|
Nietzschean Affirmation
Nietzschean affirmation (german: Bejahung) is a concept in the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche. The best example of this concept can be found in Nietzsche's ''The Will to Power'': Opposition to Schopenhauer Walter Kaufmann wrote that Nietzsche "celebrates the Greeks who, facing up to the terrors of nature and history, did not seek refuge in "a Buddhistic negation of the will," as Schopenhauer did, but instead created tragedies in which life is affirmed as beautiful in spite of everything." Schopenhauer’s negation of the will was a saying "no" to life and to the world, which he judged to be a scene of pain and evil. " rectly against Schopenhauer’s place as the ultimate nay-sayer to life, Nietzsche positioned himself as the ultimate yes-sayer…." Nietzsche's affirmation of life's pain and evil, in opposition to Schopenhauer, resulted from an overflow of life. Schopenhauer's advocacy of self-denial and negation of life was, according to Nietzsche, very harmful."For me t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900) developed his philosophy during the late 19th century. He owed the awakening of his philosophical interest to reading Arthur Schopenhauer's ''Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung'' (''The World as Will and Representation'', 1819, revised 1844) and said that Schopenhauer was one of the few thinkers that he respected, dedicating to him his essay ''Schopenhauer als Erzieher'' (''Schopenhauer as Educator''), published in 1874 as one of his ''Untimely Meditations''. Since the dawn of the 20th century, the philosophy of Nietzsche has had great intellectual and political influence around the world. Nietzsche applied himself to such topics as morality, religion, epistemology, poetry, ontology, and social criticism. Because of Nietzsche's evocative style and his often outrageous claims, his philosophy generates passionate reactions running from love to disgust. Nietzsche noted in his autobiographical '' Ecce Homo'' that his philosophy developed and evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everlasting Yea
Thomas Carlyle (4 December 17955 February 1881) was a Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher. A leading writer of the Victorian era, he exerted a profound influence on 19th-century art, literature and philosophy. Born in Ecclefechan, Dumfriesshire, Carlyle attended the University of Edinburgh where he excelled in mathematics, inventing the Carlyle circle. After finishing the arts course, he prepared to become a minister in the Burgher Church while working as a schoolmaster. He quit these and several other endeavours before settling on literature, writing for the ''Edinburgh Encyclopædia'' and working as a translator. He found initial success as a disseminator of German literature, then little-known to English readers, through his translations, his ''Life of'' ''Friedrich Schiller'' (1825), and his review essays for various journals. His first major work was a novel entitled ''Sartor Resartus'' (1833–34). After relocating to London, he became famous with his ''French Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amor Fati
is a Latin phrase that may be translated as "love of fate" or "love of one's fate". It is used to describe an attitude in which one sees everything that happens in one's life, including suffering and loss, as good or, at the very least, necessary. is often associated with what Friedrich Nietzsche called " eternal recurrence", the idea that, over an infinite period of time, everything recurs infinitely. From this he developed a desire to be willing to live exactly the same life over and over for all eternity ("...''long for nothing more fervently'' than this ultimate eternal confirmation and seal”). Is also talked about in Stoicism. Nietzsche The concept of has been linked to Epictetus. It has also been linked to the writings of Marcus Aurelius, who