removed from such animals. Since it is difficult to perform ''nikkur'' on the hind part of domestic animals, the entire hind part is usually sold to the non-Jewish market in Ashkenazi Jewish communities. However, among Yemenite Jews, ''nikkur'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porge
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''. Sources states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtered "as I have instructed you", but nowhere in the Torah are any of the practices of ''shechita'' described. Instead, they have been handed down in Rabbinic Judaism's Oral Torah, and codified in ''halakha''. Species The animal must be of a permitted species. For mammals, this is restricted to ruminants which have split hooves. For birds, although biblically any species of bird not specifically excluded in would be permitted, doubts as to the identity and scope of the species on the biblical list led to rabbinical law permitting only birds with a tradition of being permissible. Fish do not require kosher slaughter to be considered kosher, but are subject to other laws found in which determine whether or not they are kosher (having both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
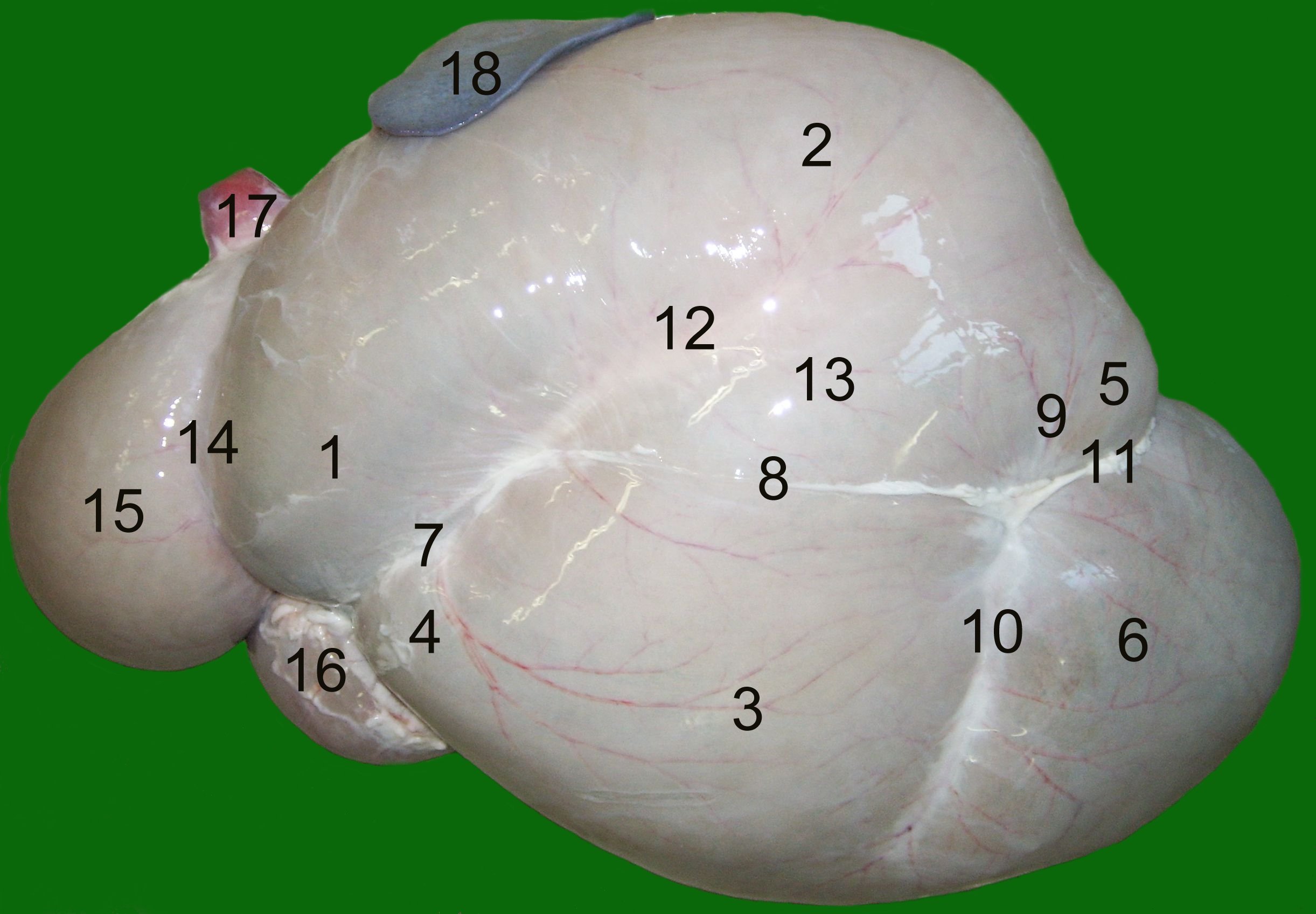
Chelev
Chelev ( he, חֵלֶב, ''kheylev'' or ''ẖelev''), or what is also known as "suet", is the animal fats that the Torah prohibits Jews and Israelites from eating (). Only the ''chelev'' of animals that are of the sort from which offerings can be brought in the Tabernacle or Temple are prohibited (). The prohibition of eating ''chelev'' is also, in addition to the Torah, one of the 613 commandments that, according to the Talmud, were given to Moses on Mount Sinai. Hebrew Bible Hebrew language In Biblical Hebrew, the word for fat is ''chelev'' (חֵלֶב), and it is first used for the "fats" of Abel's offering, and most often used for fats of animal sacrifices on the altar of the Tabernacle or Temple. The same word is also used in the phrase "the fat of the land." Rabbinical interpretation The punishment for eating ''chelev'' bemeizid (on purpose) is kareth (exclusion from the after life). The atonement for eating it by mistake is to bring a korban hattath (atonement sacri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suet