did not use the words (he wrote in Greek, not Latin). However, it found its most explicit expression in Nietzsche, who made love of fate central to his philosophy. In "Why I Am So Clever" '' Ecce Homo'', section 10, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry. The meaning of the term "humanism" has changed according to the successive intellectual movements that have identified with it. During the Italian Renaissance, ancient works inspired scholars in various Italian cities, giving rise to a movement now called Renaissance humanism. With Enlightenment, humanistic values were re-enforced by the advances in science and technology, giving confidence to humans in their exploration of the world. By the early 20th century, organizations solely dedicated to humanism flourished in Europe and the United States, and have since expanded all over the globe. In the current day, the term generally refers to a focus on human well-being and advocates for human freedom, autonomy, and progress. It views humanity as responsible for the prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing And Difference
''Writing and Difference'' (french: L'écriture et la différence) is a book by the French philosopher Jacques Derrida. The work, which collects some of the early lectures and essays that established his fame, was published in 1967 alongside '' Of Grammatology'' and '' Speech and Phenomena''. Summary Cogito and the History of Madness The collection contains the essay ''Cogito and the History of Madness'', a critique of Michel Foucault. It was first given as a lecture on March 4, 1963, at a conference at the '' Collège philosophique'', which Foucault attended, and caused a rift between the two,Powell (2006), pp. 34–5 possibly prompting Foucault to write '' The Order of Things'' (1966) and ''The Archaeology of Knowledge'' (1969).Carlo Ginzburg (1976), ''Il formaggio e i vermi'', translated in 1980 as The Cheese and the Worms: The Cosmos of a Sixteenth-Century Miller', trans. Anne Tedeschi (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press), xviii. Violence and Metaphysics In "Violen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure, Sign, And Play In The Discourse Of The Human Sciences
"Structure, Sign, and Play in the Discourse of the Human Sciences" (french: La structure, le signe et le jeu dans le discours des sciences humaines) was a lecture presented at Johns Hopkins University on 21 October 1966 by philosopher Jacques Derrida. The lecture was then published in 1967 as chapter ten of '' Writing and Difference'' (french: L'écriture et la différence). "Structure, Sign, and Play" identifies a tendency for philosophers to denounce each other for relying on problematic discourse, and argues that this reliance is to some degree inevitable because we can only write in the language we inherit. Discussing the anthropology of Claude Lévi-Strauss, Derrida argues that we are all '' bricoleurs'', creative thinkers who must use the tools we find around us. Although presented at a conference intended to popularize structuralism, the lecture is widely cited as the starting point for post-structuralism in the United States. Along with Derrida's longer text ''Of Gramm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
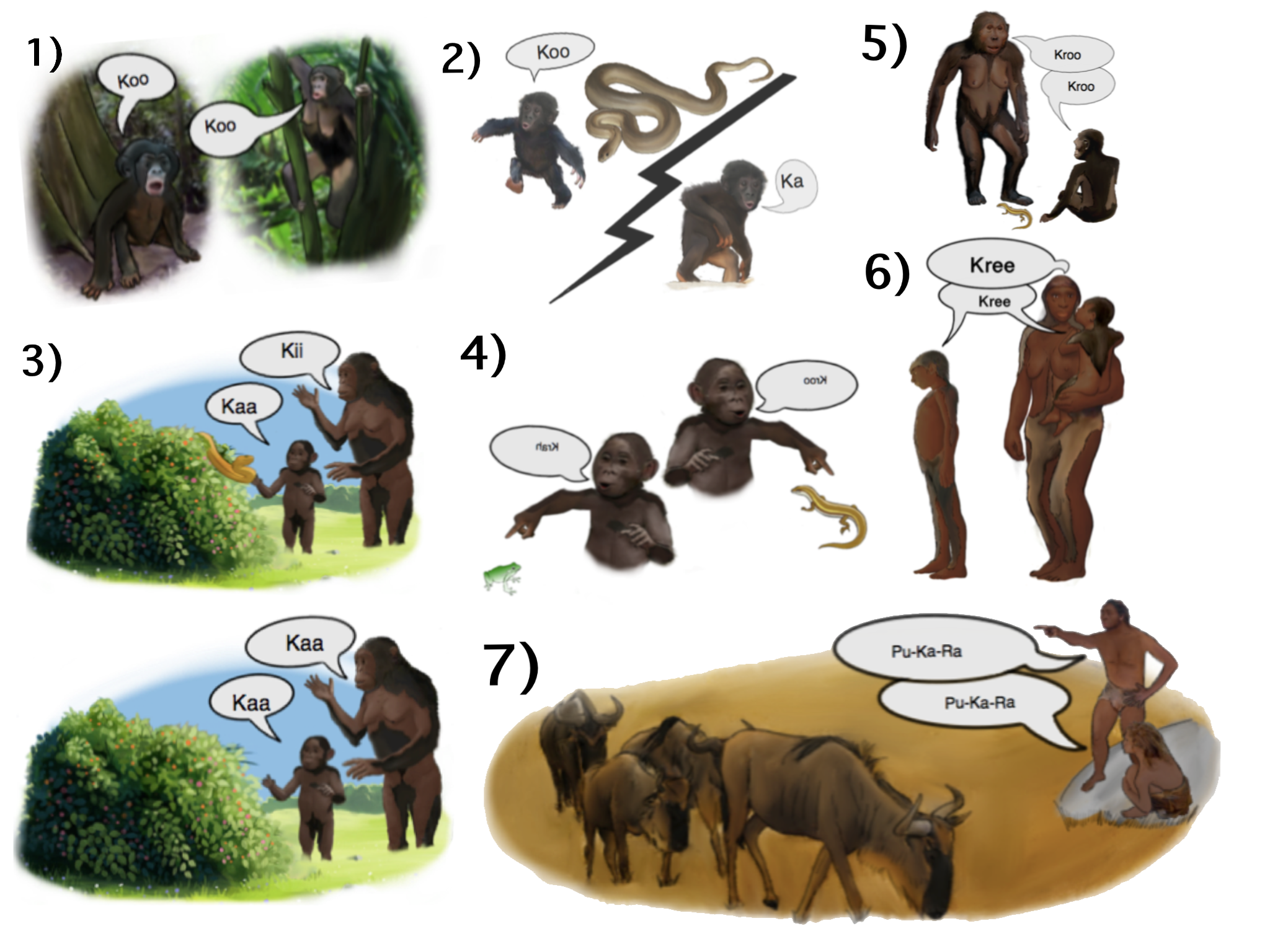
Origin Of Language
The origin of language (spoken and signed, as well as language-related technological systems such as writing), its relationship with human evolution, and its consequences have been subjects of study for centuries. Scholars wishing to study the origins of language must draw inferences from evidence such as the fossil record, archaeological evidence, contemporary language diversity, studies of language acquisition, and comparisons between human language and systems of communication existing among animals (particularly other primates). Many argue that the origins of language probably relate closely to the origins