Suet is the raw, hard fat of beef, lamb or mutton found around the loins and kidneys. Suet has a melting point of between 45 °C and 50 °C (113 °F and 122 °F) and congelation between 37 °C and 40 °C (98.6 °F and 104 °F). Its high smoke point makes it ideal for deep frying and pastry production. The primary use of suet is to make tallow, although it is also used as an ingredient in cooking, especially in traditional baked puddings, such as British Christmas pudding. Suet is made into tallow in a process called rendering, which involves melting fats and extended simmering, followed by straining, then cooling. The entire process is then usually repeated to refine the product. Etymology The word ''suet'' is derived from Anglo-Norman , from Old French , from Latin ("tallow", "grease", "hard animal fat"). ''Sebum'' is from the Proto-Indo-European root *''seyb''- ("pour out, trickle"), so it shares a root with sap and soap. Trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kol Bo
''Kol Bo'' (Hebrew: כל-בו, "all is in it") is a collection of Jewish ritual and civil laws. Its author has not yet been ascertained. The work in content resembles other codes, as, for instance, the ''Orḥot Ḥayyim'', though in its form it is very different. Its contents and peculiarities The ''Kol Bo'' does not pretend to any order; the laws that were later arranged in Orach Hayyim are found together with those that were later arranged in ''Yoreh De'ah'' and ''Even haEzer''. Likewise, many laws are entirely missing in the ''Kol Bo''. It is peculiar also in that some of the laws are briefly stated, while others are stated at great length, without division into paragraphs. After the regular code, terminating with the laws of mourning (No. 115), there comes a miscellaneous collection, containing the "takkanot" of R. Gershom and of Rabbeinu Tam, the ''Ma'aseh Torah'' of Judah haNasi, the legend of Solomon's throne, the legend of Joshua b. Levi, a kabbalistic dissertation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Vertebrae
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. Individual vertebrae are named according to their region and position, and can be used as anatomical landmarks in order to guide procedures such as lumbar punctures. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord. There are about 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human vertebral column is one of the most-studied examples. Many different diseases in humans can affect the spine, with spina bifida and scoliosis being recognisable examples. The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in mammals, reptiles, and birds. The shape of the vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, רבי שלמה יצחקי; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 – 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a comprehensive commentary on the Talmud and commentary on the Hebrew Bible (the '' Tanakh''). Acclaimed for his ability to present the basic meaning of the text in a concise and lucid fashion, Rashi appeals to learned scholars and beginning students, and his works remain a centerpiece of contemporary Jewish studies. His commentary on the Talmud, which covers nearly all of the Babylonian Talmud (a total of 30 out of 39 tractates, due to his death), has been included in every edition of the Talmud since its first printing by Daniel Bomberg in the 1520s. His commentaries on the Tanakh—especially his commentary on the Chumash (the "Five Books of Moses")—serves as the basis of more than 300 "supercommentaries" which analyze Rashi's choice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halachot Gedolot
Halachoth Gedoloth (lit. great halachoth) is a work on Jewish law dating from the Geonic period. It exists in several different recensions, and there are sharply divergent views on its authorship, though the dominant opinion attributes it to Simeon Kayyara. Authorship controversy Kayyara's chief work is believed by some to be the ''Halakhot Gedolot'' (הלכות גדולות) whereas Moses ben Jacob of Coucy ("the ''Semag''") wrote that it was in fact composed by Rav Yehudai Gaon. Based on anachronistic discrepancies, the ''Semags opinion that it was Rav Yehudai Gaon who composed the work Halachoth Gedoloth was thought to be an error. Rabbi David Gans may have been the first to suggest that the ''Semag'', in referring to "Rav Yehudai" as the author, was actually alluding to Rav Yehudai Hakohen ben Ahunai, Gaon of the Sura Academy (served 4519 - 4524 of the Hebrew calendar) As to the time of its composition, all the older authorities are silent. Abraham ibn Daud alone has an all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yitzhak Alfasi
Isaac ben Jacob Alfasi ha-Cohen (1013–1103) ( ar, إسحاق الفاسي, he, ר' יצחק אלפסי) - also known as the Alfasi or by his Hebrew acronym Rif (Rabbi Isaac al-Fasi), was a Maghrebi Talmudist and posek (decider in matters of halakha - Jewish law). He is best known for his work of ''halakha'', the legal code Sefer Ha-halachot, considered the first fundamental work in ''halakhic'' literature. His name "Alfasi" means "of Fez" in Arabic, but opinions differ as to whether he ever lived in Fez. Biography He was born in Qalaat Hammad, which is understood by most historians of the past 100 years to be Qalaat Beni Hammad in modern-day Algeria, capital city of the Hammadid rulers of central Maghreb.Leonard Levy, ''R. Yitzhaq Alfasi's application of principles of adjudication in Halakhot Rabbati'', footnotes 11-27 However, older sources believe Qalaat Hammad refers to a village near Fez. In the former case, Alfasi's name would indicate that his family had ancestry in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
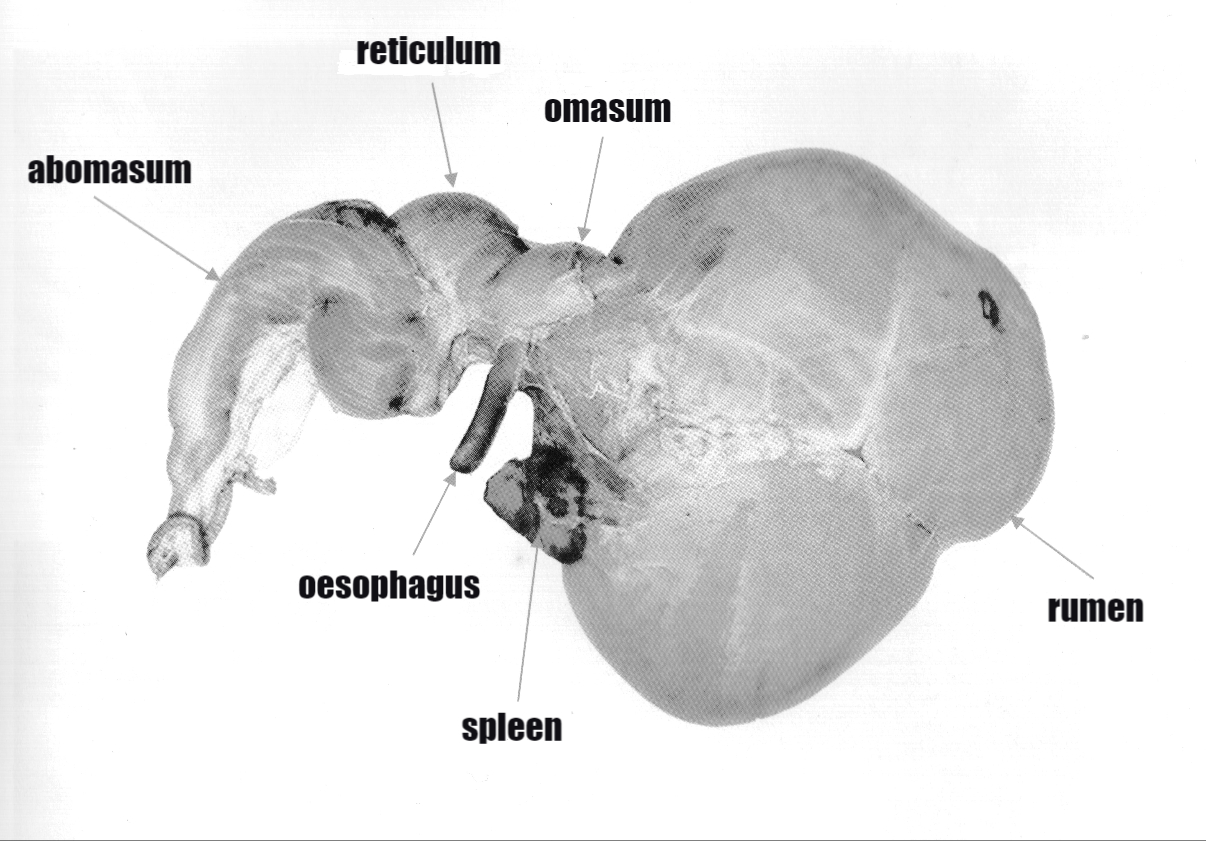