of modern human behavior, but there is little agreement about the facts and implications of this connection. The shortage of direct, empirical evidence has caused many scholars to regard the entire topic as unsuitable for serious study; in 1866, the Linguistic Society of Paris banned any existing or future debates on the subject, a prohibition which remained influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolution and the development of modern political, economic, and educational thought. His '' Discourse on Inequality'' and ''The Social Contract'' are cornerstones in modern political and social thought. Rousseau's sentimental novel '' Julie, or the New Heloise'' (1761) was important to the development of preromanticism and romanticism in fiction. His ''Emile, or On Education'' (1762) is an educational treatise on the place of the individual in society. Rousseau's autobiographical writings—the posthumously published '' Confessions'' (composed in 1769), which initiated the modern autobiography, and the unfinished ''Reveries of the Solitary Walker'' (composed 1776–1778)—exemplified the late 18th-century " Age of Sensibility", and featured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Derrida
Jacques Derrida (; ; born Jackie Élie Derrida; See also . 15 July 1930 – 9 October 2004) was an Algerian-born French philosopher. He developed the philosophy of deconstruction, which he utilized in numerous texts, and which was developed through close readings of the linguistics of Ferdinand de Saussure and Husserlian and Heideggerian phenomenology.Jacques Derrida . ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Britannica.com. Retrieved 19 May 2017. He is one of the major figures associated with post-structuralism and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecce Homo (book)
''Ecce Homo: How One Becomes What One Is'' (german: Ecce homo: Wie man wird, was man ist) is the last original book written by philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche before his death in 1900. It was written in 1888 and was not published until 1908. According to one of Nietzsche's most prominent English translators, Walter Kaufmann, the book offers "Nietzsche's own interpretation of his development, his works, and his significance." The book contains several chapters with self-laudatory titles, such as "Why I Am So Wise", "Why I Am So Clever", "Why I Write Such Good Books" and "Why I Am a Destiny". Kaufmann's '' Nietzsche: Philosopher, Psychologist, Antichrist'' notes the internal parallels, in form and language, to Plato's ''Apology'' which documented the Trial of Socrates. In effect, Nietzsche was putting himself on trial with this work, and his sardonic judgments and chapter headings can be seen as mordant, mocking, self-deprecating, or sly. Within this work, Nietzsche is self-con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scepticism
Skepticism, also spelled scepticism, is a questioning attitude or doubt toward knowledge claims that are seen as mere belief or dogma. For example, if a person is skeptical about claims made by their government about an ongoing war then the person doubts that these claims are accurate. In such cases, skeptics normally recommend not disbelief but suspension of belief, i.e. maintaining a neutral attitude that neither affirms nor denies the claim. This attitude is often motivated by the impression that the available evidence is insufficient to support the claim. Formally, skepticism is a topic of interest in philosophy, particularly epistemology. More informally, skepticism as an expression of questioning or doubt can be applied to any topic, such as politics, religion, or pseudoscience. It is often applied within restricted domains, such as morality (moral skepticism), atheism (skepticism about the existence of God), or the supernatural. Some theorists distinguish "good" or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)