Reticulum
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed between October and December, and save for one main star visible in ideal conditions, cannot be seen from north of the 30th parallel north. History A constellation in this area was introduced by Isaac Habrecht II in his celestial globe in 1621, who named it ''Rhombus''. It was replaced with a somewhat different constellation by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the eighteenth century; during his stay at the Cape of Good Hope, he named the constellation le Réticule Rhomboide to commemorate the reticle in his telescope eyepiece. The name was later Latinized to Reticulum in his star catalogue ''Coelum Australe Stelliferum''. In 1810, the stars of Reticulum were used by William Croswell to produce the constellation ''Marmor S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omasum
The omasum, also known as the bible, the fardel, the manyplies and the psalterium, is the third compartment of the stomach in ruminants. The omasum comes after the rumen and reticulum and before the abomasum. Different ruminants have different omasum structures and function based on the food that they eat and how they developed through evolution. Anatomy The omasum can be found on the right side of the cranial portion of the rumen. The omasum receives food from the reticulum through the reticulo-omasal orifice and provides food to the abomasum through the omaso-abomasal orifice. The omasum is spherical to crescent shape and has multiple leaflets similar to that of a book called omasal laminae. The omasal laminae are made of thin muscular layers covered with a nonglandular mucous membrane. The omasal laminae come from the sides of the large curvature and project towards the inside of the omasum, extending from the reticulo-omasal orifice to the omaso-abomasal orifice. The lamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed. The smaller part of the reticulorumen is the reticulum, which is fully continuous with the rumen, but differs from it with regard to the texture of its lining. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of several muscular sacs, the cranial sac, ventral sac, ventral blindsac, and reticulum. The lining of the rumen wall is covered in small fingerlike projections called papillae, which are flattened, approximately 5mm in length and 3mm wide in cattle. The reticulum is lined with ridges that form a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. The ridges are approximately 0.1–0.2mm wide and are raised 5mm above the reticulum wall. The hexagons in the reticulum are approximatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.png)